![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
benign epithelial neoplasms
|
adenoma
papilloma cystadenoma papillary cystadenoma polyp |
|
|
adenoma
|
benign epithelial neoplasm from glands or forming glandular structures
thyroid, bronchial, renal tubular, hepatic cell adenomas |
|
|
papilloma
|
benign epithelial neoplasm forming finger like projections or warty projections
choroid plexus papilloma, intraductal papilloma of the breast |
|
|
cystadenoma
|
benign epithelial neoplasm forming from cystic structure; common site is ovary
|
|
|
papillary cystadenoma
|
papillary projections on its internal surface; ovary is common site
|
|
|
polyps
|
produce visible protrusion above the mucosal surface; colonic (tubular adenoma) and uterine; benign and malignant; malignant = polypoid cancers
|
|
|
mesenchymal tissues--benign
CT? |
lipoma, fibroma, chondroma, osteoma
|
|
|
endothelial and related tissue
|
hemangioma, lymphangioma, meningioma
|
|
|
muscle?
|
smooth (leiomyoma), and striated (rhabdomyoma)
|
|
|
Lipoma
|
tumor of adipose tissue; well circumscribed mass of mature adipose tissue; cut surface is yellow; most common benign tumor in males
|
|
|
fibroma
|
benign mesenchymal tumor of fibrous tissue; seen in ovary
|
|
|
chondroma
|
tumor of hyaline cartilage; nodular configuration; well circumscribed nodules of hyaline cartilage with hyaline matrix and neoplastic chondrocytes in lacunae
|
|
|
osteoma
|
tumor of bone; composed of woven and lamellar bone
|
|
|
hemangioma
|
benign tumor of blood vessels; closely packed blood vessels on micro
|
|
|
lymphangioma
|
characterized by cystic or cavernous spaces; seen in skin or deeper regions of the neck, axilla, mediastinum, and retroperitoneum
|
|
|
leiomyoma
|
benign tumor of smooth muscle; uterus is common location; also noted in the GI tract; most common tumor in females
|
|
|
rhabdomyoma
|
benign mesenchymal tissue of striated muscle; heart is common site
|
|
|
hydatidiform mole
|
benign neoplasm of chorionic villi; grossly appear like bunch of grapes
|
|
|
melanocytic nevus
|
benign tumor of melanocytes
|
|
|
pleomorphic adenoma (mixed tumor)
from more than one cell type from one layer. |
benign neoplasm of salivary gland (parotid); neoplastic cells have two different morphologic patterns but derive from same germ cell layer.
|
|
|
teratoma
|
from totipotent cell and is common in gonads; benign form is mature teratoma. dermoid cyst (mainly ectodermal differentiation); malignant form is an immature teratoma or teratocarcinoma
|
|
|
malignant tumors
mesenchymal? immune system? hematologic? epithelial? |
sarcomas
lymphomas leukemias carcinomas |
|
|
squamous cell carcinoma
|
malignant epithelial neoplasm that arises from squamous epithelium; microscopically pavement epithelium and keratin pearls are noted; lung, skin, cervix, esophagus.
|
|
|
adenocarcinoma
|
malignant epithelial neoplasm that forms glands or arises from glandular tissue; colon, lung, stomach, endometrium
|
|
|
transitional cell carcinoma
|
malignant epithelial neo that arises from transitional epithelium; common site is urinary bladder
|
|
|
malignant mesenchymal tumors
(sarcomas) |
lipo, fibro, chondro, osteogenic, angio, leiomyo, rhabdomyo
|
|
|
osteosarcoma
|
malignant tumor of bone; micro: malignant osteoid is noted; seen in young males
|
|
|
choristoma
|
ectopic rest of normal tissue//normal tissue misplaced within another organ. pancreatic tissue in Meckel's diverticulum; adrenal tissue in renal cortex
|
|
|
hamartoma
|
non=neoplastic overgrowth of disorganized tissue indigenous to a particular site; bronchial hamartoma that contains cartilage
|
|
|
dysplasia
|
loss of uniformity and architectural orientation; carcinoma in situ-- dysplastic cells that involve the entire epithelial thickness and do not penetrate the BM; pre-invasive stage
|
|
|
carcinoma in situ; can't tell which is top and which is bottom b/c epithelium looks similar throughout. has not invaded BM
|
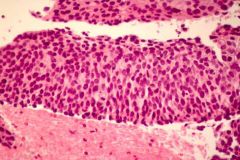
what is this
|
|
|
differentiation and anaplasia
|
-extent to which parenchymal tumor cell resembles a comparable normal cell
-lack of differentiation and it is a feature of malignancy benign tumors are well differentiated; |
|
|
functional changes in malignant cells
|
well differentiated SCC produces keratin; hepatocellular Ca produces bile; endocrine tumors elaborate hormones
|
|
|
rate of growth?
