![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
170 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Intestinal Nematodes |
Anclostoma duodenale, Ascaris lumbricoides, Enterobius vermicularis, Necator americanus, Strongyloides stercoralis, Trichinella spiralis, Trichirus trichiura
|
|
|
|
Tissue and blood nematodes
|
Brugia malayi, Loa loa, Onchocerca volvulus, Wuchereria bancrofti
|
|
|
|
Oral cavity of roundworms
|
Buccal cavity
|
|
|
|
The outer surface of roundworms; this surface resists digestion
|
Cuticle
|
|
|
|
Third stage larva, infective, non- feeding, sheathed. Has a long slender esophagus
|
Flariform larva
|
|
|
|
Embryo stage of filarial parasite, usually in the blood or tissue of definitive host. Ingested by arthropod intermediate host
|
Microfilaria
|
|
|
|
Roundworms
|
Nematodes
|
|
|
|
First stage larva, non-infective, feeding. Has an hourglass shaped esophagus
|
Rhabitiform larva
|
|
|
|
Body parts of nematodes
|
Nerve cord, digestive tract, complex reproductive organs
|
|
|
|
How to diagnose Ascaris lumbricoides
|
Eggs in feces
|
|
|
|
Where do Ascaris lumbricoides develop to become infective?
|
1 month in soil
|
|
|
|
How long do Ascaris lumbricoides remain infective?
|
Years
|
|
|
|
How do humans acquire Ascaris lumbricoides?
|
Ingesting infective eggs
|
|
|
|
Can Ascaris lumbricoides leave the body?
|
Yes; through nose, mouth or anus
|
|
|
|
How does Ascaris lumbricoides move about a human body?
|
Larva from the eggs penetrate the intestinal wall and migrate to the lungs, larva are coughed up and swallowed and return to the intestine to mature
|
|
|
|
Where would you find Ascaris?
|
Appalachia
|
|
|
|
What species is often found with Ascaris?
|
Trichuris trichiura
|
|
|
|
Largest adult nematode?
|
Ascaris. 22-35 cm
|
|
|
|
Most common intestinal worm infection worldwide, 2nd most common in US
|
Ascaris
|
|
|
|
How many eggs do female Ascaris lay a day?
|
250,000
|
|
|
|
Fertile eggs
|
Corticated
|
|
|
|
Pinworm or Seatworm
|
Enterobius vermicularis
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic and infective stage of Enterobius vermicularis
|
Egg
|
|
|
|
How does Enterobius vermicularis/ pinworm/ Seatworm lay eggs?
|
Migrates out the anus to deposit eggs on perianal folds
|
|
|
|
How long does infectivity of Enterobius vermicularis/ pinworm/ Seatworm last?
|
A few days
|
|
|
|
When and how are eggs of Enterobius vermicularis/ pinworm/ Seatworm sought?
|
Tape prep in the morning
|
|
|
|
Can Enterobius vermicularis/ pinworm/ Seatworm eggs be found in air?
|
Yes
|
|
|
|
Most common worm infection in US
|
Enterobius vermicularis/ pinworm/ Seatworm
|
|
|
|
When does Enterobius vermicularis/ pinworm/ Seatworm migrate in body? What does it cause?
|
At night, bed wetting, sleeplessness, itching
|
|
|
|
Hookworm
|
Necator americanus
|
|
|
|
Where is hookworm found
|
North and South America, Asia and Africa
|
North and South America, Asia and Africa
|
|
|
Old world Hookworm
|
Anclyostoma duodenale
|
|
|
|
Where is Anclyostoma duodenale found?
|
North Europe, S America, Asia, Africa and the Caribbean
|
|
|
|
How can Ancylostoma infect?
