![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
67 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What will you see in the clinical presentation of someone with NEPHROTIC syndrome?
|

Lower extremity swelling
Pitting edema Low albumin 4+ proteinuria Spot urine protein creatinine ratio = 10.8 |
|
|
What will you see in the clinical presentation of someone with NEPHRITIC syndrome?
|

BP high
Blood urea nitrogen high Creatinine high Dysmorphic RBCs Spot urine creatinine ratio = 1 |
|
|
What are key differences between nephrotic and nephritic syndrome?
|

Nephrotic = prominent edema, inactive urinary sediment, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, non-inflammatory, normal BP, normal serum creatinine, key cell involved = visceral epithelial cell (podocyte) --> endothelial for nephritic
|
|
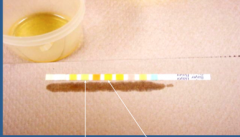
What is indicated by the arrows?
|
Urinary dipstick
Left = protein Right = blood |
|
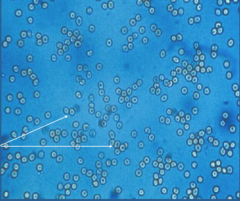
What is shown here?
|
Normal appearing RBCs
|
|
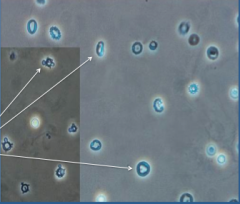
What is shown here?
|
Dysmorphic RBCs
|
|
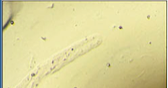
What is this?
|
Urinary sediment: hyaline cast
|
|
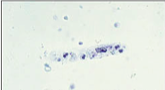
What is this?
|
Urinary sediment: white cell cast
|
|

What is this?
|
Urinary sediment: red cell cast
|
|
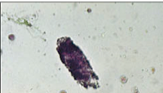
What is this?
|
Urinary sediment: granular cast
|
|
|
What is the main target cell in nephrotic syndrome without glomerular inflammation?
Describe the injury types: |
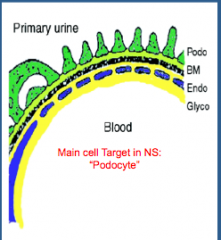
Podocyte
Minimal change disease Segmental glomerulosclerosis |
|
|
What happens in the case of immune complex formation and complement activation in the subepithelial space?
|
Membranous nephropathy
|
|
|
What are some glomerular capillary wall deposition diseases?
|
Amyloidosis, light chain deposition disease, nephropathy
|
|
|
What is the main target cell in nephritic syndrome with glomerular inflammation?
|
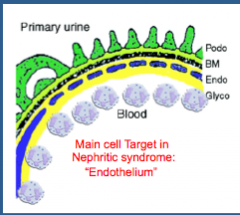
Endothelium
|
|
|
What are some causes of subendothelial space or mesangial immune complex formation and complement activation?
|
Post-infectious glomerulonephritis
IgA nephropathy Lupus nephritis |
|
|
What is the disease when antibodies are directed at the glomerular basement membrane?
|
Anti-glomerular basement disease
|
|
|
What is the disease that results in necrotizing injury and inflammation of the vascular and GCW?
|
Antibodies against neutrophil cytoplasmic antigens (ANCA)-disease
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of glomerular disease? ASYMPTOMPATIC
|

|
|
|
What is the presentation of glomerular disease? MACROSCOPIC HEMATURIA
|

|
|
|
What is the presentation of nephrotic syndrome?
|

|
|
|
What is the presentation of NEPHRITIC SYNDROME?
|

|
|
|
What is the presentation of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis?
|

