![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
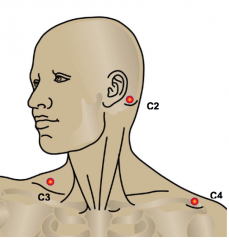
|
C2: occipital protuberance C3: supraclavicular fossa C4: top of AC joint |
|
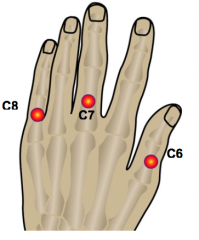
|
C6: thumb C7: 3rd finger C8: 5th digit |
|
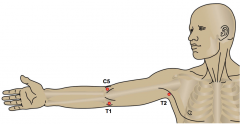
|
C5: lateral elbow T1: medial elbow |
|
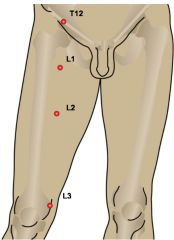
|
L1: inguinal region L2: mid ant thigh L3: medial knee |
|
|
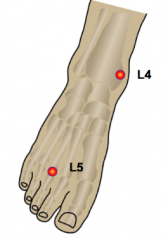
L4: medial malleolus L5: dorm of foot at 3rd MTP |
|
|
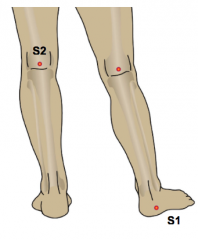
S1: below lateral malleolus S2: popliteal fossa |
|
|
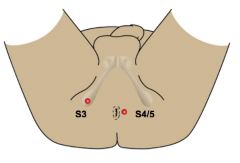
S3: ischial tuberosity |
|
|
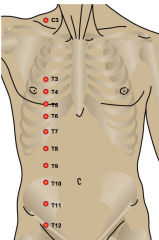
T4: nipple line T10: umbilicus |
|
|
Superficial Sensations |
-sharp/dull (pain) -temperature -light touch -pressure |
|
|
Deep Sensations DCML |
-kinesthesia -proprioception -vibration |
|
|
Combined Cortical Sensations |
-stereognosis -tactile localization -2 point discrimination -double simultaneous stimulation -graphesthesia -recognition of texture -barognosis |
|
|
Cognitive Processes |
-knowing -understanding -awareness/orientation -judgement -decision making -attention -memory |
|
|
Executive function |
-plan -manipulate information -initiate/terminate activity -recognize errors -problem solve -abstract thinking |
|
|
Perception |
-select stimuli that require attention -integrate multiple stimuli -interpret stimuli |
|
|
Cognition Impairments |
-attention disorders -memory disorders |
|
|
Executive Functions Impairments |
-volition -planning -purposeful action -assessing own performance |
|
|
Perception Impairments |
-body scheme/body image -spatial relations -agnosias -apraxias |
|
|
Perception Impairments body scheme/body image |
-unilateral neglect -anosognosia (denial of paralysis) -somatoagnosia (difficulty distinguishing body parts & start directions) -R/L discrimination -finger agnosia |
|
|
Perception Impairments spatial relations (COMPLEX PERCEPTION) difficulty in perceiving the relationship between self and 2 or more objects |
-figure ground
-form discrimination -spatial relations (relationship of one object in space to another) -position in space ("up, down, under, raise") -topographic disorientation (relationship of locations) -depth/distance perception -vertical disorientation (may affect upright posture) |
|
|
Perception Impairments agnosisas (SIMPLE PERCEPTION) inability to recognize/make sense of incoming information despite intact sensory capabilities |
-visual: inability to recognize familiar objects -auditory: inability to recognize/discriminate non-speech sounds -tactile (asterognosis): difficulties w/ADLs) |
|
|
Perception Impairments apraxia inability to perform purposeful movements |
IDEAMOTOR: can't perform motor action on command, but can do it automatically IDEATONIAL: can't understand overall concept of task BUCCOFACIAL: difficulty performing mov. w/lips, checks, larynx, pharynx on command (can do it automatically) |
|
|
Remedial Approaches |
-attempt to treat perceptual deficit -based on neuroplasticity RETRAINING APPROACH SENSORY INTEGRATION APPROACH NEUROFUNCTIONAL APPROACH |
|
|
Adaptive Approaches |
-focus on functional tasks -use of intact behaviors to compensate -adapt environment -try to make tasks as close to pt's real environment |
|
|
MAS 1 |
slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch and release or by minimal resistance at the end of ROM, when the affected parts is moved into flex/ext |
|
|
MAS 1+ |
slight increase in muscle tone, manifested by a catch, followed by minimal resistance through out the remainder (< half) of the ROM |
|
|
MAS 2 |
more marked increase in muscle tone through most of the ROM, but affected parts easily moved |
|
|
MAS 3 |
considerable increase in muscle tone, passive movement is difficult |
|
|
MAS 4 |
affected parts rigid in flex or ext |
|
|
Motor Assessment |
-tone -reflex integrity: 1.DTR 2.cutaneous reflexes 3.primitive and tonic reflexes -CN integrity -muscle performance:1.atrophy 2.strength, power, endurance -voluntary movement patterns (synergies) -functional tasks -EMG and NCV testing |
|
|
Electromyography EMG |
-records electrical act of muscle based on motor unit activity (when it fires, it released small electrical current [MUAP]) -fibrillations: not visible through skin, always indicate pathology |
|
|
pathologies detected by Nerve Conduction Velocity Test |
-nerve compressions neurapraxia (e.g. CTS) axonotmesis neurotmesis -motor neuron degenerative disease polio ALS -myopathies |
|
|
Corticospinal Tract |
-skilled fine movement, especially distal limbs -most important |
|
|
Corticobulbar Tract |
face and throat through cranial nerves |
|
|
Tectospinal Tract |
neck movement and head control |
|
|
Reticulspinal Tract |
controls muscle tone & reflexes (especially in the LE) |
|
|
Vestibulospinal Tract |
controls postural reactions, coordinates eye & head movement |
|
|
Rubrospinal Tract |
primitive act that has been taken over by the corticospinal tract in humans |
|
|
Basal Ganglia Pathology |
-poverty and slowness of movement -involuntary, extraneous movement -alterations in posture and muscle tone -rigidity |

