![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define intra-axial and extra-axial.
Is ependymoma intraaxial or extraaxial? |
intra-axial - inside the CNS parenchyma (arise from neurons or glial cells)
Extra-axial - outside the CNS parenchyma (e.g. meninges and ventricular lining) Ependymoma is extra-axial. |
|
|
What does synaptophysin stain? S100?
|
Synpatophysin - neurons and neuroendcorine tumors
S100 - stains Schwanommas and melanoma (stains neural crest derived cells) |
|
|
An increase in ICP causes many types of herniation.
Describe 7 consequences of increased ICP discussed in lecture |
1. flattened gyri
2. cingulate herniation 3. ventricular shift 4. uncal herniation 5. Kernohan's notch 6. Cerebellar tonsilar herniation 7. Duret hemorrhage |
|
|
What is kernohan's notch?
Describe the Sxs due to this notch |
Kernohan's notch is compression of cerebral peduncle on the contralateral side of uncal herniation
Causes ipsilateral hemiparesis (ipsilateral side of the mass) |
|
|
What artery is compressed with cingulate herniation? with downward cerebellar tonsilar herniation?
What are Sxs due to this herniation |
Cingulate herniation compresses anterior cerebral artery --> Lower extremity paresis and urinary incontinence
downward Cerebellar tonsilar herniation - compression of posterior cerebral artery |
|
|
What is Duret Hemorrhage?
|
Hemorrhage in the pons.
|
|
|
What is the most common CNS tumor? 2nd most common? 3rd most common?
|
1st - astrocytoma
2nd - oligodendroglioma 3rd - ependymoma |
|
|
Name 4 types of astrocytoma and indicate their grades.
|
Grade I - noninfiltrative (pilocytic) astrocytoma
Grade II - diffuse (fibrillary) astrocytoma Grade III - anaplastic astrocytoma Grade IV - Glioblastoma multiforme |
|
|
Hemorrhagic, butterfly-shaped, intraparenchymal CNS tumor.
Name? grade? |
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) grade IV
|
|
|
List 5 histologic features of GBM (glioblastoma multiforme).
|
1. Dense cellularity and anaplasia of tumor cells
2. vascular proliferation with endothelial proliferation (glomeruloid structures) 3. Presence of necrosis 4. Pseudopalisading tumor cells around necrotic area 5. high mitosis |
|
|
A 20 YO pt with well-circumscribed cystic mass in the cerebellum.
Histology reveals: very thin long cells GFAP positive Lots of Rosenthal fibers What CNS tumor? grade? |
non-infiltrating (pilocystic) astrocytoma
grade I |
|
|
Name this CNS tumor and its grade.
Gross: hemorrhage, calcification of gray/white gel mass Micro; uniform, round cells, fried egg looking cells, chicken wire vessels with calcification. no pleomorphism. |
Oligodendroglioma grade II
|
|
|
What genetic alteration is associated with anaplastic oligodendroglioma?
Is this a good or poor prognosis? |
Loss of heterozygosity of chromosomes 1p and 19q
Good prognosis |
|
|
A 10 YO pt has following findings in the spinal cord
Presence of true rossettes and pseudorossettes. what are true rossettes and pseudorossettes? What CNS tumor? grade? |
True rossette - tumor cells surrouding a lumen
Pseudo rosstte - tumor cells surruoding a vessel Ependymoma grade II |
|
|
A 5 YO pt has a lesion in the cerebellum. His clinical findings are:
Small blue cells, Homer Wright Rossettes. What are Homer wright Rossette? What CNS tumor is it? If this tumor is not in the cerebellum, what is it called? |
Homer Wright Rossette - tumor cells around a neuropil
Medullablastoma PNET (primitive neuroectodermal tumor) |
|
|
A firm, extra-axial mass noted. Its findings include:
Whorls of cells and psammoma bodies. What tumor? grade? Associated with what gene? what chromosome |
Meningioma grade I
Associated with NF-2 on chrom 22. |
|
|
Name 3 hemorrhagic metastatic CNS tumors.
|
MR. C
Melanoma Renal cell carcinoma Choriocarcinoma |
|
|
List 5 primary sites of CNS metastasizing tumors.
|
Lung, Breast, Melanoma, Kidney, GI tract
|
|
|
bilateral firm gray masses at the cerebello-pontine angle is noted.
