![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
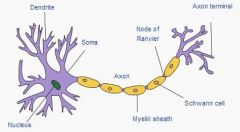
know these locations
|
|
|
|
dendrites are ?
|
they are where the neuron receives its signal
|
|
|
cells have an electrical potential gradient with charge inside the cell being _____ compared with outside the cell
|
outside the cell is more positive than inside the cell
|
|
|
sodium and potassium pumps use ATP to move ____ outside the cells?
After, they move ___ inside the cell? How many phosphates from ATP is used initially? |
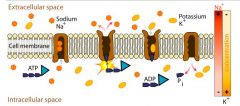
3 sodium ions are moved outside the cell using ATP. One phosphate group of ATP is used to energize the transfer. then 2 potassium ions are moved into the cell
|
|
|
the axon is surrounded by myelin sheith because the myelin sheath acts like an
|
it acts like an insulator to resist current leakage from the axon
|
|
|
nodes of ranvier exist to
|
help boost the electric current in the neuron via the Na+/K+ ATPases, Na+/Ca2+ exchangers and high density of voltage-gated Na+ channels that generate action potentials. this effectively jump-starts the current... this is saltatory conduction.
|
|
|
When the electric potential gets more positive (ex: going from -70 to -55), this inhibits or activates a signal?
|
increasing the electric potential causes an electrical charge signal within the neuron.
|
|
|
Multipolar, Unipolar, and Bipolar neurons are different how?
|
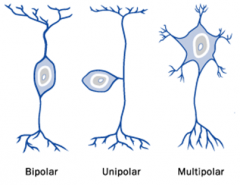
Name is referring to # of exits from the soma
Multipolar is classic neuron shape with a single axon connected to two or more dendrites, most common in CNS unipolar neurons have a continuous dendrite and axon with the cell body off to the side somewhere, more common in PNS bipolar neurons have one dendrite and one axon with the cell body between them (instead of off to the side like unipolar), used in special sense organs |
|
|
two main types of neural cells
|
neurons and glial cells (aka neuroglia)
|

