![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
729 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
YOur patient weighs 64 kg. His urinary output for the last three hours combined was 120 mL. You would then --
A. Administer diuretics B. Increase LR infusion rate C. Reassess in 15 minutes D. Administer vasopressin |
A - he is not peeing enough
|
|
|
Your patient was treated for hypervolemia with diuretics. The veins in the neck are non-distended, pulse 74, bp 88/58, clear lung sounds and input for the last two hours was 100. What evaluation value concerns you --
A. Pulse B. U/O C. BP D. Veins |
C
|
|
|
You would question giving vasopressin to this patient --
A. Diabetes Insipidus B. SIADH C. Bedwetter D. Damaged Adrenal glands |
B
|
|
|
Your patient has bp = 166/80, distended neck veins, edema and a bounding pulse. Your best positioning for this client regarding fluid balance --
A. Prone B. Semi-fowlers C. Sidelying D. Supine |
D - induces diuresis
|
|
|
Your patent has pain=9/10, sneezing, U/O = 20mL in a ten hour period, unable to sleep. You administer bumex as directed. Your anticipated result:
A. Increased urinary output B. Pain = 2/10 C. No more sneezing D. Self report of sleeping better |
A
|
|
|
You have four patients who all need IV fluids. You would set the slowest rate for --
A. 12 yo hiv patient B. 92 yo dementia patient C. 35 yo work-holoc w/ heart issues D. The 49 year old mystic who overdosed on herbal meds |
B - heart works slower, can't pump as well.
|
|
|
Not a sign of hypovolemia --
A. Decreased blood pressure B. Low urinary output C. Low cvp D. Low pulse |
D - increased pulse
|
|
|
Your patient is vommiting all night. Her BP still reads 190/90. You would administer --
A. LR B. D5W C. Tap water D. D5LR |
C - don't give hypotonic or isotonic -- more fludi in vascular space
|
|
|
You have a patient with a magnesium level of 4.5. You would expect to see all but --
A. Pulse = 120 B. Respirations = 12 C. Weak muscle tone D. Flushing/warm from Vasodilation |
A - pulse decreases
|
|
|
Your patient with a magnesium level of 3.1 will do good if you administer --
A. Calcium acetate B. Calcium magnesate C. Calcium gluconate D. Calcium carbonate |
C
|
|
|
A Ventilator will help the patient who has a magnesium level of --
A. .9 B. 1.4 C. 1.9 D. 2.6 |
D
|
|
|
Alcoholics will most likely come in the er with a magnesium of --
A. .9 B. 1.4 C. 1.9 D. 2.6 |
A
|
|
|
To assess for trouseau's sign, you would --
A. Press on radial artery, check for nailbed color changes B. Tap on the cheek and check for twitching C. Rub finger up and down the sole of the foot D. Pump blood pressure cuff |
D
|
|
|
Not a reason for hypermagnesemia --
A. Antacid consumption B. DIarrhea C. Renal failure D. Over consumption of magnesium |
B
|
|
|
To assess for chevostik's sign, you would --
A. Press on radial artery, check for nailbed color changes B. Tap on the cheek and check for twitching C. Rub finger up and down the sole of the foot D. Pump blood pressure cuff |
B
|
|
|
Good tx for a patient who has a magnesium level of .2 --
A. 100 mg magnesium sulfate B. Calcium gluconate C. Prepare ventilator D. Dialysis |
A - hypogmagnesemia
|
|
|
Your patient is given thiazides. You would assess the -______ level after --
A. Magnesium B. Sodium C. Calcium D. Iodine |
C
|
|
|
Fleets enema would be good for a patient with an overdose of --
A. Magnesium B. Calcium C. Potassium D. Iodine |
B
|
|
|
Immobilization can lead to --
A. Hypomagnesium B. Hypothyroidism C. Hyperkalemia D. Hypercalcemia |
D - Remember, if you don't bear weight, calcium gets stripped from the bone and into the blood
|
|
|
Your patient has a calcium level of 12.1. Most pertinent nursing dx --
A. Risk for infection B. Risk for injury C. Risk for sepsis D. Risk for fluid balance increase |
B
|
|
|
Not a cause of hypercalcemia --
A. Thiazide consumption B. Hypoparathyroidism C. Radical neck surgery D. Thyroidectomy |
A
|
|
|
Your patient tested positive for cheevostick's sign. You would expect this reading --
A. Potassium = 3.1 B. Sodium = 159 C. Magnesium level = 2.9 D. Calcium = 7 |
D - low calcium
|
|
|
Your patient has a calcium reading of 6.4. You would question this on the MAR --
A. Calcium carbonate B. Calcium acetate C. Calcium carbonate D. Caclium lactitate |
C
|
|
|
Your patient has a calcium level of 8.3. You would hold renegel if the patient has --
A. Heart failure hx B. Liver issues C. Kidney issues D. Diabetes |
C
|
|
|
T/F - IV calcium should be administered quickly to avoid shock --
|
F - slowly
|
|
|
Not an expected sign of hypernatremia --
A. Headache B. Thirsty C. Dry mouth D. Swollen tongue |
A - hyp natremia
|
|
|
Expected finding for a patient with siadh --
A. Potassium 5.4 B. Magnesium 2.1 C. Sodium 131 D. Phosphorous 128 |
C - hypokalemia - hemodilution
|
|
|
Expected finding in patient with CHF --
A. Potassium 5.4 B. Magnesium 2.1 C. Calcium 9.9 D. Sodium 131 |
D
|
|
|
Not a good idea for a patient with a sodium count of 121 --
A. 3% NS B. 5% NS C. Tap water D. Both A and B E. Both B and C |
C
|
|
|
Your patient has hyperkalemia. You would not expect to see --
A. Muscle twitching B. Cramps C. Weakness D. Paralysis |
B
|
|
|
