![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Function of nervous system |
To integrate and interpret stimuli and to direct an appropriate response |
|
|
|
2 parts of nervous tissue |
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system |
|
|
|
Central nervous system |
The brain and the spinal cord Control center of the entire nervous system No CT support- Extremely soft and delicate tissue |
|
|
|
2 parts of CNS |
1. Neurons 2. Neuroglia |
|
|
|
Neurons (of CNS) |
Cannot regenerate Damage to CNS is permanent |
|
|
|
Neuroglia |
Neurons are supported by cells called this... Out number neurons 50:1 |
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system |
Nerves assisted with other organs of body Communicates with CNS
|
|
|
|
2 parts of PNS |
1. Spinal nerves 2. Cranial nerves Connect to peripheral tissues |
|
|
|
Spinal nerves and cranial nerves |
Connect to peripheral tissues These nerves of PNS are tough because of CT sheath and sometimes also a myelin sheath |
|
|
|
Peripheral nerve fiber |
Can repair itself if it is damaged or cut out |
|
|
|
Afferent/efferent pathways |
The nervous system processes information through these 2 ways... Distinguished by direction of the flow of information Each neuron can only send info in 1 direction |
|
|
|
Afferent neurons |
(Sensory neurons) nerve processes that carry information from the PNS in muscles and glands to CNS |
|
|
|
Efferent neurons |
(Motor neurons) Nerve processes that convey responses from the CNS to muscles and glands |
|
|
|
Sensory neurons |
(Afferent pathway) Transmit sensations from periphery to CNS (Communication between the CNS & PNS |
|
|
|
Motor neurons |
(Efferent pathway) transmit impulses from CNS to muscles and other organs to elicit a response |
|
|
|
2 types of motor neurons |
1. Somatic 2. Autonomic |
|
|
|
Somatic motor neurons (sensory) |
(Skeletal) cranial and spinal nerves that provide innervation to the skeletal muscles Can be sensory, motor, or mixed |
|
|
|
Voluntary muscles |
Under conscious control (somatic motor neurons) |
|
|
|
Autonomic motor neurons |
(Smooth) (cardiac) Innervates internal organs Controls smooth and cardiac muscle Involuntary muscles and glands Not conscious controlled |
|
|
|
2 parts of autonomic motor neurons |
1. Sympathetic 2. Parasympathetic |
|
|
|
Sympathetic |
Fight or flight |
|
|
|
Parasympathetic |
Resting State |
|
|
|
Cells of the nervous system |
1. Neurons 2. Glial cells |
|
|
|
Neurons |
Composed of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon Receive and transmit information and neurons do not multiply We are born with all of the neurons we will ever have (New research says new neurons can be "born") |
|
|
|
Glial cells |
Provide structures support and nourishment for the neurons There are more of these present than neurons |
|
|
|
Neuron |
Consists of 1. Perikaryon 2. Cytoplasmic extensions (dendrites and axon) |
|
|
|
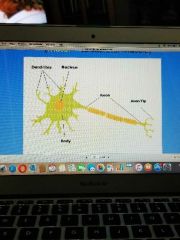
Perikaryon |
The nerve cell body contains the nucleus and the organelles |
|
|
|
Dendrites |
(Cytoplasmic extension) Receive stimuli and conduct impulses toward the cell body |
|
|
|
Axons |
(Cytoplasmic extensions) Conduct impulses away from the cell body |
|
|
|
Neuron |
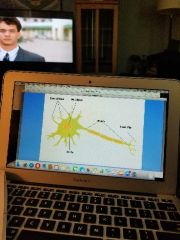
|
|
|
|
Direction of impulse |
1. Within 1 neuron 2. Between neurons |
|
|
|
Within 1 neuron |
Direction impulse: Dendrite--> cell body--> axon |
|
|
|
Between neurons |
Direction of an impulse Axon--> dendrite |
|
|
|
Synapse of neurons |

