![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Dorsal Column Pathway |
Travels ipsalaterally (crosses at medulla), position sense, vibration and point discrimination, gracilis (T5 up) and coneatus (T6 down) |
|
|
Spinothalamic Pathway |
Travels contralaterally (crosses at ventral white commissary - 2nd order neuron sits in dorsal horn of spinal cord), pain and temp, |
|
|
Spinal Reticular Pathway |
Deals with emotional affect of pain - multisynaptic |
|
|
Referred pain |
Visceral afferents conducting pain can collateralize and synapse also with somatic pain 2nd neuron |
|
|
Other ascending pathways traveling ipsalaterally |
Ventral spinocerebellar pathway, cuneocerebellar, dorsal column pathway. End in the cerebellum |
|
|
Corticospinal and pic of 3 long tracts |
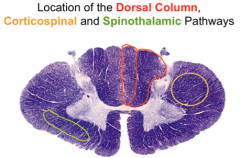
Voluntary fine movement. Upper and lower motor neuron. Upper - cell body in cerebral cortex (injury = in cortex, brainstem or spinal cord Lower - cell body in ventral horn 85% - cross at medulla, 15% cross at level they innervate |
|
|
Upper motor neuron lesion |
Hyperreflexia, spastic paralysis, increased muscle tone, clasp knife reflex, clonus, Babinski, large area of body affected |
|
|
Lower motor neuron lesion |
Decreased reflexes and muscle tone, flaccid paralysis, atrophy, segmental distribution of deficit |
|
|
Lower motor neurons (ventral horn) - segmented, flaccid paralysis, decreased reflex and muscle tone, segmented, etc |
|
|
Corticospinal - this level and below affected ipsalaterally - see exaggerated reflexes, clonus, Babinski sign, spastic paralysis, large affected area |
|

|
Corticospinal (UMN), and Spinothalamic (contralateral pain and temp loss) |
|
|
Lower motor neurons of corticospinal (flaccid paralysis, fasciculations, decreased muscle tone and reflexes, etc (polio) |
|
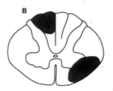
|
Dorsal column (position, vibration ipsa) and spinothalamic (pain and temp contra) - (MS) |
|
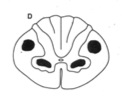
|
Upper and lower motor neurons of corticospinal tract (sensory NOT affected) - (ALS) |
|
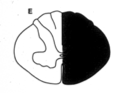
|
Brown-Sequard syndrome (hemisection) All 3 pathways affected -- must be in spinal cord |
|
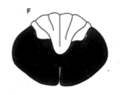
|
Spinal artery cut off - everything but Dorsal column pathway affected |
|
|
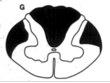
Dorsal column and corticospinal lesions (position etc; UMN - spastic, clasp knife, clonus) |
|
|
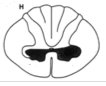
LMN of corticospinal tract (flaccid paralysis, fasciculations), and ventral white commissure (band of no pain and temp) |
|
|
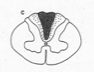
Tabes dorsalis - gracilis affected, will have Romberg sign |