|
|
|
What is the presentation of chronic glomerulonephritis?
|

|
|
|
Properties that are necessary for glomerular filtration also predispose to what?
|
Complex entrapment or formation
|
|
|
What three things can cause immune complexes to be trapped in glomeruli?
|
1. High plasma flow rate
2. High intraglomerular pressure 3. High glomerular hydraulic conductivity (permeability) |
|
|
What is the spectrum of immune complex disease dependent on?
|
Nature of antigen involved and the site of immune complex deposition.
|
|
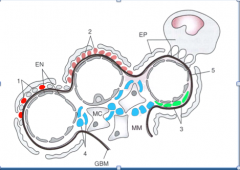
Identify the labeled parts.
|
Schematic Representation of three Glomerular Capillaries showing site of Immune Complex Formation:
1. Subepithelial Deposits: Post infectious GN and 2. Membranous Nephropathy. 3. Subendothelial and 4. Mesangial deposits: can be formed locally, but more commonly from passive entrapment of circulating ICs. 5. Anti-GBM Ab Disease: Abs bind in a linear fashion EN= Endothelial Cell; EP = Epithelial Cell; MC= Mesangial Cell; MM= Mesangial Matrix |
|
|
What are three major causes of immune complex mediated glomerular disease? Think location and indicate nephrotic or nephritic
|
1. Subepithelial deposits (nephrotic)
2. Subendothelial and mesangial deposits (nephritic) 3. Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease (usually nephritic with crescentic GN) |
|
|
What are two types of nephrotic subepithelial deposits?
|
1. Membranous nephropathy
2. Post-infectious glomerulonephritis (seen later in course of disease) |
|
|
What are causes of membranous nephropathy (type of nephrotic subepithelial deposit)?
|
1. Idiopathic
2. Systemic disorders: systemic lupus erythematosus, hepatitis B, drugs (gold, pencillamine) |
|
|
What are causes of sub endothelial and mesangial desposits (nephritic syndrome)?
|
1. Focal of diffuse proliferative Lupus
2. Post-infectious glomerulonephritis- Early Phase 3. IgA nephropathy: With prominent IgA deposits in the mesangium |
|
|
What major signs do you see in nephrotic syndrome?
|

1. Edema
2. Proteinuria 3. Hypoalbuminemia 4. Hypercholesterolemia/lipiduria |
|
|
If there is generalized edema, what should you evaluate for?
|

Proteinuria
|
|
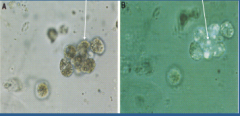
What is shown in each image?
|
Left = oval fat bodies
Right = maltese cross |
|
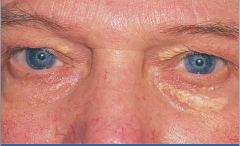
What is shown here?
|
Xanthelasma in nephrotic syndrome
|
|
|
Nephrotic vs. nephritic
Comment on the occurrence of each: Hematuria Proteinuria, Edema Hypertension |
All can occur in either
|
|
|
What is the biggest difference between nephrotic syndrome and nephritic syndrome? I'm going to really burn up if I don't answer this correctly.
|

|
|
|
What are indications for biopsy?
|
Guiding therapy or elucidating a failure to respond to therapy.
To determine diagnosis or prognosis. |
|
|
What are some contraindications for biopsy?
|
Absolute: bleeding diathesis, uncontrolled hypertension
Relative: Single kidney, high pressure hydronephrosis, adult polycystic kidney disease |
|
|
What are the slide preparations for kidney biopsy?
|
Light microscopy
Immunofluorescence Electron microscopy |
|
|
Buzz words: Give association.
1. Foot process effacement 2. Spike and dome 3. Subepithelial humps |

1. Minimal change disease
2. Membranous nephropathy 3. Post-infectious glomerulonephritis |
|
|
4. Tram tracks
5. Basketweave 6. Wire loops 7. Onion-skin |

|
|
|
The glomerular filtration barrier prevents the filtration of formed blood elements and proteins into the urinary space of Bowman’s capsule due to:
� |
1. Charge
2. Size 3. Shape |
|
|
Which are more easily filtered, small and cationic or small and anionic dextrans?
|
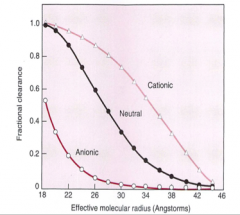
Small or cationic
|
|
|
What is the main site of size hinderance for larger molecules glomerular filtration? What is the estimated glomerular pore radius for spherical molecules?
|
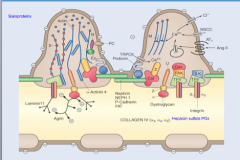
Lamina dense of GBM and slit diaphragm
42 angstroms |
|
|
What is the main side of hinderance of the anionic charge?
|
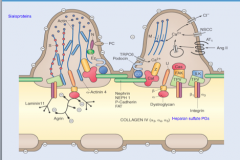
Lamina rara interna and fenestrated capillary endothelium
|
|
|
What prevents albuminuria?
What size uncharged molecules filter freely? Which size are completely restricted? Would albuminia occur if charge barrier did not exist? |

