![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Central Nervous System (CNS) |
Includes the brain and the spinal cord. |
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) |
Includes nerves and ganglia |
|
|
Ganglia |
Clusters of neuron cells bodies located along nerves |
|
|
Nerves |
Bundles of neuron processes (axons) |
|
|
Three functions of the nervous system |
• Collect information • Process and evaluate information • Initiate response to information |
|
|
Sensory Nervous System (Input) |
Responsible for receiving sensory information from receptors that detect stimuli and transmit it to the CNS. Afferent: To bring to |
|
|
Receptors |
Structures that monitor changes in the internal and external environment. |
|
|
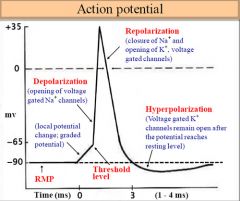
Action Potential Graph (Be able to label) |
|
|
|
Motor Nervous System (Output) |
Responsible for initiating and transmitting motor output from CNS to effectors. This system controls muscle tissues and glands. Efferent: To bring out |
|
|
Somatic Sensory |
Sensory input that is consciously perceived from receptors (ex: ears, eyes, skin)
|
|
|
Visceral Sensory |
Sensory input that is not consciously perceived from receptors of blood vessels, and internal organs (ex: heart) |
|
|
Somatic Motor |
Motor Output that is consciously or voluntarily controlled effector is skeletal muscle. |
|
|
Autonomic Motor (Visceral Motor) |
Motor output that is not consciously or is involuntarily controlled; effectors are cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands. |
|
|
List five characteristics of a neuron |
• Excitability (responsiveness to stimuli) • Conductivity (electrical change along the plasma membrane during action potential) • Secretion (release neurotransmitters in response to conductive activity) • Extreme Longevity (Most neurons can last from infancy to old age) • Amitotic (the division of a cell nucleus into two parts by constriction without the involvement of a mitotic apparatus¬) |
|
|
Cell Body (Soma) |
Enclosed by plasma membrane and contains cytoplasm surrounding a nucleus. (Neuron control center) |
|
|
Chromatophilic Substance (Nissl Bodies) |
Free and bound ribosomes together |
|
|
Dendrites |
Transmit graded potentials toward the cell body. (they receive input and then transfer it to the cell body for processing) |
|
|
Axon (Nerve Fiber) |
A longer process emanating from the cell body to make contact with other neurons, muscle cells, or glad cells. |
|
|
Synaptic Vesicles |
Inside synaptic knobs. They contain neurotransmitters. |
|
|
Multipolar Neuron |
Most common type of neuron. They have many dendrites and a single axon that extends from the cell body. |
|
|
Bipolar Neuron |
Has two processes that extend from the cell body. One dendrite (one one side) and a single axon (other side). Ex: retina of eye, olfactory epithelium in nose |
|
|
Unipolar Neuron |
Single short process that extends directly from cell and looks like a T. This is a result of two process into one long axon (Sensory nerves) |
|
|
Anaxonic Neuron |
Only dendrites not axon present (Interneurons of the CNS) |
|
|
Sensory Neurons |
Neurons of the sensory nervous system. Most are unipolar, but a few like the retina of the eye are bipolar |
|
|
Motor Neurons |
Neurons of the motor nervous system, all are multipolar |
|
|
Interneurons |
Lie entirely in the CNS. The receive, process, and store information and then decide how the body will react to stimuli |
|
|
Epineurium |
This layer of dense irregular connective tissue that encases the entire nerve. |
|
|
Perineurium |
This layer of dense irregular connective tissue that wraps the fascicles |
|
|
Fascicles |
Bundle of Axons
|
|
|
Endoneurium |
Delicate layer of areolar connective tissue that separates and electrically insulates each axon. |
|
|
Cranial Nerves |
Extend from the brain |
|
|
Spinal Nerves |
Extend from the spinal cord |
|
|
Sensory Nerves |
Contain sensory neurons that relay information to the CNS. |
|
|
Motor Nerves |
Contain motor neurons that relay information from the CNS. |
|
|
Mixed Nerves |
Contain both sensory and motor nerves. Most names nerves are mixed nerves. |
|
|
How a Glial Cells Differ from Neurons |
Out number neurons, they account for about half the volume of the nervous system. They do not transmit electrical signals. |
|
|
Glial Cells of CNS |
Astrocytes Ependymel Cells Microglia Oligodendrocytes |
|
|
Glial Cells of PNS |
Satellite Cells Nuerolemmocytes |
|
|
Satellite Cells |
Are flattened cells arranged around neuronal cell bodies in a ganglion that physically separate cell bodies from their surround interstitial fluid. |
|
|
Astrocytes (Role in Blood-Brian Barrier) |
Ends of astrocytes are covered in perivascular feet. The wrap around capillaries in the brain. Those two components together form the blood brain barrier.
Blocks toxins and allows in nutrients. |
|
|
Ependymal Cells |
Ciliated simple cuboidal or simple columnar epithelial cells that line the internal cavities (ventricles of brain and spinal cord) |
|
|
Microglia- |
Smalls cells smallest percent of CNS glial cells. They protect the CNS against microorganisms. |
|
|
Oligodendrocytes |
Large bulbous cells. wrap around and insulate axons within the CNS to form a myelin sheath. |
|
|
Nuerolemmocytes (Schwann Cellls) |
Elongated and flattened cells wrap around and insulate axons within the PNS to form a a myelin sheath. |
|
|
Myelin |
Composed of plasma membrane of glial cells and contains a large proportion of lipids and lesser amount of protiens. |

