![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
75 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
vag/o
|
Vaugs Nerve - main nerve of the parasympathetic nervous system
10th cranial nerve - branches reach to larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, aorta, esphagus & stomach |
|
|
TIA
|
Transient Ischemic Attack
temporary intererence with the blood supply to the brain. |
|
|
thrombotic
|
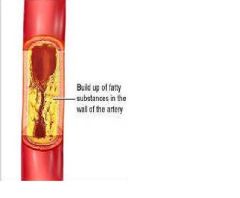
blood clot in the arteries leading to brain
|
|
|
thec/o
|
sheath (refers to the menings)
"the sheath" |
|
|
thalam/o
|
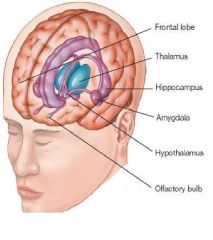
Thalamus
Main relay center of the brain. trigger center - decides what is important and what is not. |
|
|
tax/o
|
order, coordination
"you are ORDERED to pay your TAXES" |
|
|
syncop/o
|
to cut off, cut short, fainting
syncope - fainting "cut off a cop" |
|
|
synapse
|
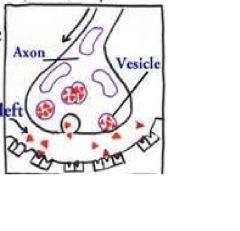
space through which a nervous impluse travels between nerve cells or between nerve and muscle or glandular cells.
a contact point. |
|
|
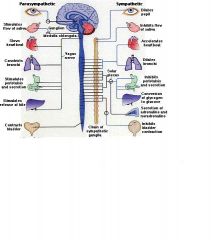
sympathetic nerves
|
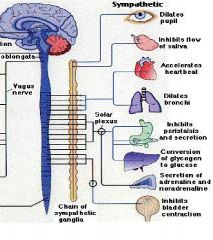
Fight or Flight
Automatic nerves that influence body functions involuntary in times of stress. |
|
|
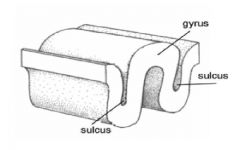
sulcus
|
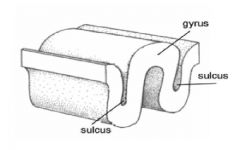
Depression or groove in the surface of the cerebral cortex.
"sulk deep into depression" |
|
|
stroma
|
connective and nonessential supporting tissue of an organ. Glial cells are the stromal tissue of the brain.
|
|
|
-sthenia
|
strength
neurasthenia - nervous exhaustion and fatigue |
|
|
sensory (afferent) nerves
|
nerve fibres -> brain
carry messages related to changes in the environment toward spinal cord and brain |
|
|
radicul/o
|
nerve root
"rediculous nerve root" |
|
|
-praxia
|
action
"practice your action" apraxia - move without purpose |
|
|
pont/o
|
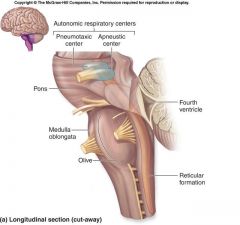
pons=bridge
Part of the brain anterior to the cerebellum and between the medulla and rest of the medbrain. connects cerebellum and cerebrum with rest of brain. |
|
|
plexus
|
Large, interlacing network of nerves
"braid" "multiplex of nerves" |
|
|
-plegia
|
paralysis
p(leg)ia - can't move your leg para/plegia oneside/paralysis dense paralysis of lower 1/2 of body. |
|
|
pia mater
|
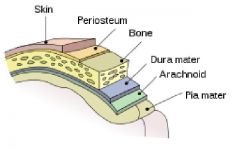
delicate mother
closest to the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
-phasia
|
speech
aphasia - can't speak |
|
|
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
|
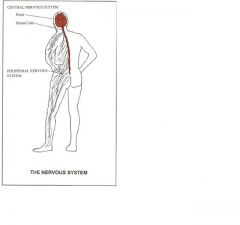
nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
used to connect CNS to limbs and organs. 12 paris of cranial nerves (12 days of Christmas) 31 pairs of spinal nerves (31 flavors of ice cream) |
|
|
-paresis
|
weakness
hemi/paresis LT/RT side / weakness slight paralysis (weakness) of RT/LT half of body |
|
|
parenchyma
|
Tissue that does the organs work.