Your patient has been prescribed insulin for hyperk. You would explain to the non-diebetic patient --
A. Potassium raises blood sugar B. Potassium disables your pancreas C. Potassium needs glucose to go back into the cell D. Potassium is not essential to insulin resistance |
C
|
|
|
Your patient has oral potassium. You would tell your patient to take with --
A. Food B. Water C. NPO D. Milk only |
A
|
|
|
T/F - Never add potassium to bag --
|
True
|
|
|
Calcium gluconate can be given for people who suffer --
A. Hyperkalemia B. Hypernatremia C. Hypermagnesemia D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
Not a finding with hyperkalemia --
A. Bradycardia B. High T waves C. Long PR interval D. PVC |
D
|
|
|
Not a finding with hyperkalemia --
A. Bradycardia B. V tach C. Long PR interval D. Wide QRS |
B
|
|
|
Not a finding with hyperkalemia --
A. U wave B. High T waves C. Long PR interval D. Flat P waves |
A
|
|
|
Your patient has reached homeostasis when his BUN has reached --
A. 8 B. 16 C. 21 D. 29 |
B 10-20
|
|
|
Your patient is free from dig toxicity when the reading comes back as --
A. 1.8 B. 2.1 C. 2.6 D. 3.0 |
A 0.5-2
|
|
|
FLeets Enema can help a patient who has --
A. Magnesium level of .01 B. Calcium level of 10.8 C. Sodium level of 5 D. Potassium level of 3.4 |
B - Fleets enema has phosphorous
|
|
|
Your patient with hypercalcemia is being administered a fleets enema. You explain that this will help because --
A. It'll make you feel better B. It'll help increase magnesium C. It is high in phosphorous D. It is low in calcium |
C
|
|
|
You will find steroids to treat --
A. Hypermagnesium B. Hyperkalemia C. Hypernatremia D. Hypercalcemia |
D -they decrease calcium
|
|
|
Your patient has hympomagnesium. Biggest n dx? --
A. Activity intolerance B. Risk for aspiration C. Risk for falls D. FLaccid musculature |
B - Can cause stridor/laryngospasm
|
|
|
DOn't give this to the patient with renal issues --
A. Calcium acetate B. Sevelamer hydrochloride C. Calcium acetate D. Aluminum hydroxide |
D
|
|
|
Your patient was given IV insulin to help with hyperkalemia. You should monitor for --
A. Hypoglycemia B. Hyperglycemia C. Hypokalemia D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
Your patient was diagnosed with hyperkalemia. You would question this recorded symptom --
A. Muscle twitching B. Muscle cramps C. Muscle weakness D. Flaccid paralysis |
B
|
|
|
Your patient has tall and peaked t waves as well as bradycardia. You would expect this reading ---
A. Potassium 5.3 B. Calcium 3.9 C. Magnesium .8 D. Potassium 3.1 |
A
|
|
|
Your male spinal cord injury patient was damaged at S2. You would tell him --
A. You will still be able to havve erections B. You will be able to have an ejaculation C. You can have erections and ejaculations D. You can have neither ejaculations nor erections |
D
|
|
|
Your client's chart says damage of cranial nerve I. Your most produent intervention --
A. Use snellen chart B. Assess using Perrla C. Have patient cover ears and ask if he can hear you. D. Have client place one finger over nostril |
D
|
|
|
Your client has listed trouble with compression of cranial nerve II. Your best intervention --
A. Perrla B. Test for nystgmus C. Use of snellen chart D. Assess ptosis |
C - II is sensory, not motor.
|
|
|
You askd your patient to watch your finger move from periphery to center. You are assessing cranial nerve --
A. II B. III C. V D. VIII |
A
|
|
|
You need to assess your patient for nystagmus. You would ask her to turn eyes --
A. Upward and outward B. Upward and inward C. Downward and outward D. Downward and inward |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is asleep. You take a pin and place the painful stimulus on her hand. She then wakes up. You would document --
A. Stupor B. Lethargy C. Alert D. Comatose |
A
|
|
|
YOu are assessing a patient. You ask patient to repeat a series of three numbers (3,5,9). You then have the patient increase each series by one number until 8 successful repetitions. Your patient does fine. You document --
A. Good recent recall B. Standard long term memory C. Proper attention span D. Immediate recall enhanced |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is a female age 56. SHe has a case of extreme recurring migraine headaches. You would educate her on prevention of --
A. Cardiovascular disease B. HIV C. Lung stability D. Slow digestion |
A
|
|
|
The doctor has Imatrex and Zomig prescribed for two different patients who suffer migraines. You will teach them both about all but ---
A. Flushing, tingling and hot feeling will reside. B. This drug is not for those with high blood pressure C. Do not take with contraception D. Not for heart disease or hypertension |
C - should take it, not good for pregnant people
|
|
|
You would mainly give indural or a NSAI forst when it comes to --
A. Abortive therapy B. Preventive therapy C. Adversive therapy D. Prodromal therapy |
B
|
|
|
Your patient is having rhythmic breathing with preiods of apnea. You would document -
A. Ataxic B. Cheyne Stokes C. Apneustic D. Decerbate |
B
|
|
|
You would find this to indicate ICP --
A. BP = 110/74 B. HR = 101 C. Respirations = 20 D. Temperature = 35.8 |
B - HR usually slows down
|
|
|
