![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
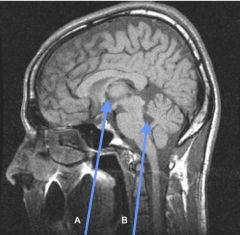
|
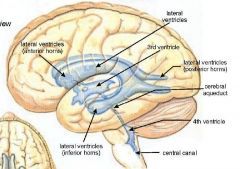
A. Third ventricle
B. Fourth ventricle |
|
|
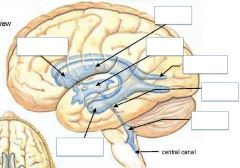
Where are the choroid plexuses located?
|
1. Lateral ventricles
– floor of body, also extending into temporal horns 2. Third ventricle - roof 3. Fourth ventricle - roof |
|
|
What difference in the capillary endothelium of the brain allows it to form the blood brain barrier?
|
- Brain Capillary endothelium: tight junctions
- Other capillary endothelium: gap junctions Therefore only: - Low molecular weight substances - Lipid-soluble substances can cross |
|
|
What are the symptoms and signs of acute hydrocephalus?
|
Symptoms
- Headache, nausea and vomiting - Lethargy, drowsiness, stupor and coma Signs - Papilledema, Diplopia - Setting sun sign - False localising signs – 6th nerve signs - Decreased level of consciousness |
|
|
What is the characteristic triad of normal pressure hydrocephalus?
|
- Gait disturbance (short shuffling, poor balance)
- Dementia - Urinary incontinence |
|
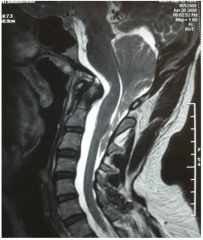
|
Chiari II Malformation
|
|
|
What action do benzodiazepines (diazepam) have on GABA receptors?
|
› Enhances the actions of GABA
› Increases the frequency of channel opening › Act on GABAA receptors containing α1, α2, α3, α5 and γ subunits › Binds at the interface between α and γ subunits |
|
|
What actions do barbituates have on GABA transmission?
|
› May act alone or enhance actions of GABA
› Prolongs the open time of the channel by slowing the dissociation of GABA from the receptor › Act on all GABAA receptors |
|
|
What action does ethanol have on GABA transmission?
|
› Enhance the actions of GABA, prolongs the open time of the channel, Binds within the transmembrane domain
|
|
|
What action do general anaesthetics have on GABA transmission?
|
› Enhance the actions of GABA, may directly stimulate receptors at high conc., Bind at the interface between α and β subunits within the transmembrane region of the channel
|
|
|
What type of seizure is described?
- Activation of neurons in a relatively small, discrete region - Clinical manifestation reflects region of brain in which they occur - Sensory or motor - Complex X – impairment of consciousness ie. Familiarity (déjà vu) or strangeness (jamais vu), automatisms, hallucinations (auditory and visual), temporal lobe epilepsy |
Partial Seizure (and Complex partial seizure)
|
|
|
What type of seizure is characterised by initial involvement of both hemispheres and widespread neuronal activation?
|
Generalised seizure
|
|
|
What are the 5 types of generalised seizures?
|
1. Tonic – extension of the extremities, rigid stretching
2. Atonic – sudden loss of muscle tone 3. Clonic (Myoclonic) – repetitive muscle twitching 4. Tonic-clonic (grand mal) – distinct tonic phase followed by a clonic phase (full body spasms with intermittent relaxation) - Generalised absence seizures (petit mal) –brief lapse of consciousness |
|
|
What are the 6 types/categories of anticonvulsant medications?
|
1. Enhance Na+ channel inactivation – reduce firing frequency of neurons
2. Inhibit excitatory amino acid release – block Ca2+ channels 3. Block excitatory amino acid action 4. Enhance GABA action 5. Inhibit GABA breakdown 6. Inhibit GABA uptake |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Phenytoin, Carbamazepine and Lamotrigine?
|
› Enhance voltage gated Na+ channel inactivation
› Use dependent (binding is dependent on the opening of Na+ channels which then leads to inactivation) › Results in a reduction of sustained high-frequency firing of action potentials - specifically act on rapidly firing neurons |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of Ethosuximide (Zarontin) and Levetiracetam (Keppra)?
|
Inhibit excitatory amino acid release – block Ca2+ channels
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of barbituates?
|
› May act alone or enhance actions of GABA
› Act on all GABAA receptors - increase affinity for GABA - increase Cl- conductance - prolongs the open time of the channel |
|
|
Vigabatrin (γ-vinyl-GABA)
|
› Synthetic structural analogue of GABA
› Specific inhibitor of GABA transaminase |
|
|
Tiagabine
|
› GABA reuptake inhibitor
› GAT1 inhibitor › Increase extracellular GABA levels |
|
|
Sodium valproate (Epilum)
|
Mechanisms 1, 2 and 5
› Use-dependent Na+ channel blocker - weaker than phenytoin and carbamazepine › Ca2+ channel blocker › Increases levels of GABA (unknown mechanism) |
|
|
Topiramate (Topomax)
|
› Mechanism 1, 3, 4
› Inhibit voltage-dependent Na+ channels › Antagonist at AMPA/Kainate receptors › Augment GABA at some GABAA receptors |
|
|
Felbamate (Felbatol)
|
› Mechanism 1, 3 and 4
› Inhibit voltage-dependent Na+ channels › Antagonist at NMDA receptors (NR2B) › Positively modulates GABAA receptors |
|
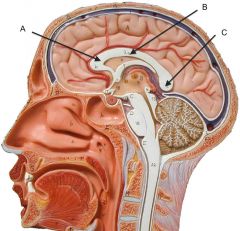
|
Corpus callosum:
A. Splenium B. Body C. Genu |
|
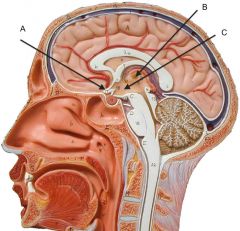
|
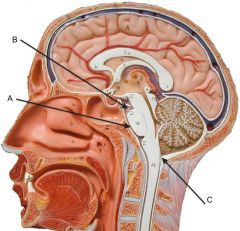
A. Optic chiasm
B. Thalamus C. Hypothalamus |
|
|
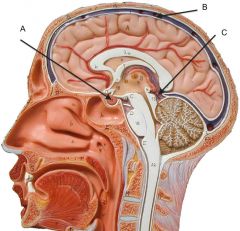
A. Pituitary
B. Superior Sagittal sinus C. Superior cistern |
|
|
A. Pontine cistern (with basilar artery)
B. Interpeduncular cistern C. Cisterna magna (cerebromedullary cistern) |
|
|
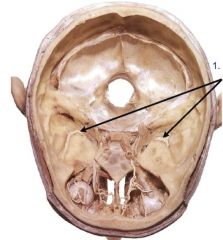
1. Middle meningeal arteries
|
|
|
Name 6 things located in the epidural space of the vertebral canal?
|
1. Loose areolar connective tissue
2. Semiliquid fat 3. Lymphatics 4. Arteries 5. An extensive plexus of veins 6. The spinal nerve roots as they exit the dural sac and pass through the intervertebral foramina |
|
|
|