Essential, distinguishing tissue of any organ or system. Neurons and nerves are the parenchyma of the nervous system. |
|
|
parasympathetic nerves
|
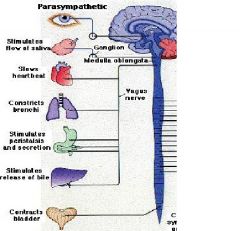
"rest and digest"
Involuntary, autonomic nerves that regulate normal body functions such as heart rate, breathing and muscles of the gastrointestional tract. |
|
|
neurotransmitter
|
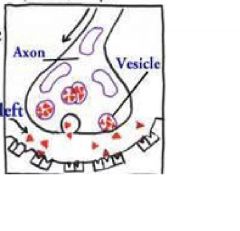
Chemical messenger released at the end of a nerve cell.
- endorphines - serotonin - dopamine - norepinephrine - acetylcholine |
|
|
neuron
|
microscopic
Nerve cell that carries impluses throughout the body. |
|
|
neur/o
|
nerve
macroscopic cord-like collection of fibres that carry electrical impluses |
|
|
multiple sclerosis
|
Distruction of the myelin sheath on neurons in the CNS and its replacement by plaques of sclerotic (hard) tissue.
muscle weakness unsteady gait paralysis |
|
|
myel/o
|
spinal cord, bone marrow
myelitis - inflamation of spinal cord myeloma - bone marrow |
|
|
myasthenia gravis
|
autoimmune neuromuscular disorder characterized by weakness of voluntary muscles.
my / a / sthenia gavis muscle /w/out /strength grave |
|
|
my/o
|
muscle
|
|
|
motor (efferent) nerves
|
nerve fibres <-- brain
nerves travel from the spinal cord and brain to muscles of the body. |
|
|
meningi/o
|
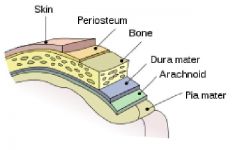
meninges, membranes
Three protective membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord Pia mater - Arachnoid - Dura mater |
|
|
medulla oblongata
|
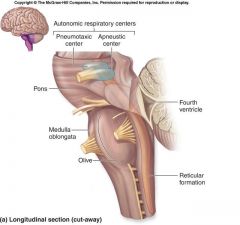
part of the brain just above the spinal cord. controls breathing, heartbeat and size of blood vessels.
nerve tracts cross from LT to RT and RT to LT. connects cerebellum to spinal cord. |
|
|
lex/o
|
word, phrase
dyslexia - reading, writing, learning disorder |
|
|
lept/o
|
thin, slender
it takes thin and slender fingers to be a klepto |
|
|
-lepsy
|
seizure
narcolepsy - seizure of sleep epilepsy - seizure upon |
|
|
kinesi/o
|
movement
|
|
|
hypothalamus
|
portion of the brain beneath the thamalmus. controls sleep, appeitie, body temp and secretions from pituitary glands.
|
|
|
herpes zoster
|
shingles
viral infection affecting peripheral nerves. blister and pain spread along periperal nerves caused by inflamation due to hypervirus. reactivation of chicken pox. |
|
|
hemorrhagic
|
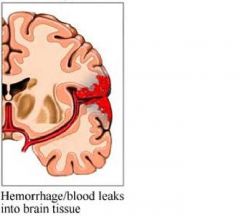
cerebral arterial wall ruptures
|
|
|
gyrus
|
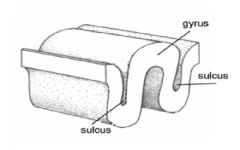
sheet of nerve cells that product a rounded edge on the surface of the ceberal cortex.
"the part that sticks up" |
|
|
gli/o
|
glial cells - glue - stromo
supportive and connective nerve cell that does not carry nervous impulses |
|
|
ganglion
|
"gang of cells"
collection of nerve cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system. |
|
|
esthesi/o
es-THE-ze-a |
feeling, nervous sensation
anesthesia - without feeling, lack of sensation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
encephal/o
|
brain
|
|
|
embolic
|
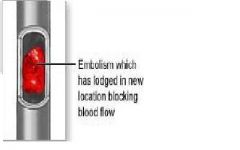
dislodged thrombus travels to cerebral arteries and blocks small vessel.
