![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the basic functional unit of the nervous system? |
neuron |
|
|
What does the neuron do? |
Transmits information |
|
|
Can neurons reproduce? |
NO |
|
|
Neurons have a high requirement for
______________________ |
oxygen |
|
|
If a neuron is damaged but the cell body remains intact, what is possible? |
the neuron can regenerate cell processes |
|
|
Which cells are "helpers" to the neuron, providing structural & functional support and protection? |
neuroglia |
|
|
Neuron structure:
what is the largest part of the neuron? |
the central cell body |
|
|
What are the two types of cell processes and what are their functions? |
Axons - conduct nerve impulses AWAY
Dendrites - receive nerve stimuli |
|
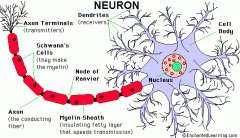
Parts of Neuron
(8) |
|
|
|
Dendrites _____________ stimuli from other parts
of the body and _______________ stimuli to the
_____________ ______________. |
receive
conduct
neuron cell body |
|
|
Dendrites serve as sensory receptors for:
(6 things) |
|
|
|
Axons conduct impulse _____________ from the
___________ toward _____________ ____________. |
away
cell
another neuron |
|
|
3 Physical characteristics of dendrites |
1. short
2. numerous
3. multi-branched |
|
|
3 physical characteristics of axons: |
1. long process
2. single
3. may be coated with myelin |
|
|
Myelinated axons conduct impulses
________________ than unmyelinated ones. |
faster |
|
|
What is the myelin sheath? |
cell membrane of glial cells tightly wrapped
around the AXON |
|
|
Which cells are found IN the brain & spinal cord? |
oligodendrocytes |
|
|
Which cells are found OUTSIDE the brain and
spinal cord? |
Schwann cells |
|
|
What is the node of Ranvier? |
the gap between adjacent glial cells |
|
|
What does the Central Nervous System include? |
brain & spinal cord |
|
|
What does the Peripheral Nervous System include? |
everything else
(cranial nerves + spinal nerves) |
|
|
Direction of nerve impulse:
Afferent nerves conduct impulses _____________
the Central Nervous System |
TOWARD |
|
|
Afferent nerves are also called: |
sensory nerves |
|
|
What do afferent nerves do? |
conduct sensations from sensory receptors in the skin & other place in the body TO the CNS |
|
|
Efferent nerves conduct impulses ______________
the central nervous system. |
away from |
|
|
Efferent nerves are also called _________________. |
motor nerves |
|
|
What do efferent nerves do? |
cause skeletal muscle contraction & movement |
|
|
What does the Autonomic Nervous System do? |
controls and coordinates automatic functions |
|
|
Give an example of the autonomic nervous system at work. |
Slowing of heart rate in response to increased
blood pressure. |
|
|
What is myelin? |
white matter
(the "crescent roll" around the hot dog) |
|
|
What disease is a result of impaired or lack of myelin? |
multiple sclerosis |
|
|
What does the Somatic Nervous System do? |
controls actions under voluntary, conscious
control |
|
|
If a nerve has a myelin coat, where does it have to go through the depolarization / depolarization process? |
only at the node of Ranvier |
|
|
Which type of nerve tells you to pull your hand back from the hot stove?
(afferent or efferent?) |
efferent |
|
|
Which nervous system coordinates learned muscle control?
(like a toddler learning to put hands out when falling) |
autonomic |
|
|
the resting state of the nerve is a state of being: |
polarized |
|
|
what returns the cell to its polarized state? |
the Na / K pump |
|
|
In depolarization, which channel opens? |
Sodium |
|
|
In repolarization, which channel opens? |
Potassium |
|
|
In a polarized (resting) state, is the sodium inside or outside of the cell? |
outside |
|
|
What is the threshold stimulus? |
All or nothing response
(neuron depolarizes to its maximum strength or not at all) |
|
|
During a polarized (resting) state, what kind of charge does the cell have? |
negative |
|
|
What is the refractory period? |
Time period during which a neuron is insensitive to additional stimuli |
|
|
What is the benefit of the refractory period? |
It allows the message to only go in one direction:
forward |
|
|
What is saltatory conduction? |
rapid means of conducting an action potential
(depolarization in myelinated axons at node of Ranvier) |
|
|
What is a synapse? |
the junction between 2 neurons
(or between a neuron & a target cell) |
|
|
What is the synaptic cleft? |
the gap between adjacent neurons |
|
|
What goes across the synaptic cleft to the post-synaptic membrane? |
neurotransmitters |
|
|
What do excitatory neurotransmitters do? |
cause an INFLUX of SODIUM
(which causes post-synaptic membrane to move TOWARD THRESHOLD) |
|
|
What do inhibitory neurotransmitters do? |
move the charge within the post-synaptic cell further AWAY from the threshold |
|
|
Name 3 types of neurotransmitters |
1. Acetylcholine
2. Catecholamines
3. GABA |
|
|
Is acetylcholine excitatory or inhibitory? |
can be either depending on location in body |
|
|
What are 3 examples of a catecholamine? |
1. epinephrine
2. norepinephrine
3. dopamine |
|
|
Name the 4 parts of the brain |
1. cerebrum
2. cerebellum
3. diencephalon
4. brain stem |
|
|
What is the cerebrum made of (2 things) |
1. white matter
2. gray matter |
|
|
Which matter makes up the outer layer of the brain? |
gray matter |
|
|
What is the cerebrum responsible for? (3 things) |
higher order behaviors -
|
|
|
What is the cerebellum responsible for?