|
Flariform larvae can infect orally and possibly by transmammary or transplacental passage
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic stage of hookworm
|
Egg in feces
|
|
|
|
Development of hookworm
|
Egg develops to rhabitiform larva in soil (1-2 days); matures to flariform larva (infective)
|
|
|
|
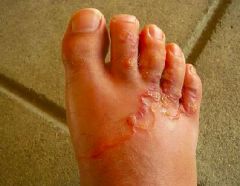
How does hookworm infection occur?
|
When flariform larva penetrates the skin; usually on the feet
|
|
|
|
How does hookworm migrate through the body?
|
Larva migrates through lungs, coughed up and swallowed and returns to intestines to mature
|
|
|
|
Hookworms are often found with
|
Ascaris and Trichuris
|
|
|
|
How does Strongyloides stercoralis infection occur?
|
Larva penetrates skin
|
|
|
|
How does threadworm larva move around the body?
|
Larva migrates through the blood to the lungs, and from the lungs to the intestine. Larva may also be found in the sputum.
|
|
|
|
Where does Strongyloides stercoralis reside in the body?
|
In the intestinal mucosa
|
|
|
|
Where is Strongyloides found? (Types of regions)
|
Worldwide in warm areas, tropics and subtropics
|
|
|
|
How big is Strongyloides?
|
Only 2-3 mm
|
|
|
|
Strongyloides Identification
|
Eggs not usually seen, look similar to Hookworm eggs; recovered with Enterotest capsule Larva must be differentiated from Hookworm Flariform- Strongyloides has short buccal cavity and hourglass shaped esophagus
|
|
|
|
Trichosis
|
Trichinella spiralis
|
|
|
|
What does hookworm consume?
|
Blood, heavy infections can result in severe blood loss 100 mL/ day
|
|
|
|
What percentage of human population is infected with hookworm?
|
25%
|
|
|
|
What happens if hookworm fecal exam is delayed?
|
Hatching of eggs with larva
|
|
|
|
Which worms have a long buccal cavity?
|
Hookworms
|
|
|
|
Threadworm
|
Strongyloides stercoralis
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic stage of threadworm
|
Rhabitiform larva
|
|
|
|
Where do Strongyloides stercoralis eggs hatch?
|
In the intestinal mucosa
|
|
|
|
Whose larva can develop to infective stage in the intestine and reinfect the host?
|
Strongyloides stercoralis
|
|
|
|
Can live non parasitically in soil
|
Threadworm
|
|
|
|
Hookworms are often found with
|
Ascaris and Trichuris
|
|
|
|
How does Strongyloides stercoralis infection occur?
|
Larva penetrates skin
|
|
|
|
How does threadworm larva move around the body?
|
Larva migrates through the blood to the lungs, and from the lungs to the intestine. Larva may also be found in the sputum.
|
|
|
|
Where does Strongyloides stercoralis reside in the body?
|
In the intestinal mucosa
|
|
|
|
In what regions is Strongyloides found?
|
Worldwide in warm areas, tropics and subtropics
|
|
|
|
How big is Strongyloides?
|
Only 2-3 mm
|
|
|
|
Strongyloides Identification
|
Eggs not usually seen, look similar to Hookworm eggs; recovered with Enterotest capsule Larva must be differentiated from Hookworm Flariform- Strongyloides has short buccal cavity and hourglass shaped esophagus
|
|
|
|
Trichosis
|
Trichinella spiralis
|
|
|
|
What does hookworm consume?
|
Blood, heavy infections can result in severe blood loss 100 mL/ day
|
|
|
|
What percentage of human population is infected with hookworm?
|
25%
|
|
|
|
What happens if hookworm fecal exam is delayed?
|
Hatching of eggs with larva
|
|
|
|
Which worms have a long buccal cavity?
|
Hookworms
|
|
|
|
Threadworm
|
Strongyloides stercoralis
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic stage of threadworm
|
Rhabitiform larva
|
|
|
|
Where do Strongyloides stercoralis eggs hatch?
|
In the intestinal mucosa
|
|
|
|
Whose larva can develop to infective stage in the intestine and reinfect the host?