You would find this to indicate ICP --
A. Pulse pressure = 170/59 B. HR = 49 C. Respirations = 20 D. Temperature = 35.8 |
A
|
|
|
The MOST IMPORTANT item on your alzheimer's patient's itinerary --
A. That these events are spaced throughout the day B. That these events include the patient's family C. That the events start at the same time as the day before D. That the events aren't boring |
C - Routine is important
|
|
|
Your patient has alzheimer's and you're trying to counter incontinence. You would help by --
A. Having the bedpan next to the patient B. Writing a note at the board to go to the bathroom C. Show a video about the advantages of urination D. Place a pciture of a commode on the bathroom door |
D
|
|
|
An alzheimer's patient fell and says he thinks he broke his neck. Your first intervention --
A. Head lift, chin tilt to open airway B. Turn head to side to drain secretions C. Assume it's a spinal cord injury until ruled out otherwise D. Assess patient's ability to walk |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is a female and has had a spinal cord injury. You would instruct her that --
A. You can have an orgasm, but pregnancy depends on the extent of the injury B. You can conceive, but you will never menstruate again C. You can have sex, conceive, but you cannot have an orgasm D. You can have normal sex and menstruation with orgasm, but you cannot become pregnant |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is in spinal shock. You would question this med on the mar --
A. Atropine B. Prednisone C. Baclofen D. Disgoxin |
D - You want the heart to start beating fast, not slow down
|
|
|
Your patient went into spinal shock yesterday. You would question this finding from yesterday's charting --
A. Ejection fraction = 45% B. BP = 99/59 C. HR = 102 D. Bowel sounds = hypoactive |
C - bradycardia goes with spinal shock
|
|
|
Your patient went into spinal shock yesterday. You would question this finding from yesterday's charting --
A. Ejection fraction = 45% B. Extremities moist C. HR = 49 D. Bowel sounds = hypoactive |
B - extremities usually warm and dry
|
|
|
Your patient is about to undergo autonomic dysreflexia. You prepared for this when your patient said --
A. Why are my legs pale? B. Why do I have goosebumps? C. My automatic blood pressure thing says 189/100 D. I had a headache come out of nowhere |
D - earliest sign
|
|
|
Your patient went into autonomic dysreflexia. The tech ran out and told you. You would question this observation --
A. Face was flushed B. Legs were white C. Patient stated no pain, but was sweating big time D. Patient reported extreme nausea |
C - headache is part of it
|
|
|
Your patient has autononomic dysreflexia. You would FIRST --
A. Check for impaction B. Place hob in HIGH FOWLERS C. Prepare for catheterization D. Lossen tight clothing |
B
|
|
|
Your patient just asked the patient to pull up the arms after a suspected spinal cord injury. You are assessing --
A. C3 B. C5-6 C. C8 D. T2 |
B
|
|
|
You are giving teaching to a patient who has a halo. You would urge the patient not to take a --
A. Bath B. SPonge bath C. Shower D. All are okay |
C
|
|
|
Your patient just had a spinal fusion. You would allwo the patient --
A. NPO until flatus B. Ice chips C. Water as needed D. Milkshake to prevent aspiration |
A
|
|
|
Your patient has a halo. You need to assess the skin under the vvest for breakdown. You would --
A. Remove vest, place back when done B. Use special x-ray to see through the vest C. Use a flashlight to inspect D. Rely on report of skin discomfort |
C
|
|
|
Your patient had an VP shunt put in for hydrocephalus. You would keep kid --
A. Flat B. On operated side C. If no ICP, then raise 15-30 degrees D. All of the above |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is on an anticonvulsant medication. Your patient says he has pinkish urine. You would --
A. Reduce dosage B. Call doctor C. Assess vitals D. Tell him this is normal |
D
|
|
|
Your patient has myesthenia gravis and is taking tensilon. You would have this antidote nearby --
A. Narcan B. Atropine C. Enalapril D. Digoxin |
B
|
|
|
Your patient has an antiparkinonian medication. You would question this teaching --
A. Take an hour before breakfast B. Monitor for OH C. Use a low protein for sinemet D. Can cause some chest pain |
A
|
|
|
You would keep naloxone on hand for the patient that is taking --
A. Morphine B. Tensilon C. Meperdine D. Dilaudid |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is prescribed Darvon. You would teach about --
A. Aspirin toxicity B. Increased respirations C. Neurolgia relapse D. Intractible manifestations |
A - contains aspirin
|
|
|
Your patient is on ritalin, an emphetamine. He should take his medicaiton --
A. Before lunch B. During lunch C. After lunch D. Before bed |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is on ritalin and enalapril. YOu would question this order from the nourishment room --
A. Peppermint tea B. Chocholate milk C. Cocacola D. Pineapple juice |
C - too much caffeine
|
|
|
Your patient just received his dose of mannitol. Your most important assessment fifteen minutes from now --
A. Pain level B. Lung sounds C. Urinary output D. Blanching of skin |