(4 things) |
1. coordinated movement
2. balance
3. posture
4. complex reflexes |
|
|
What is the diencephalon? |
passageway between brain stem & cerebrum |
|
|
Name 3 structures of the diencephalon? |
1. thalamus
2. hypothalamus
3. pituitary gland |
|
|
What is the function of the thalamus? |
relay station for regulating sensory input to cerebrum |
|
|
What is the function of the hypothalamus? |
interface between nervous & endocrine systems |
|
|
What is the job of the pituitary gland? |
"master gland" of endocrine system |
|
|
What causes cerebellar hypoplasia in kittens? |
If the mother contracts FIV or FeLV while pregnant. |
|
|
What is the brain stem responsible for? |
basic body support |
|
|
Brain stem connects brain to ______________. |
spinal cord |
|
|
What are the 3 components of the brain stem? |
1. medulla oblongata
2. pons
3. mid-brain |
|
|
Many of which type of nerves originate from the brain stem? |
Cranial nerves |
|
|
What are the meninges? |
connective tissue layers that surround the brain & spinal cord. |
|
|
What are the 3 layers of the meninges in order from OUTER to INNER? |
1. Dura mater
2. Arachnoid mater
3. Pia mater |
|
|
What is the function of cerebrospinal fluid? |
cushioning & protection of brain & spinal cord |
|
|
What does the blood-brain barrier separate? |
capillaries in the brain
from
nervous tissue |
|
|
Name some things that can pass through the blood-brain barrier? |
inhalant anesthesia
alcohol
|
|
|
Only things that are ____________________ are able to cross the blood-brain barrier. |
lipophilic |
|
|
define liphophilic |
able to combine with or dissolve in FAT |
|
|
Obese patients - the fat in their body harbors
_____________________. |
anesthesia |
|
|
How does anesthesia affect obese patients in terms of coming out of anesthesia? |
it takes them longer than normal to wake up |
|
|
If an obese animal is 15 lbs and needs anesthesia, what should you do when determining how much to give them? |
Treat them as if they weigh less - maybe 12 lbs. |
|
|
What are the 12 cranial nerve pairs? |
1. olfactory 7. facial 2. optic 8. vestibulocochlear 3. oculomotor 9. glossopharyngeal 4. trochlear 10. vagus 5. trigeminal 11. spinal accessory 6. abducent 12. hypoglossal |
|
|
mnemonic device for 12 cranial nerves: |
O O O! To Take A Family Vacation!
Go Vegas After Hours! |
|
|
Spinal Cord: Medulla
1. What is it?
2. What is it composed of?
3. What is the center of it? |
1. the central part of the spinal cord
2. gray matter
3. central canal |
|
|
Spinal Cord: CORTEX
1. what is it?
2. where is it?
3. what is it made of? |
1. the outer part of the spinal cord
2. surrounds the gray matter
3. white matter |
|
|
What type of cells are found in the gray & white matter of the spinal cord?
|
CNS oligodendrocytes |
|
|
Cerebrospinal fluid is taken from what part of the spinal cord? |
cortex |
|
|
Spinal Cord:
What do dorsal nerve roots contain? |
sensory fibers |
|
|
Spinal Cord:
What do ventral nerve roots contain? |
motor fibers |
|
|
Dorsal horns are neurons in the gray matter that forward ___________________ nerve impulses to the brain or to other parts of the spinal cord. |
sensory |
|
|
Ventral horns are neurons in gray matter that forward _______________ (_____________) nerve impulses to the spinal nerves. |
motor (efferent) |
|
|
Autonomic Nervous System is made up of which two nervous systems? |
1. Sympathetic
2. Parasympathetic |
|
|
Autonomic nervous system controls functions at the ____________________________ level. |
subconcious |
|
|
In the sympathetic nervous system, where do the nerves emerge from? |
the thoracolumbar system
(thoracic & lumbar regions) |
|
|
In the parasympathetic nervous system, where to the nerves emerge from? |
cranial-sacral
(the brain and sacral-vertebral) |
|
|
Parasympathetic neurons travel directly from the CNS to its ________________ _________________. |
target organ |
|
|
In the sympathetic nervous system, the 1st nerve is ______________ and the 2nd nerve is __________. |
1st nerve = SHORT
2nd nerve = LONG |
|
|
In the parasympathetic nervous system, the 1st nerve is ______________ and the 2nd nerve is __________. |
1st nerve = LONG
2nd nerve = SHORT |
|
|
What is the primary neurotransmitter of the PARASYMPATHETIC nervous system? |
norepinephrine |
|
|
Adrenergic receptors (catecholamine) to epinephrine or norepinephrine are found in the blood vessels in which 3 areas of the body? |
1. skin
2. GI tract
3. skeletal muscle |
|
|
What are the 3 types of adrenergic receptors? |
Alpha 1
Beta 1
Beta 2 |
|
|
What are Alpha 1 receptors responsible for? |
vasoconstriction of the:
|
|
|
What are Beta 1 receptors responsible for? |
increase heart RATE & FORCE of contraction |
|
|
What are Beta 2 receptors responsible for? |
bronchodilation |
|
|
Somatic reflexes involve contraction of _____________________ muscle. |
skeletal |
|
|
Autonomic reflexes regulate what 3 things? |
1. smooth muscle
2. cardiac muscle
3. endocrine glands |
|
|
Contralateral reflex - where does it start and where does it go? |
Starts on one side of the body and travels to the opposite side. |
|
|
Name an example of a contralateral reflex. |
1. catching yourself as you fall (other foot steps forward)
(pull one cat's foot as they sleep and the other foot will respond) |
|
|
In an ipsilateral reflex, the _____________ and the ________________ are on the same side of the body. |
stimulus & response |