|
Strongyloides stercoralis
|
|
|
|
Can live non parasitically in soil
|
Threadworm
|
|
|
|
Hookworms are often found with
|
Ascaris and Trichuris
|
|
|
|
How does Strongyloides stercoralis infection occur?
|
Larva penetrates skin
|
|
|
|
How does threadworm larva move around the body?
|
Larva migrates through the blood to the lungs, and from the lungs to the intestine. Larva may also be found in the sputum.
|
|
|
|
Where does Strongyloides stercoralis live?
|
In the intestinal mucosa
|
|
|
|
Where is Strongyloides found?
|
Worldwide in warm areas, tropics and subtropics
|
|
|
|
How big is Strongyloides?
|
Only 2-3 mm
|
|
|
|
Strongyloides Identification
|
Eggs not usually seen, look similar to Hookworm eggs; recovered with Enterotest capsule Larva must be differentiated from Hookworm Flariform- Strongyloides has short buccal cavity and hourglass shaped esophagus
|
|
|
|
Trichosis
|
Trichinella spiralis
|
|
|
|
Zoonotic disease, carnivorous mammals are the primary host
|
Trichosis
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic stage is larva encysted in striated muscle "nurse cells"
|
Trichinella spiralis
|
|
|
|
What does hookworm consume?
|
Blood, heavy infections can result in severe blood loss 100 mL/ day
|
|
|
|
What percentage of human population is infected with hookworm?
|
25%
|
|
|
|
What happens if hookworm fecal exam is delayed?
|
Hatching of eggs with larva
|
|
|
|
Which worms have a long buccal cavity?
|
Hookworms
|
|
|
|
Threadworm
|
Strongyloides stercoralis
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic stage of threadworm
|
Rhabitiform larva
|
|
|
|
Where do Strongyloides stercoralis eggs hatch?
|
In the intestinal mucosa
|
|
|
|
Whose larva can develop to infective stage in the intestine and reinfect the host?
|
Strongyloides stercoralis
|
|
|
|
Can live non parasitically in soil |
Threadworm
|
|
|
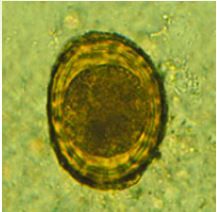
|
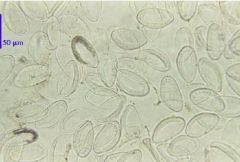
Ascaris lumbricoides egg |
|
|
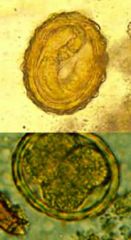
|
Ascaris lumbricoides egg |
|
|
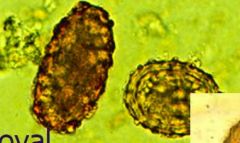
|
Ascaris lumbricoides egg |
|
|
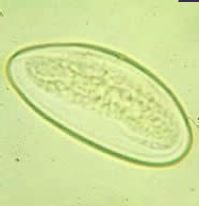
|
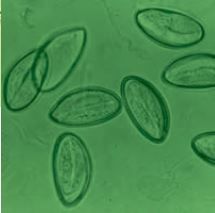
Enterobius vermicularis |
|
|
|
Enterobius vermicularis |
|
|
|
Enterobius vermicularis |
|
|
|
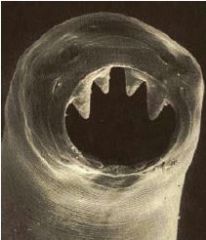
Hookworm |
|
|
|
Hookworm |
|
|
|
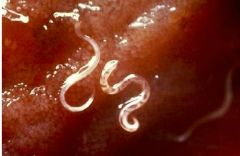
Hookworm |
|
|
|
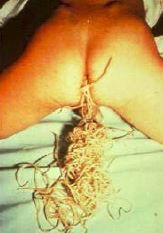