B - TOo much fluid backs up in lungs
|
|
|
Your patient is on morphine and asks why you are checking lung sounds? You tell her --
A. Morphine makes you breathe funny B. Morphine administration properly, notes malfunctioning lungs C. Morphine supressess the cough reflex D. Morphine makes you retain lung fluid |
C
|
|
|
Your patient just had a spinal x-ray. You would make your patient --
A. Walk up and down the hall 2x B. Lay on side, practice hip abduction C. Lay high fowlers, passive rom D. Immobile until results known |
D
|
|
|
Your LPN said a patient is flushing and has a metallic taste. Your instincts tell you it would be this patient --
A. The one with the MRI B. The one with the cerebral angiography C. The one with the lumbar puncture D. The one with the CT scan |
D
|
|
|
T/F - Patient post lumbar lies flat --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient is getting a myelography (spinal dye contrast). If there is an air infusion, you would position the patient --
A. High fowler's B. Semi fowler's C. Lateral recumbant D. Flat |
D
|
|
|
Your patient MUST BE NPO before --
A. Cerebral angiography B. Lumbar puncture C. CT scan D. X-Ray |
A
|
|
|
Your patient just had a cerebral angiography. Your instructions to patient --
A. Bedrest for 3 hours lying semi-fowlers B. Bedrest for 12 hours laying flat C. Periodic rest, alternating between flat and high fowlers D. No rest, starvation |
B
|
|
|
Your patient should drink this before an EEG --
A. Coca cola B. Coffee C. Tea D. Milk |
D - no caffeine
|
|
|
Your patient needs to demonstrate swallowing movements. You would assess for cranial nerve --
A. V B. VIII C. X D. XI |
D
|
|
|
Your patient can't slow his heart rate. You would assess for damage of cranial nerve --
A. III B. VIII C. X D. XII |
C
|
|
|
Your patient can't sense carotid pressure. You would assess nerve --
A. III B. VIII C. IX D. XII |
C
|
|
|
Not true about Vagus nerve --
A. Senses carotid pressure B. Senses taste C. Controls heart rate D. Controls digestion rate |
A
|
|
|
Not a medication for a person with elevated ICP --
A. Rennedine B. Mannitol C. Morphine D. Prednisone |
C
|
|
|
Not a s/s of ICP --
A. Increased temp B. Increased hr C. Increased bp D. Increased pain |
B - bradycardia
|
|
|
Irregular breathing with pauses at end and beginning of inspirations --
A. Apneustic B. Cheyne-stokes C. Irregular apneustic D. Clusters |
A
|
|
|
Your patient would receive zorivex if he has --
A. Guilliene barr B. Bell's Palsey C. Cerebral anuerism D. Encephalitis |
D
|
|
|
Your patient reports chest pain. You would assess for --
A. Meningococal meningitis B. SIADH C. Viral meningitis D. Salpinger's meningitis |
C
|
|
|
Your patient had a stroke on the Right brain. You question this charting on this patient --
A. Left side neglect B. Poor spacial definiton C. Unable to calculate addition D. NO concept of time |
C
|
|
|
Your patient had a stroke on the Right brain. You question this charting on this patient --
A. Left side neglect B. Increased awareness of limitation C. Unable to calculate addition D. Poor spacial definiton |
B
|
|
|
Your patient just had a stroke. You would question this charting --
A. Cheyne stokes B. Fatigue C. BP 99/40 D. Pulse 87 |
C - BP usually high
|
|
|
Your patient suffered a blow in the wernicke's area of the temperoral lobe. You would expect --
A. Cannot understand you B. Can understand, can't speak C. Can speak, but can't understand or move D. Can't understand what he or she can't perceive |
A
|
|
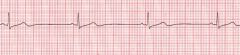
Your patient has been fatigued and sleepy. This is what his ekg strip looks like. You would question this drug order --
A. Atropine B. Epinepherine C. Dopamine Drip E. Nitroglycerin |
E- Nitroclycerin is contraindicated
|
|
|
Bad sign for patient with accute stroke --
A. Pulse = 87 B. BP = 120/80 C. Lung sounds clear D. Cap refill >3 |
B Need to keep it high
|
|
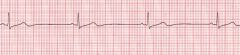
Your FIRST intervention for this would be to --
A. Assess thrombosis B. Call Code C. Check the leads D. Hold back metoprolol |
C - A and B don't figure into this and You would check the leads before witholding beta blockers
|
|
|
Not an obvious sign of autonomic dysreflexia --
A. Flushing below the lesion B. Distended bowell C. Intense headache D. BP = 210/90 |
A - Should be pale below the lesion
|
|
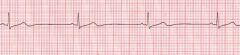
Your patient was given a dopamine drip. The dopamine, epinepherine nor does the atropine seem to have an effect. You would tell your patient --
A. We are going to work with a non-invasive pacemaker B. We will fit you in for a cardioversion C. After the TEE, you will be on anticoagulant therapy D. You will need coumadin for life |
A - the others fit an Afib scenario
|
|
|
T/F - Bradycardia and paralytic ileus are signs of spinal shock --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient is on decadron knowing that this med will --
A. Decrease sweating B. Enhance serotonin reuptake C. Decrease edema D. None of the above |
C
|
|
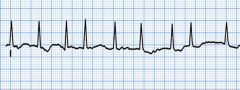
Your patient has not responded well to the digoxin or amiodorone. Your next move would be to prep the patient for --
A. Cardioversion B. TEE C. Ablation D. Maze therapy |