Size and charge barrier
|
|
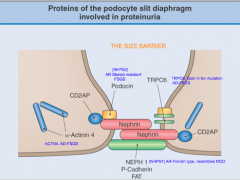
Some info about this during class?
|
Maybe?
|
|
|
Epithelial cells that line the proximal tubule take up protein by what mechanism?
What is considered a HMW protein? What is intermediate? What is LMW protein? |
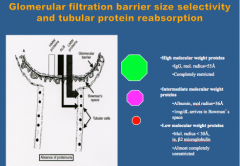
Endocytosis
Endocytic vesicles --> fusion with lysosomes --> proteins hydrolyzed back into amino acids --> cross the basolateral membrane of the tubular epithelial cell and re-enter circulation |
|
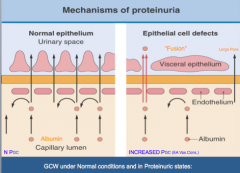
Add notes from class.
|
Add notes from class.
|
|
|
Compare excretion of small molecular weight dextrans, clearance of large molecular weight dextrans, and excretion of IgG in nephrotic patients with normal subjects.
|
Nephrotic patients:
1. Lower excretion of small MW dextrans (<48) secondary to loss of filtration surface area 2. Increased clearance of large MW dextrans with radius around 52 A (increase in large pores) 3. Increased excretion of IgG (neutral charge) due to loss of size barrier |
|
|
What are the three types of proteinuria?
|
Glomerular
Tubular Overflow |
|
|
What is glomerular proteinuria? What is dominant protein in urine?
|

|
|
|
What is tubular proteinuria? What is it secondary to?
|

|
|
|
What is overflow proteinuria? What is a condition where this occurs?
|

|
|
|
What protein does urine dipstick measure?
|
Albumin!
|
|
|
What is the typical range of protein excreted by healthy kidney? Upper range of normal? Healthy kidneys excrete about how much albumin per day? At what rate is Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein excreted per day?
|
40-80 mg/day
150 mg/day 30 mg/day 30-50mg/day |
|
|
When is the urine dipstick able to detect protein excretion?
What is the normal albumin/creatinine ratio? |
> 300-500 mg/day
Normal <30 mg/g |
|
|
What is defined as microalbuminuria?
|
30-300 mg/day
Persistant |
|
|
What is normal for each?
Urine dipstick 24 hour collection Spot urine protein creatinine ratio |
Urine dipstick = absent
24 hour collection = <150 mg Spot urine protein creatinine ratio = <.15 |
|
|
What is an abnormal urine dip stick?
What would the values be for the following in nephrotic range proteinuria? 24-hour urine collection: spot urine protein creatinine ratio: |
1+, 2+. 3+
24 hour urine collection: >3.5 grams Spot urine protein creatinine ratio: >3.5 |
|
|
What is the goal of managing primary nephrotic syndrome?
What is the most important predictor? |
Goal: preserve kidney function
Most important predictor: proteinuria |
|
|
What are some supportive measures of proteinuria?
|
Control hypertension (do this by having a low salt diet, angiotensin enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blocker).
|
|
|
What are the two disease modifiers of proteinuria?
TREAT THE CAUSE |
1. Steroid
2. Immunosuppressive drugs (cyclophosphamide, cyclosporin, mycophenolate mofeitil, tacrolimus) |
|
|
Read summaries in lecture.
|
Read summaries in lecture.
|
|
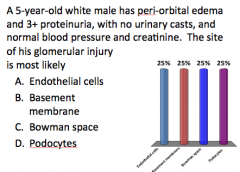
Answer this!
|
?
|
|
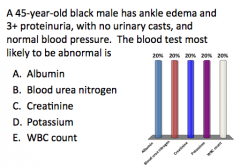
Answer this!
|
?
|