Ascaris infection |
|
|

|
Hookworm egg |
|
|

|
Hookworm egg |
|
|
|
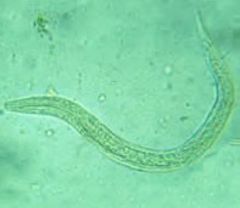
Hookworm larva |
|
|
|
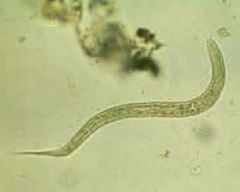
Hookworm larva |
|
|
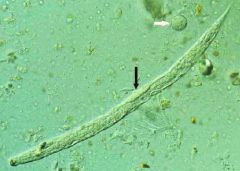
|
Strongyloides stercoralis |
|
|
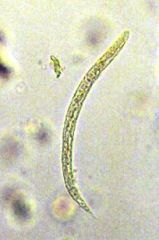
|
Strongyloides stercoralis |
|
|

|
Strongyloides stercoralis |
|
|

|
Trichuris trichuria egg |
|
|
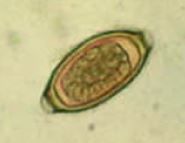
|
Trichuris trichuria egg |
|
|
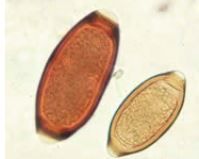
|
Trichuris trichuria egg |
|
|
|
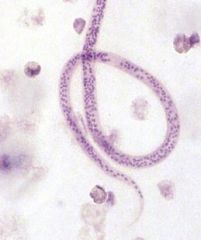
Wucheria bancroft |
|
|
|
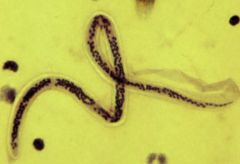
Wucheria bancroft |
|
|
|
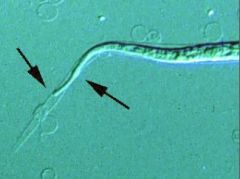
Brugia malayi |
|
|

|
Brugia malayi |
|
|
|
How does Strongyloides infect a human?
|
Larva penetrates skin
|
|
|
|
How does Strongyloides move about the body?
|
Larva migrates the blood to the lungs, and from the lungs to the intestine , larva may also be found in sputum
|
|
|
|
How big are Strongyloides stercoralis?
|
2-3mm
|
|
|
|
US infection rate of Trichinella spiralis
|
~4%
|
|
|
|
Distribution of Trichinella spiralis
|
World-wide in meat eating populations, but rare in the tropics
|
|
|
|
Trichuris trichiura
|
Whipworm
|
|
|
|
How to diagnose Trichuris trichiura
|
Eggs in feces
|
|
|
|
Where do Trichuris trichiura eggs mature?
|
In soil, infective in one month
|
|
|
|
How do humans acquire Trichuris trichiura infection?
|
Eating eggs
|
|
|
|
How does whipworm travel through body?
|
Larva hatch in small intestine, develop in villi and mature in colon
|
|
|
|
Who has Barrel shaped eggs with plugged ends and a smooth surface
|
Trichuris trichiura
|
|
|
|
Which worm produces living embryos, microfilariae, that migrate into lymphatics , blood or skin
|
Filariae
|
|
|
|
Filariae intermediate host is who and does what
|
Arthropod ingests microfilariae
|
|
|
|
Where do adult Strongyloides live?
|
In the intestinal mucosa
|
|
|
|
Who shows periodicity and why
|
Microfilariae become more prevalent at certain times during the day- these seem to correlate with the feeding patterns of the arthropod hosts
|
|
|
|
Where is Strongyloides found?
|
In warm areas, tropics and subtropics
|
|
|
|
Strongyloides Identification
|
Eggs: not usually seen, look similar to hookworm eggs, may be recovered using Entero-Test capsule. Larvae: must differentiate between Strongyloides rhabitiform larva and Hookworm Filariform larva.