The pt displays deafness and has no VOR. What CNS tumor? List 3 common histological features of this tumor. What gene is implicated in this tumor? |
Scwannoma
Antoni A and B areas, verocay bodies NF-2 |
|
|
What is Von Recklinghasen's disease?
The gene for this disease is on which chromosomes? What tumor is associated with disease? |
NF-1 associated diseases
on chrom 17 All forms of neurofibroma |
|
|
What 2 tumors are associated with central neurfibromatosis?
What is the gene called? what chromosome? |
Schwannoma and meingiomas
NF2 and chromosome 22 |
|
|
What gene is associated with Bourneville's disease? what chromosomes?
What CNS tumor is associated with this disease? |
Tuberous sclerosis
TSC1 gene on chrom 9 and TSC2 on chrom 16 Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma. |
|
|
CNS hemangioblastoma is associated with what gene? on what chrom?
|
VHL (von-Hippel-Lindau) gene on chrom 3.
|
|
|
What is the most common tumor at conus medullaris/cauda equinna that causes chronic back pain?
|
Myxopapillary ependymoma
|
|
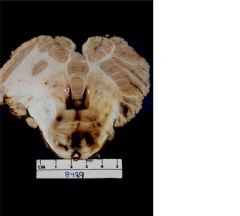
What type of hemorrhage is this?
|
Duret
|
|
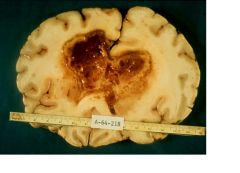
What type of CNS tumor?
What stain is positive? |
GBM (butterfly lesion and hemorrhagic)
GFAP |
|
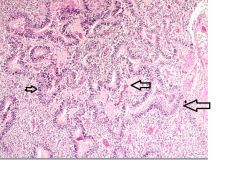
This is a slide of GBM
The arrows are pointing at basophilic structures. What are they? |
Pseudopalisading tumor cells
|
|
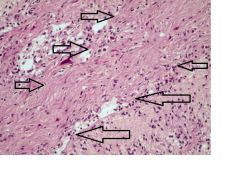
This is a slide of brain.
what is indicated inside the arrows? Which CNS is associated with this feature? |
Rosenthal fibers
noninfiltrating (pilocystic) astrocytoma (grade I) |
|
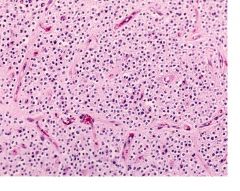
A section of cerebrum is shown.
What 2 histological features are shown here? What CNS tumor? |
Chicken wire vessels and fried egg appearing cells
Oligodendroglioma, grade II |
|
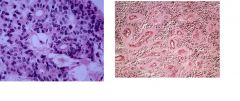
What histological features are shown on the Left picture? Right picture?
What CNS tumor is associated with above pictures? |
Left - true rossettes
Right - Pseudo-rossettes Ependymoma |
|
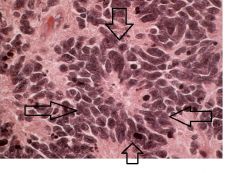
This is a section of cerebellum. In other region of the slide, many small blue cells were observed.
What is this histological structure? What CNS tumor is associated with this? |
Homer-Wright Rossette
Medulloblastoma |
|
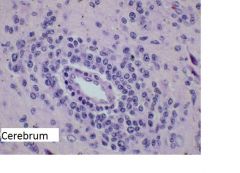
Above section is taken from AID's pt's brain.
What histological feature is shown? What CNS tumor do you suspect? What is the cell origin of the tumor? Which virus is commonly associated? |
Angiocentric pattern of lymphocytes. (lymphocytes surrounding the vessel)
Primary brain lymphoma B cells EBV |
|
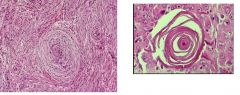
What CNS tumor is indicated by above histological features?
What gene is associated with this? What is the right picture called? |
Meningioma (grade I)
NF-2 on chrom 22 Psamomma body |
|
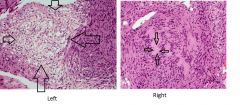
This is a section was taken from the cerebellopontine angle.
What structure is surrounded by arrows on the left picture? What structure is surrounded by the arrows on the right picture? |
Left picture - Antoni type B
Right picture - A verocay body |
|
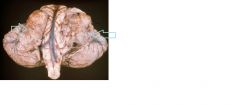
What CNS tumor is indicated by the blue arrows?
What gene is associated? what chromosome? |
bilateral schwanomma
NF-2 gene on chrom 22 |

