![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1. The student will be able to measure and record visual acuity according to generally agreed upon conventions.
|
What cranial nerve functions in sight?
|
CN-II
|
|
|
What are the functions of CNII?
|
Visual acuity
Visual fields Fundoscopy Pupillary reflex testing (includes CN III) |
|
|
|
How far should a pt stand from a wall chart?
|
20 feet
|
|
|
|
How far should pt hold a hand held eye chart?
|
14 inches
|
|
|
|
How do you determine what the person's visual acuity is?
|
Read down to the smallest characters possible or until reaching the 20/20 line, whichever comes first.
The acuity is the last line correctly read.***** EXAM |
|
|
|
How should you test a person's vision?
|
Test and record one eye at a time
always go R to R or L to L |
|
|
|
2. The student will be able to correlate lesions in the visual system and their associated visual field deficits.
|
Make sure you know the visual filed defects!
|
|
|
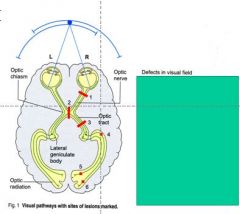
Know lesions at site 1-6
|
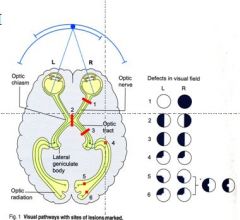
|
|
|
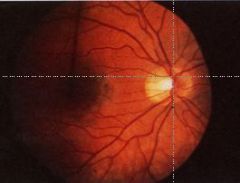
What is this a picture of?
|
Nl funfus
|
|
|
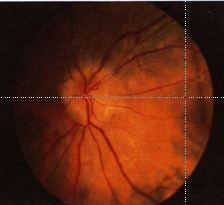
What is this?
|
mild papilloedema
|
|
|
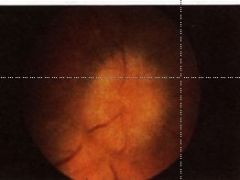
What is this?
|
Severe papilloedema
|
|
|
|
3. The student will be able to delineate the parasympathetic pathway responsible for constricting pupils and the sympathetic pathway responsible for dilating pupils and describe how lesions in either system influence pupillary size and reactivity.
|
What should you do before you check pupil constriction?
|
See if the pupils are equal or not before you begin the exam
|
|
|
When you shine a light into the eye what is the NORMAL response?
|
Constriction
|
|