B
Cardioversion comes after TEE, Ablation and Maze therapy kick if cardioversion doesn't work. |
|
|
Your patient has a myesthenia gravis exacerbation. You would see all but --
A. Increase of disease B. Increased pulse C. Decreased bp D. Decreased urinary output |
C
|
|
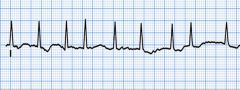
Your patient's EKG. You would administer --
A. Dopamine drip B. Aropine C. Cough CPR D. Amiodorone |
D
|
|
|
No rectal temps should be administered for the patient who has --
A. Cerebral hemorrhage B. Cerebral Anuerism C. Cranitomy D. EGG |
B
|
|
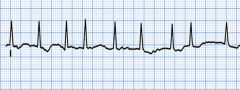
Your doctor, for this problem, ordered six weeks of coumadin to prepare for the --
A. Elective Cardioversion B. TEE C. Maze therapy D. Ablation |
A
|
|
|
Patient that cannot have an autologous donation --
A. Leukemia patient B. HIV patient C. Sickle cell patient D. ICP patient |
A
|
|
|
Not a side effect of TCA class medications --
A. Polyuria B. Decreased tears C. Dry mouth D. Dizziness |
A
|
|
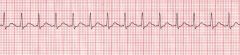
Your patient's ekg rhythm. THe patient is concious, cracked membranes in the mouth and a little nervous. Your best intervention --
A. Administer IV fluids B. Reduce caffeine intake C. Raise the head of the bed D. Call a code |
A. Though raising the head of the bed helps with breathing it doesn't address the issue at hand, which is hypovolemia
|
|
|
Your patient is on amitriptyline, a TCA antidepressant. Your instructions should include all but --
A. Take at night B. Used for OCD and some depressed, not first choice C. Give suicidal people only one week's stock D. Warn patient about frequent urination as side effect |
D - Anticholinergic
|
|
|
Your patient is on Prozac and celexa. You would warn your patient about --
A. Decreased sweating B. Sexual dysfunction C. Weight gain D. Addictive |
B
|
|
Your patient is about to arrive for cardioversion. You need to ask all but --
A. Did you withold digoxin? B. First I need to have you sign the informed consent C. Will you be comfortable with the O2 mask being on while you get shocked? D. You haven't been applying topical nitroglycerin have you? |
C - always hold dig, sign informed consent and hold topical nitroglycerin
|
|
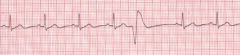
This is what your patient is suffering. It would be important to look at this lab value --
A. K+ B. Na+ C. Ca D. Mg |
A - Hypokalemia causes pvc's
|
|
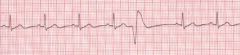
Patient has this problem. What would be the last med you would consider giving --
A. Lidocaine B. Pronestyl C. Amiodorone D. You can give these in any order E. None of these meds apply |
B - THis is given if amiodorone and ldocaine don't work
|
|
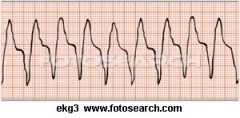
Your patient has a hr of 84 and no symptoms of perfusion lack. This would be your intervention --
A. Pronestyl B. Cough CPR C. Epinepherine IV push D. Call Code |
A
|
|
|
Not a sign of MAO --
A. Fever B. Sweating C. Anxiety D. Bradycardia |
D - Tachycardia
|
|
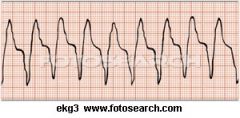
Your patient has a pulse of 84, but the capillary refil is >4 and signs of cyanosis. You would recommend all but --
A. Cough CPR B. Cardioversion C. O2 D. Defibrillator |
D
|
|
|
Old school antypsychotic --
A. Haldol B. Risperdal C. Zyprexa D. Clozaril |
A
|
|
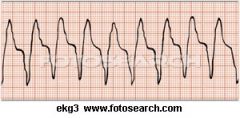
Your patient has no pulse. You would --
A. Give CPR B. Encourage cough cpr C. Defibrillate D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
Your pirority assessment when having a patient on zyprexa --
A. Pulse B. BP C. Dysphagia D. Hyperreflexia |
C - Airway problems
|
|
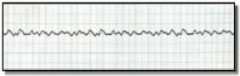
What order are your interventins --
A. Assess LOC B. CPR until ventilator available C. Call Code D. A'B'C's |
A
D C B |
|
|
Your patient has tonic contractions of muscle, mouth and torso, which can affect breathing. You would document --
A. Troponin B. Dystonia C. Dystanicia D. Myoalgia |
D
|
|
|
Your patient has dystonia. You would give treatment using --
A. Ambulation B. Benedryl C. Trendelberg positioning D. Metoprolol |
B
|
|
|
Your patient is on cruthches. You instruct that the handgrips have to be at what level --
A. 1 inch above hip B. at hip level C. 1 inch below D. At mid torso level |
B
|
|
|
Your patient is about to travel upstairs with crutches. You would instruct the patient to put this foot first --
A. Good B. Bad C. Place crutches up and lift with arms D. Place crutches behind you and jump up, using crutches to stabilize you |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is instructed to do the four point gait. You would instruct --
A. Left crutch, Right foot, left food, right crutch B. Left and right crutch, left foot, then right C. Left crutch, right foot, right crutch, left foot D. Left foot, left crutch, right foot, right crutch |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is about to travel downstairs with crutches. You would instruct the patient to put this foot first --
A. Good B. Bad C. Place crutches up and lift with arms D. Place crutches behind you and jump up, using crutches to stabilize you |
B
|
|
|
Your patient has a cane. What is the right hand to place the cane in?