|
correlates with degree of differentiation--slow with well differentiated and rapid with poorly differentiated
|
|
|
what is feature that differentaites benign from malignant?
|
local invasion
|
|
|
metastases
|
tumor implants discontinuous with the primary tumor; the presence of metastases indicates a tumor is malignant (rare benign metastasizing lesions have been reported)
|
|
|
pathways of spread
|
1. seeding
2. lyphatic spread 3. hematogenous spread |
|
|
seeding of body cavities
|
malignant cells exfoliate from the surface and implant and invade tissue; primary ovarian cancers and peripherally located lung cancers
|
|
|
lymphatic spread
|
usual for carcinomas; spreads to nodes along route of drainage; lung to hilar nodes; breast to axillary nodes
|
|
|
hematogenous spread
|
usual for sarcomas; cells entering the portal vein go to liver; cell entering vena cava go to lung; renal cell and hepatocellular ca, lymphatic and hematogenous.
|
|
|
bone metastasis
|
vertebral column is most common site
osteoblastic metastasis: prostate ca, radiodensities, increased serum alkaline phosphatase indicates reactive bone formation osteolytic: lung cancer; radiolucencies, pathologic fractures, hypercalcemia |
|
|
grade of cancer
|
based on degree of differentiation; correlates with aggressiveness; four grades; I is well differentiated and IV is poorly differentiated
|
|
|
stage of tumor
|
determines extent of spread; based on Tumor size, spread to lymph Nodes, and presence or absence of Metastases. two major staging systems; TNM staging; AJC
|
|
|
Dukes' for Colon ca
|
A: carcinoma limited to wall of GI tract
B: extends to pericolic fat C: involvement of LN D: visceral mets |
|
|
predisposing factors
|
geographic/ethnic
environment/culture age/childhood cancer hereditary and cancer |
|
|
nasopharyngeal
|
EBV, far east
|
|
|
esophageal
|
alcohol and tobacco, poor, african american
|
|
|
stomach
|
japan
|
|
|
colorectal
|
US, low fiber, high fat
|
|
|
hepatocellular
|
hep B, aflatoxin B in diet
|
|
|
skin
|
color of skin and exposure to sunlight; new zealand and australia
|
|
|
breast ca
|
north america and europe
|
|
|
cervix
|
HPV, multiple partners
|
|
|
choriocarcinoma
|
pacific rim
|
|
|
prostate
|
high in american blacks
|
|
|
testicular
|
high in african blacks
|
|
|
penile
|
nonexistant in circumscribed
|
|
|
urinary bladder
|
squamous cell ca in area where schistosomal infection
|
|
|
burkitt
|
common in africa
|
|
|
multiple myeloma
|
american and south african blacks
|
|
|
chronic lymphocytic leukemia
|
elderly in europe and north america
|
|
|
asbestos
|
lung, GI tract, pleural, and peritoneal mesotheliomas
|
|
|
alcohol
|
oropharynx, larynx, esophagus, hepatocellular
|
|
|
aflatoxin B
|
hepatocellular
|
|
|
arsenic
|
skin, lung, hemangiosarcoma
|
|
|
alkylating agents
|
acute leukemia
|
|
|
aniline dyes, aromatic amines, beta naphthylamine
|
TCC of bladder
|
|
|
benzene, ethylene oxide
|
acute leukemia
|
|
|
cigarette smoke
|
mouth, pharynx, larynx, lungs, esophagus, pancreas, bladder
|
|
|
sun
|
SCC, BCC, and melanomas of skin
|
|
|
mitrosamines (smoked fish)
|
gastric adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
polyvinyl chloride and thorotrast
|
hepatic angiosarcomas
|
|
|
nickel, chromium & uranium, radon, beryllium
|
lung
|
|
|
DES
|
clear cell Ca of vagina
|
|
|
low fiber diet
|
adenocarcinoma of colon
|
|
|
high fat diet
|
breast ca
|
|
|
hereditary and cancer
|
inherited cancer syndrome AD
familial cancers AR syndromes of defective DNA repair |
|
|
familial cancer
|
early onset; tumors arising in 2 or more close relatives of index case; multiple and bilateral tumors; not assoc with specific marker phenotypes; sibs have relative risk between 2-3
|
|
|
AR syndrome
|
XP- basal and squamous cell ca of skin
ataxia telangiectaia- acute leukemia bloom's syndrome--acute leuk fanconi's anemia-- acute leuk |
|
|
chronic atrophic gastritis of pernicious anemia
|
gastric adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
actinic keratosis of skin
|
SCC
|
|
|
ulcerative colitis
|
adenocarcinoma of colon
|
|
|
chromosomal breakage syndrome
|
leukemia
|
|
|
leukoplakia of oral cavity, vulva, and penis
|
squamous cell carcinoma
|