bol/o |
|
|
dur/o
|
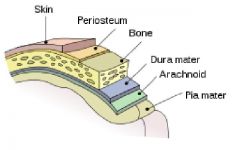
dura mater
|
|
|
dura mater
|
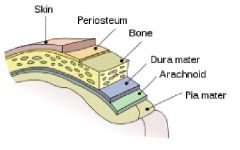
tough mother
outer most meninx around the brain and spinal cord. |
|
|
CVA
|
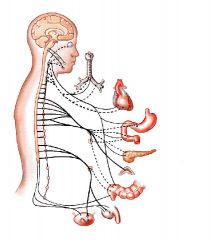
cerebrovascular accident
distruption in normal blood supply to the bain. Stroke |
|
|
comat/o
|
deep sleep (coma)
|
|
|
CNS
|
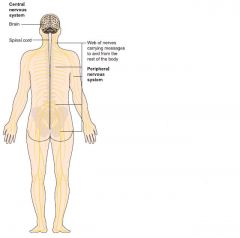
Central Nervous System
brain and spinal cord |
|
|
cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
|
disruption in the normal blood supply to the brain: stroke.
Thrombotic - blood clot in arteries. Embolic - dislodge thromus clogs small artery. Hemorrhagic - blood vessel brusts open. |
|
|
cerebral cortex
|
outer region of the cerebrum containing sheets of nerve cells.
|
|
|
cerebr/o
|
Cerebrum
Largest part of the brain. Responsible for voluntary muscle activity, vision, speech, taste, hearing, through and memory. |
|
|
cerebell/o
|
Cerebellum
Posterior part of the brain that coordinates muscle movements and maintains balance/posture |
|
|
cause/o
|
burning
"caustic - drano would burn" causalgia - Intese burning pain following an injury to sensory nerve. |
|
|
cauda equina
|
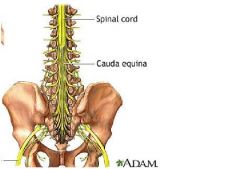
"horses tail"
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord. |
|
|
brainstem
|
lower portion of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord.
includes pons and medulla oblongata |
|
|
bol/o
|
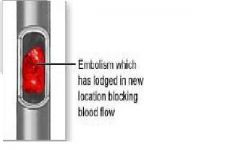
cast or throw
embolic dislodged thrombus travels to cerebral arteries and blocks small vessel |
|
|
automatic nervous system (ANS)
|
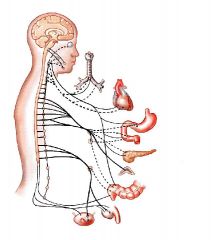
nerves that control involuntary body functions of muscles, glands and internal organs
|
|
|
arachnoid membrane
|
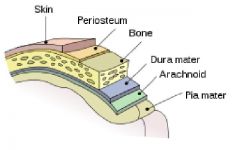
"spider-like"
Middle layer meninges around brain and spinal cord |
|
|
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
|
Degenerative disorder of motor neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem.
|
|
|
alzheimer disease
|
Brain disorder marked by grandual and progressive mental deterioration, personality change and impairment of daily functioning.
|
|
|
-algia
|
pain
neuralgia - pain in the nerve |
|
|
alges/o
|
excessive sensitivity to pain
analgesia - without excessive sensitivity to pain. |
|
|
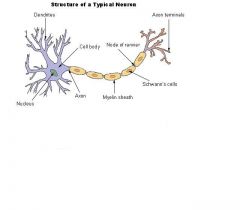
axon
|
extending from the cell body
|
|
|
myelin sheath
|
fatty tissue that insulates the axon and spped transmission of impulses
|
|
|
dendrites
|
branching fibers of a neuron. Where the stimulus begins an impluse.
|
|
|
Astrocyte cell
|

star-like in appearance
transport water and salts between capillaries and neurons. |
|
|
Microglial cells
|
small cells with many brancing processes (dentrites)
|
|
|
Oligodendroglial cells
|
few dendrites. These cells form the myelin sheath in the CNS.
|
|
|
Ependymal cells
|
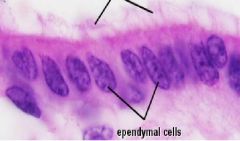
makes (CSF) cerebropsinal fluid circulates
|
|
|
epilepsy
|
chronic brain disorder characterized by recurrent seizure activity.
"grand mal" - loss of consciousness, falling down "petit mal" - minor - consciousness - loss of awareness |

