![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the loss of the ability to differentiate (or a reversion to a primitive form). A common characteristic of cancer cells.
|
Anaplasia
|
|
|
What is the point at which a cell no longer responds to the normal controls for growth. The point of autonomy or self sufficiency in growth signalling. A property shared by all neoplasms.
|
Transformation
|
|
|
What is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer?
|
Malignant Transformation
|
|
|
What is a normal gene that can become an oncogene through mutation or over-expression? These code for proteins that help to regulate cell growth and differentitation.
|
Proto-oncogene
|
|
|
What is a modified gene, or a set of nucleotides that code for a protein believed to cause cancer?
|
Oncogene
|
|
|
Wha codes for anti-proliferation signals and proteins that suppress mitosis and cell growth? These are transcription factors that are activated by cellular stress or DNA damage. They are also known as anti-oncogenes?
|
Tumor suppressor genes
|
|
|
What genes are the accelerators and brakes for cellular proliferation?
|
Oncogenes (Growth Promoting)
Anti-Oncogenes (Tumor Suppressor Genes) |
|
|
What are genes that do not directly control tumor growth, but affect genomic stability called?
|
Caretaker Genes
(mismatch repair genes, apoptosis, and other putative repair genes) |
|
|
At which point in the Caretaker pathway does the gatekeeper pathway intersect?
|
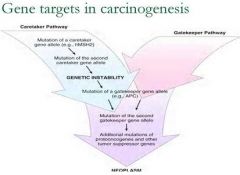
Right before mutation of the second gatekeeper gene allele
|
|
|
What is the two hit theory of carcinogenesis (Knudson Hypothesis)?
|
Neoplasms can only be initiated when a cell contains two mutant alleles
An individual who inherits one mutant allel must experience a second somatic mutation to initiate tumorigenesis. Individuals who inherit mutant genes frequently develop tumors in more than one site |
|
|
T/F
One oncogene can fully transform non-immortalized cells in vitro |
FALSE
DNA transfection experiments revealed that no single oncogene can fully transform non-immortalized cells in vitro, but that such cells can generally be transformed by combinations of oncogenes. |
|
|
The ____ oncogene induces cells to secrete growth factors and enables them to grow withou anchorage to a normal substrate, whereas the ____ oncogene renders cells more sensitive to growth factors and immortalizes cells. These two genes, acting in conjunction, can transform non-immortalized mouse fibroblasts in culture.
|
RAS
MYC |
|
|
Describe the dramatic example of incremental acqusistion of the malignant phenotype is documented by the study of colon carcinoma.
|
The lesions evolve through a series of morphologically identifiable stages:
1. Colon epithelial hyperplasia 2. Epithelial dysplasia 3. Adenoma that progressively enlarge and ultimately undergo malignant transformation A. Inactivation of APC tumor suppressor gene B. Activation of RAS C. Loss of genes on 18q (SMAD2 & SMAD4) D. Loss of p53 & TGF-beta receptor II genes |
|
|
Which gene is a suppressor gene for breast cancer that leads to a greatly increased risk for breast cancer when mutated?
|
BRCA1 suppressor gene
(it also affectsovarian, fallopian tube, prostate and colon cancers) |
|
|
What are the stages in the development of cancer?
|
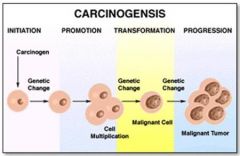
1. Initiation
2. Promotion 3. Transformation 4. Progression |
|
|
Which step in carcinogenesis causes a genetic change to the DNA in a normal cell, making it more vulnerable to other genetic changes?
|
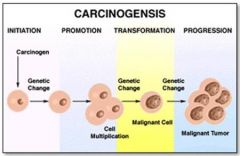
Initiation
|
|
|
Would cancer form if carcinogenesis ended at initiation and the cell did not grow and replicate?
|
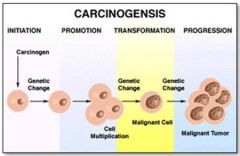
No
|
|
|
Which stage of carcinogenesis occurs when the initiated cell is exposed to an agent that enhances its growth into a larger mass (clonal expansion)?
|
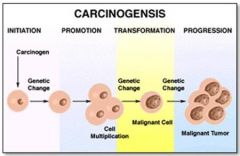
Promotion
|
|
|
What stage in carcinogenesis robs normal cells of O2 & nutrients and tumor grows uncontrollably, interfering with function of liver?
|
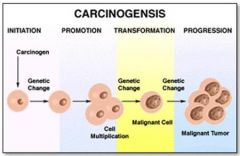
Progression
|
|
|
Which stage in carcinogenesis has:
1. Altered gene expression 2. Vitamin A metabolism 3. Suppressed immune response 4. Enhanced cell division |
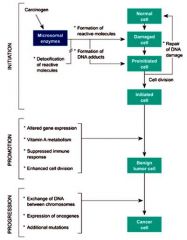
Promotion
|
|
|
Which stage of carcinogenesis has:
1. Exchange of DNA between chromosomes 2. Expression of oncogenes 3. Additional mutations |
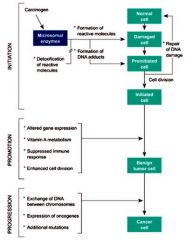
Progression
|
|
|
What are some potential interventions for the proliferation stage of carcinogenesis?
|
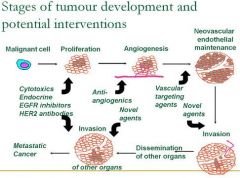
Cytotoxics & Endocrine
|
|
|
What are potential interventions to carcinogenesis during angiogenesis?
|
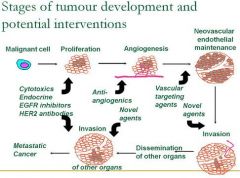
Anti-angiogenics
|
|
|
What are potential interventions to carcinogenesis during Neovascular endothelial maintenance?
|
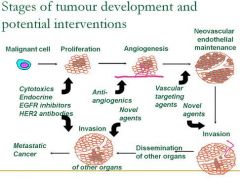
Vascular targeting agents
|
|
|
What are potential interventions to carcinogenesis during Invasion?
|
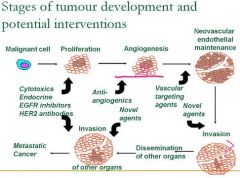
Novel agents
|
|
|
What are potential interventions to carcinogenesis during dissemination of other organs?
|
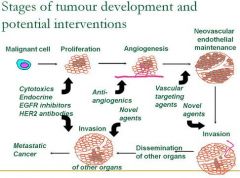
Novel agents
|
|
|
What are potential interventions to carcinogenesis during progression to metastatic cancer?
|
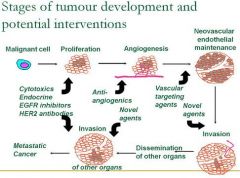
EGFR inhibitors
HER2 antibodies |