|
|
|
|
Types of neurons |
1. Multipolar neurons 2. Bipolar neurons 3. Unipolar neurons 4. Interneurons |
|
|
|
Multipolar neurons |
Many dendrites arising from the cell body (motor- to skeletal muscle) (efferent) |
|
|
|
Basic neuron types |
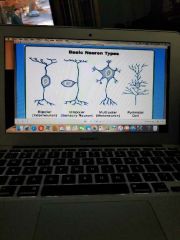
|
|
|
|
Bipolar neurons |
One process emerges from each pole of the cell body (interneuron) Lie within the CNS -receive & link sensory and motor impulses tonhrinf about the appropriate response -Bipolar shape |
|
|
|
Unipolar neurons |
Nerve cell body has one single process which divides close to the cell body into 2 branches Sensory neuron 1 branch goes to the PNS 1 branch goes to the CNS |
|
|
|
CT coverings of PNS |
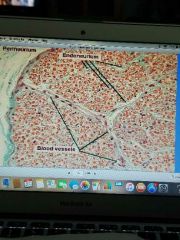
1. Endoneurium 2. Perineurium 3. Epineurium |
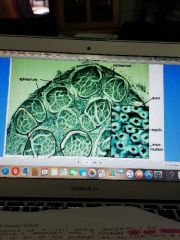
|
|
|
Interneurons |
Lie within the CNS |
|
|
|
Types of glial cells |
1. Astrocyte 2. Oligodendrocyte 3. Microglia 4. Schwann cell |
|
|
|
Astrocyte |
(CNS) star shaped Provides nutrition to neurons |
|
|
|
Microglia |
(CNS) phagocytic scavenger cell |
|
|
|
Oligodendrocyte |
Produces myelin (CNS) -lipid covering of axon -myelin sheath increases speed of electrical conduction -degeneration of myelin sheath covering of nerves in the CNS results in multiple sclerosis |
|
|
|
Schwann cell |
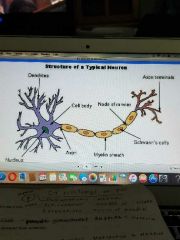
Produces myelin (PNS) -responsible for increasing the speed of conduction of an impulse along the neuron |
|
|
|
Node of ranvier |
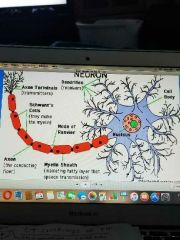
Gaps between the myelin sheath |
|
|
|
Synapse |
Are of communication between 2 neurons or between a neuron and it's effector (muscle or gland) |
|
|
|
Synapse |
Adjacent neurons transmit the impulse from the axon of 1 neuron, across a synapse, to the dendrites, of another neuron with the aid of neurotransmitters |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters location |
Only in axon in synaptic vesicles
This ensures that nerve transmission is in one direction only
|
|
|
|
Some types of neurotransmitters |
Acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters |
Increase the permeability of the cell membranes to Na and K ions so impulses can be relayed from one cell to another |
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter (NT) in synapse |

|
|
|
|
Resting potential of a neuron |
-70mV |
|
|
|
Action potential |
Occurs when there is a depolarization of the membrane Na rushes into the cell and K rushes out and the neuron becomes more positively charged. This is when the neurotransmitter reaches the receptor site |
|
|
|
Action potential |
A change in the electrical charge from negative to positive The "signal" is located at the point where the axon is positively charged |
|
|
|
Action potential graph |

|
|
|
|
Action potential |
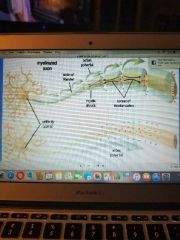
|
|
|
|
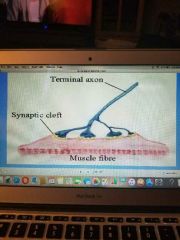
Motor end plate (somatic motor nerve endings) |
The place where a motor nerve fiber (efferent) innervates s muscle Stimulation through the T-tubule system will cause a release of calcium and result in muscle contraction |
|
|
|
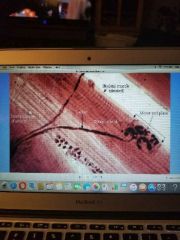
Motor end plate |
|
|
|
|
Sensory nerve endings |
1. Free nerve ending 2. Encapsulated nerve endings |
|
|
|
Free nerve ending |
The ends of sensory axons that are not covered by schwann cells -"naked fibers" -responsible tactile sensations-found in the oral epithelium and The dental pulp |
|
|
|
Encapsulated nerve endings |
-made up if several portions of afferent axons surrounded by capsule -capsule is made of several schwann cells (without a myelin sheath), and some CT |
|
|
|
Encapsulated nerve endings |
-act as touch/pressure receptors -found in the periodontal ligament -found in the lamina propria of the oral mucosa (Meissner's corpuscles) -also found as muscle spindles- detect the position of the muscle |
|
|
|
Pacinian corpuscle |
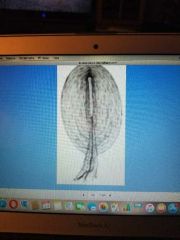
Deep pressure receptor Ex. Hands and feet |
|
|
|
Merkel cell (submucosa) |
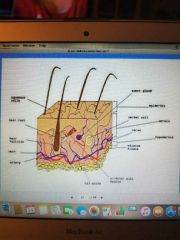
|
|