A. Either or B. Hand opposite of unaffected leg C. Hand opposite of affected leg D. Depends on where the pain is at |
C
|
|
|
When your patient with a cane is going up stairs. You should use what leg first? --
A. Good B. Bad C. Place crutches up and lift with arms D. Place crutches behind you and jump up, using crutches to stabilize you |
A
|
|
|
Your patient has a walker. You would instruct all but --
A. When backing up, have legs back into chair before sitting B. Keep walker one step ahead of you C. Walk with affected leg D. Use good leg first when going up stairs |
D - Never do stairs
|
|
|
Your patient has been pescribed ferrous sulfate. You would be wrong when you instruct your patient to --
A. Watch for GI and tarry stools B. Must be taken PO C. Have with straw, stains teeth D. Take with milk |
D - Not with dairy or antacids
|
|
|
Your patient is not reacting well to ferrous sulfate. You would then offer --
A. Dextran B. B12 C. Folic Acid D. Eopoietin |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is on Vit. B12 for pernicoious anemia. You are correct when you say --
A. This will be lifelong B. B12 is needed for RBC creation C. This will be a IM injection D. Both A and B E. A, B and C |
E
|
|
|
Your patient is on Eupoeitin Alpha. You would make sure to do all but --
A. Avoid sq shots B> Monitor BP after C. Shake the bottle well D. Assess rbc count |
C - DONT SHAKE
|
|
|
Your patient is on coumadin. You would have this as an antitode on hand --
A. Calcium gluconate B. Vitamin K C. Magnesium sulfate D. Desmopressin |
B
|
|
|
T/F - WIth mannitol, we have to watch out for a rebound effect --
|
True
|
|
|
Not a good dietary choice for patient on thiazide diuretic --
A. Milk B. Pork C. Bananna D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
E
|
|
|
One of the first signs of respiratory acidosis --
A. Hypoxia B. Hypocalcemia C. Hypocarbondioxide D. Cyanosis |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is on morphine, rr is at 12/min and bp 119/80. You would watch for --
A. M. Alkalosis B. R. Alkalosis C. M. Acidosis D. R. Acidosis |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is in the late phase of respiratory acidosis. You would watch for --
A. Restlessness B. Increased blood pressure C. Bradycardia D. Delusions |
C - Bradycardia and cyanosis are late signs
|
|
|
You ask your patient to breathe into a aper bag. You would know this client has --
A. M. Alkalosis B. R. Alkalosis C. M. Acidosis D. R. Acidosis |
B
|
|
|
You ask the patient who has this disorder _________________ if he had any aspirin in the last two hours --
A. M. Alkalosis B. R. Alkalosis C. M. Acidosis D. R. Acidosis |
B
|
|
|
DKA can cause --
A. M. Alkalosis B. R. Alkalosis C. M. Acidosis D. R. Acidosis |
C
|
|
|
Starvation can cause --
A. M. Alkalosis B. R. Alkalosis C. M. Acidosis D. R. Acidosis |
C
|
|
|
Explain how starvation leads to metabolic Acidosis? (Fill in the blank)
|
Fats and proteins are broken down, produce ketones
|
|
|
T/F - A patient's respirations are shallow. I keep thinking they would retain CO2 and therefore get respiratory acidosis? --
|
True
|
|
|
Your ptient suffered a major burn. You then ask if the burn was in an open or closed space. Reason? --
A. To assess airway patency B. To assess Residual burns C. To assess Carbon monoxide amt. D. To assess patient's well-being |
C
|
|
|
You need to assess patient's cmonoxide posioining. Your spao2 says 99%. The patient doesn't appear hypoxic. You would --
A. Document B. Assess pulse C. Run a carboxyhemoglobin test D. Take blood culture |
C
|
|
|
Burns: Give SA% for --
1) Head 2) Trunk 3) Arms 4) Legs 5) Inguinal |
4.5
18 4.5 9 1 all X2 except inguinal |
|
|
Your a nurse who sees a traumatic burn patient. Prophyllactically, you would expect to see first --
A. Tracheostomy B. Intubation C. Arterial stents D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
B - least invasive first
|
|
|
Your patient was burned on 20%, weighs 100 kg and was burned at 9am. Patient arrives at hospital at 11am. Correct fluid administration for first batch --
A. 2000 mL between 11am-11pm B. 4000 ml between 11am-7pm C. 3500 ml between 11am-5pm D. 2000 ml between 9am-11pm |
B
|
|
|
Your patient was burned on 20%, weighs 100 kg and was burned at 9am. Patient arrives at hospital at 11am. Correct fluid administration hourly fir first 8 hrs --
A. 200 ml B. 300 ml C. 400 ml D. 500 ml |
D
|
|
|
Your patient was burned on 20%, weighs 100 kg and was burned at 9am. Patient arrives at hospital at 11am. How much would you give starting at 7pm?