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of Strongyloides larva
|
Short buccal cavity, hourglass shaped esophagus
|
|
|
|
Zoonotic disease, carnivorous mammals are the primary hosts
|
Trichosis
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic stage of Trichinella spiralis
|
Larva encysted in striated muscle "nurse cells"
|
|
|
|
How does Trichinella spiralis infection occur?
|
Undercooked infected meat is eaten
|
|
|
|
How long must infected meat be frozen to kill Trichinella spiralis?
|
20 days
|
|
|
|
Trichinella spiralis movement through the body
|
Larva is freed when meal is digested, rapidly develop into adults. Adults live on intestine. Female releases larva into submucosa. Larva disseminate via the blood stream
|
|
|
|
Knott's technique
|
Blood can be concentrated and the RBCs lysed before staining to concentrate microfilariae
|
|
|
|
How is microfilariae identified
|
By the presence or absence of a sheath around the larva and whether there are nuclei present in the tip of the tail and if there is a pattern to their distribution
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic stage of Filariae
|
Microfilariae
|
|
|
|
Adults live in subcutaneous tissue, migrate actively
|
Loa loa; eyeworm
|
|
|
|
Loiasis/ Calabar swellings
|
Loa loa
|
|
|
|
Elephantiasis a
|
Wucheria bancrofti
|
|
|
|
Adults live in the lymphatics, blockage causes extreme edema
|
Wuchereria bancrofti
|
|
|
|
Wucheria bancrofti intermediate host
|
Mosquito
|
|
|
|
Microfilariae have a sheath but have no nuclei in tail tupmicto
|
Wucheria bancrofti
|
|
|
|
Microfilariae are found in the blood
|
Wucheria bancrofti
|
|
|
|
Tightly coiled, sheath present, nuclei tightly packed, terminal and sub- terminal nuclei extend to tip of the tail. Adults live in lymphatics. Mosquito arthropod host.
|
Brugia malayi
|
|
|
|
Eyeworm
|
Loa loa
|
|
|
|
Loa loa arthropod host
|
Chrysops (Deerfly)
|
|
|
|
Sheath present nuclei present in tail, continuous
|
Loa loa
|
|
|
|
Diagnostic stage of Filariae
|
Microfilariae
|
|
|
|
Adults live in subcutaneous tissue, migrate actively
|
Loa loa; eyeworm
|
|
|
|
Loiasis/ Calabar swellings
|
Loa loa
|
|
|
|
Elephantiasis a
|
Wucheria bancrofti
|
|
|
|
Adults live in the lymphatics, blockage causes extreme edema
|
Wuchereria bancrofti
|
|
|
|
Wucheria bancrofti intermediate host
|
Mosquito
|
|
|
|
Microfilariae have a sheath but have no nuclei in tail tupmicto
|
Wucheria bancrofti
|
|
|
|
Microfilariae are found in the blood
|
Wucheria bancrofti
|
|
|
|
Tightly coiled, sheath present, nuclei tightly packed, terminal and sub- terminal nuclei extend to tip of the tail. Adults live in lymphatics. Mosquito arthropod host.
|
Brugia malayi
|
|
|
|
Eyeworm
|
Loa loa
|
|
|
|
Loa loa arthropod host
|
Chrysops (Deerfly)
|
|
|
|
Sheath present nuclei present in tail, continuous
|
Loa loa
|
|
|
|
Black fly is the arthropod host. Major cause of blindness in Africa
|
Onchocerca volvulus
|
|
|
|
Adults live in subcutaneous tissue, nodules form around the adult
|
Onchocerca volvulus
|
|
|
|
River blindness
|
Onchocerciasis
|
|
|
|
Black fly is the arthropod host. Major cause of blindness in Africa
|
Onchocerca volvulus
|
|
|
|
Adults live in subcutaneous tissue, nodules form around the adult
|
Onchocerca volvulus
|
|
|
|
River blindness
|
Onchocerciasis
|
|

