![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Whole Numbers |
All the Natural numbers plus 0 |
|
|
|
Integers |
All the whole Numbers plus negative numbers |
|
|
|
Real numbers |
All the integers plus fractions and decimals |
|
|
|
Fractions |
Parts of a whole |
|
|
|
Decimals |
Any real number expressed in base 10 |
|
|
|
Numerator |
The part of a fraction that is above the line and signifies the number of parts of the denominator |
|
|
|
Denominator |
The part of the fraction below the line that signifies division |
|
|
|
Multiplication |
An abbreviated process of adding an integer to itself a specified number of times |
|
|
|
Product |
The total of a multiplication process |
|
|
|
Dividend |
The number to be divided |
|
|
|
Divisor |
The number by which a dividend is divided |
|
|
|
Quotient |
The answer to division equations |
|
|
|
Lowest common denominator (LCD) |
The least common multiple of the denominators |
|
|
|
Addition Fractions |
1. Find lowest common denominator as needed 2. Change numerator as needed 3. Add numerators; carry denominator |
|
|
|
Combination Numbers |
1. Convert one to the other 2. Perform addition |
|
|
|
Subtraction Fractions |
Same process as adding fractions, except subtract |
|
|
|
Subtraction Integers |
1. Change sign of number to be subtracted 2. Proceed as addition |
|
|
|
Multiplication Fractions |
1. Multiply numerators 2. Multiply denominators 3. Reduce fractions as necessary |
|
|
|
Cancellation |
When a numerator and an opposite denominator can be reduced to work with smaller numbers |
|
|
|
Mixed Numbers |
1. Change to improper fractions A) multiply denominator by whole Numbers B) add the numerator |
|
|
|
Division fractions |
1. Invert the divisor 2. Perform multiplication of fractions A) multiply numerators then denominator. Reduce fraction change to mixed number as necessary |
|
|
|
Combination Equations |
1. When grouping symbols, () or [], are used to simplify these parts first, working from the inside out 2. Perform multiplication or division from left to right 3. Per from addition or subtraction from left to right 4 when the parentheses are preceded by a minus sign, then the sign of each term within the parentheses will change |
PEMDAS |
|
|
Proportions |
A) a proportion is a statement of equality between two ratios B) equal sign is read "as", therefore 20 over 30 = 2 over 3 would read 20 is to 30 as 2 is to 3 C) formula a/b = c/d applies, therefore a×d = b×c |
|
|
|
Variable |
A quantity whose value is free to vary. The letters at the end of the alphabet are usually used to represent variables (w,x,y, and z) |
|
|
|
Constant |
A quantity whose value remains the same throughout a particular problem. |
|
|
|
Fixed Constants |
Have values that never change 5, -3, 1/3, x |
|
|
|
Arbitrary Constants |
Can be assigned different values for different problems. The letters at the beginning of the alphabet are usually used: a,b,c, and d |
|
|
|
Algebraic expression |
Any combination of numbers, variables, and symbols that represent some numbers 3x . 3y - b2 |
|
|
|
Term |
The parts of an algebraic expression that are connected by plus (+) and minus (-) signs |
In the expression 3z+xy, 3z and xy are the terms |
|
|
Monomial |
An expression of only one term |
2b, z2, xy |
|
|
Polynomial |
An algebraic expression of many terms |
7a-4ab+2a |
|
|
Coefficient |
Any factor or group of factors of a term by which the remainder of the term is to be multiplied |
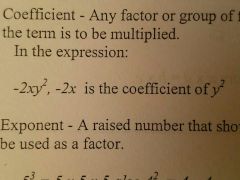
|
|
|
Exponent |
A raised number that shows the number of times the base number is to be used as a factor |
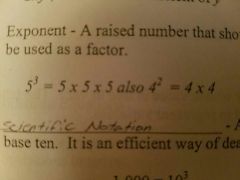
|
|
|
Scientific Notation |
A method of writing numbers in terms of base ten. It is an efficient way of dealing with very large or small numbers |
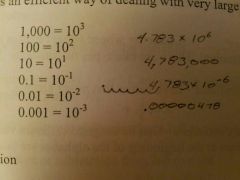
|
|
|
Addition/Subtraction (algebra) |
A) Only like terms can be added or subtracted B) exponents will remain the same. |
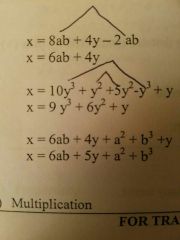
|
|
|
Multiplication (algebra) |
A) Any variables or Constants within a term can be multipled B) Exponents are added |
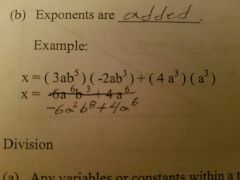
|
|
|
Division (algebra) |
A) Any variables or Constants within a term can be divided B) exponents are subtracted C) when dividing like terms, there will be no letters in the quotient |

|
|
|
Geometry |
The measurement of areas, planes, shapes, and angles |
|
|
|
Pi |
The ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter. It is a constant value of 3.141592 symbolized by the Greek letter Pi |
|
|
|
Radius |
A fixed distance from the center to any point on the circumference of a circle |
|
|
|
Diameter |
The distance through the center of a circle |
|
|
|
Right angle |
An angle measuring 90 degrees |
|
|
|
Right triangle |
A triangle having a right angle |
|
|
|
Hypotenuse |
The longest side of a right triangle |
|
|
|
Circle |
A) to find the diameter, multiply radius by 2 B) to find the radius, divide diameter by 2 |
|
|
|
Circumference |
1. The radius or diameter must be known 2. The radius or diameter can be found if the circumference is known |

|
|
|
Pythagorean Theorem |
In a Right Triangle, the sum of the squares of the legs equal the square of the hypotenuse and the square root of the sum equals the hypotenuse. |
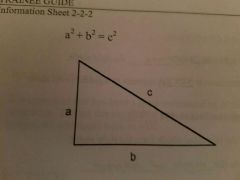
|
|
|
Hypotenuse (trigonometry) |
The side of a right triangle opposite the right angle 1) the angle opposite the hypotenuse is always 90 degrees |
|
|
|
Leg of a right angle |
One of the two sides which form the right angle |
|
|
|
Opposite leg |
The leg opposite the angle of interest |
|
|
|
Adjacent leg |
The leg adjacent to the angle of interest |
|
|
|
Acute angle |
An angle measuring between 0 degrees and 90 degrees |
|
|
|
Sine ratio |
The Sine of an acute angle equals the leg opposite the angle divided by the hypotenuse |
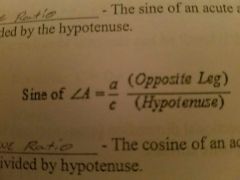
|
|
|
Cosine ratio |
The cosine of an acute angle equals the leg of the adjacent side divided by hypotenuse |
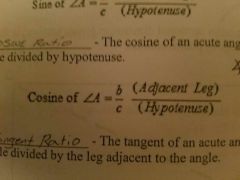
|
|
|
Tangent ratio |
The Tangent of an acute angle equals the leg opposite the angle divided by the leg adjacent to the angle |
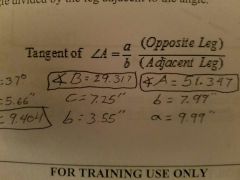
|