A. 2000 ml B. 3000 ml C. 4000 ml D. 5000 ml |
A
|
|
|
Your burn patient is on fluid replacement. He becomes restless suddenly. You would assess for --
A. Fluid volume B. Pain C. Allergic reaction D. Hypoxia |
D
|
|
|
Your burn patient is getting fluid replacement. You monitor progress by evaluating --
A. Weight B. Pain level C. Skin color D. U/O |
D
|
|
|
You are off work and you find a man on fire. You would do all but --
A. Cover with blanket B. Place ice on the burn C. Place cool water on the burn D. Remove jewelry |
B - too much vc
|
|
|
Your burn patient has received albumin. What is a vital assessment after the administration --
A. Lung sounds B. Pulse pressure C. Skin color D. Weight |
A - More fluid, more volume -
|
|
|
Your patient has been given albumin for a very bad burn. Your patient feels week and sedate. A vital nursing dx --
A. Decreased C/O B. Risk for injury C. Fluid volume deficit D. Disturbed sleeping pattern |
C - A doesn't apply, because albumin would increase -- c - can get to the lungs nad cause bad o2 exchange
|
|
|
Your patient is receiving a rapid infusion of fluids. You should measure --
A. BP B. Pulse C. Respirations D. CVP |
D
|
|
|
You have a burn patient with albumin prescribed. You would administer it --
A. When arrived B. During the first round of fluid infusion C. After the first 24 hours D. When lOC is normal |
C
|
|
|
You have a burn patient and you administer a tetanus toxoid and immune globulin. They ask why both? You explain --
A. Both ensure viruses don't enter the blood stream B. Neither of them work unless they work together C. The tetanus toxoid takes too long and the immunoglobulin kicks in the immunity D. The immunoglobulin helps slow down because the tetanus toxoid works too quickly. |
C
|
|
|
You have a burn patient. Which patient would most likely get the tetanus shot --
A. HIV patient B. Elderly patient C. Patient with prednisone D. Patient with Heart history |
D - not to immunosupressed patients
|
|
|
When you check a circumferential burn on an extremity, you are sure to check all but --
A. Skin temp B. Grip strength C. Color D. Pulse |
B
|
|
|
T/F - With burns, you might get a foley catheter might not get a return --
|
False
|
|
|
Abnormal urine color post burn --
A. Yellow B. Orange C. Brown D. Black |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is on dobutamine. An expected result --
A. Stabilized bp B. Increased C/O C. Decreased Respirations D. Vascular stabilization |
B
|
|
|
When does a burn patient's NG tube get removed --
A. When the abdominal girth lowers B. When the abdomen becomes soft C. Upon bowel sounds D. When gag reflex occurs |
C
|
|
|
Great diet for burn victim that needs wound healing --
A. Fats and vitamin A B. Protein and vitamin C C. Carbohydrates and vitamin B12 D. Low fat, high carb |
B
|
|
|
T/F - If you aspirate stomach content and the residual is 55 ml, empty contents and turn off suction --
|
F - Yes, turn off suction, but give back residual to the patient
|
|
|
Your patient's pre-Albumin is 22. You would --
A. Document B. Check U/O C. Call Doctor D. Call crash cart |
A - Pre is 17-40
|
|
|
Normal range for Albumin --
A. 2.1 B. 3.1 C. 4.9 D. 5.8 |
C - 3.4-5.4
|
|
|
Your patient has a superficial burn. You would expect only damage to the --
A. Epidermis B. Epidermis and some dermis C. All of the epidermis D. You die |
A
|
|
|
T/F - With prtial thickness, burns occur to the entire epidermis and some fat --
|
F - some epidermis, partial dermis
|
|
|
Your client has some burns on his hands. How would you wrap the hands --
A. Wrap hand tightly B. Wrap fingers together to protect bacteria C. Wrap fingers speerately D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
E
|
|
|
Your patient has a burn on anterior neck. You would posiiton --
A. Hyperextend - no pillows B. Light flexion, one pillow C. Midline D. Rotated to give healing to air |
A
|
|
|
Silver sulfadiazine(silvadine) is a drug used to --
A. Decrease eschar B. Topical wound treatment C. Decrease bacteria D. Enhance pain relief |
B
|
|
|
Your patient has been prescribed with collagenase (santyl). You would give it to this burn patient --
A. Pregnant woman with 3rd degree B. Full thickness burn patient with exposed full body cavity C. Patient withfull thickness burn over perineal area D. Paitent with terrible burn over sciatic nerve |
C - No pregnant, not on face, not on nerves and not on hollow body cavity
|
|
|
Your patient was just administered silver sulfadiazine (silvadine). You would look at this lab --
A. Potassium B. Albumin C. Sodium D. WBC |
D - Can lower wbc count
|
|
|
You do a visual assessment of your patient who took silver sulfadiazine. To look for SE, you would look for a --
A. Rash B. Leaking fluid C. Loss of chest hair D. Crust around mouth |
A
|
|
|
After takin gMafenide acetate, you should check --
A. BP B. PH C. Pulse D. RR |
B - think acetate ACIDtate
|
|
|
Silver over the burn victim need --
A. Wet dressings B. Dry dressings C. Electrolyte monitoring D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
Broad spectrum antibiotics will be used on the patient until --
A. WBC count lowers B. Blood cultures have returned C. Until the Doctor fives the order D. None of the above |
B
|
|
|
Not an alarm find for a patient on a mycin drug --
A. Loss of hearing B. BUN Levels C. Potassium number D. Reduced urinary output |
C
|
|
|
Your burn victim has a graft. The donor site would be --
A. Always open to air B. Non-pressure dressing applied and left on even after surgery C. Pressure dressing removed once bleeding has stopped then open to air D. Dressing removed after surgery and then closed in a silvudine dressing |
C
|
|
|
Your patient needs to rid herself of a fungus. You would prescribe --
A. Acyclovir B. Fluconazole C. Neosporin D. Bactroban |
B
|
|
|
Your patient ius on tramadol to reduce pain. You would help out the ptient by --
A. Putting on seizure precautions B. Can cause insomnia C. Can cause diarrhea D. Can cause hematuria |
A - can cause seizures, drowzy, vomiting, constipation
|
|
|
Your patient has an ear infection. You tell your patient that acetesol will help with --
A. Bacterial B. Virus C. Fungus D. Protozoa |
C
|
|
|
For ear meds with a 2 year old, you should pull pina --
A. Down and back B. Up and back C. Up and forwrd D. Down and forwrd |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is receiving cipro for an ear infection. You give the medication. You then have patient --
A. Get up and shake head while breathing deeply B. Rise and dangle feet C. Lie supine for five minutes D. Turn over on unaffected side for five minutes |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is being administered aurulagan. You would then assess --
A. WBC count B. Platelet count C. U/O D. Pain level |
D
|
|
|
Typical result after your ptient has been on decadron --
A. BG = 80 B. Thinned out appearance C. K+ = 3.2 D. N+ = 8.3 |
C - high sodium, high water, low potassium
|
|
|
YOu aare conducting central line blood draw. It is important to --
A. Inject NS through a 3ml syringe B. Discard first 10 ml of blood C. Have IV fluids run at all times during procedure D. Both A and B E. Both B and C |
B
|
|
|
Your infant patient is burned on front only. From head to toe. % --
A. 72 % B. 18 % C. 82% D. 99% |
C
|
|
|
Break down Baby's dimensions for burns --
Head = Torso= Arms= Legs= Perineal= Buttocks= Back= |
Head = 21
Arms = 10 Torso = 13 Legs = 13.5 Perineal =1 Back = 13 |
|
|
BIggest risk factor for cancer is the patient who --
A. Is aging B. Is a smoker C. Is a drinker D. Is immunosuppressed |
A - Aging is the bigger
|
|
|
Your female patient should start doing her monthly self-breast exam when --
A. Once a month (calendar) B. A year after the first period begins C. As soon as breasts fully develop D. As soon as menstruation starts |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is a 27 year old woman who wants to know how often she should get a breast exam from a doctor --
A. Q 1 yr B. Q 2 yr C. Q 3 yr D. Q 5 yr |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is a 44 year old woman who wants to know how often she should get a breast exam from a doctor --
A. Q 1 yr B. Q 2 yr C. Q 3 yr D. Q 5 yr |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is a 27 year old woman who wants to know how often she should get a pelvic exam from a doctor --
A. Q 1 yr B. Q 2 yr C. Q 3 yr D. Q 5 yr |
A
|
|
|
Your patient wants to know when she should do a self-breast exam. You advise --
A. Two days before period start B. After the period C. In the middle of the period D. Right at the start of the period |
B
|
|
|
Your patient has had NO Problems in any sexual way. How often should they get a pap-smear? --
A. Q 5 mos B. Q 1 yr C. Q 3 yr D. Q 4 yr |
C
|
|
|
Your patient needs more teaching regarding a pap smear if she says --
A. "I can't have sex beforeheand" B. "I can't smoke at all" C. "I can't douche before because that wil alter cells D. I have no problems so, after this I will see you in 3 years. |
B
|
|
|
Your patient should have how many views at a mammogram --
A. one each breast B. One on affected breast C. Two on affected breast D. Two on each |
D
|
|
|
Your patient has come in for a mammogram. She will be asked to remove all but --
A. Perfume B. Baby powder under her arms C. Deoderants D. Breast lotion |
A
|
|
|
Your patient asks why no deodorant for mammogram. You say that it will --
A. Give a false negative B. Can retain calcium deposits C. Will cause an allergic reaction D. Will cause OH |
B
|
|
|
For males, they should get the --
A. Annual digital rectal B. Yearly PSA C. Both Annually D. Both every other year |
C
|
|
|
List general CAUTIONary s/s of cancer --
|
Bowell habit changes
A sore that does not heal Unusual bleeding Thickening of tissue Indigestion or difficulty swallowing Obvious change in mole Nagging cough |
|
|
Your patient has cachexia. YOu would monitor --
A. Body wasting B. B. Pressure C. Nutrition D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is scheduled for brachytherapy.You would warn the patient of --
A. Sheeding of skin B. Decrease in fiber diet C. Altered taste is possible D. Errythmia is possible |
B - others apply to external
|
|
|
Your patient is prescribed sealed breacytherapy. You would tll the patient that the --
A. Urine will be affected B. Out of the system in 48 hours C. Implanted close to the tumor D. Saliva will emit radiation too |
C
|
|
|
You would feel most threatened getting this brachytherapy patient's saliva on you --
A. Sealed B. Unsealed C. Solid D. Lasered |
B
|
|
|
You give your patient an unsealed radiation isotope. You tell him --
A. This can be given PO or IM B. This will exit out in 96 hours C. Your body only will emit radiation D. Your fluids will radiate |
D
|
|
|
Your patient can be given sealed radiation for brachytherapy via (picki all that apply )
A. PO B. SC C. IM D. IV |
A and D
|
|
|
You have a patient with internal radiation (sealed). You would allow this one family member to visit --
A> Pregnant cousin B. FIve year old son C. Mom with cancer history D. Cousin with UTI |
C - no preggors, kids under sixteen
|
|
|
Your patient is on radiation (unsealed). You would encourage your patient to --
A. Give his mother a hug B. Ask that he restricts his pregnant cousin to just phone calls with him C. Limit each visitor to 2hrs a day D. All the above |
B - Six feet from source. Visitors one hour a day
|
|
|
Your patient is on brachytherapy. You would suspect more education is needed when the patient says --
A. I will have to get a freakin' foley B. I will be on bedrest C. I need more fruits and veggies D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
C
|
|
|
T/F - If you have a patient with an radio imlant and it becomes dislodged and we see it, we should put on gloves, forceps and place it in lead container --
|
True
|
|
|
With a patient with internal implant, you should wear the film badge --
A. During hygiene B. Only during blood draws C. Until the radiation level declines D. At all times |
D
|
|
|
Your patient has external radiation for cancer. You can expect --
A. Low RBC B. Low WBC C. Low Platelets D. Both A and C E. A, B and C |
E
|
|
|
Your patient had EXTERNAL radiation therapy. He should wait ____ until he can expose site to sun --
A. 1 month B. 4 months C. 8 months D. 1 year |
D
|
|
|
Your patient on external radiation says "this water tastes funny." There is nothing in the water. You would --
A. Document B. Take vitals C. Call Doctor D. Assess membranes and document |
D
|
|
|
Your patient's wbc count is 3000 and is about to begin chemo. You would --
A. Administer B. Delay for an hour C. Call Dr. and delay D. Abort procedure |
A
|
|
|
Not a symptom of cervical cancer --
A. Sciatic pain B. BLood tinged vaginal discharge C. Painful bleeding D. Bck/flank pain |
C
|
|
|
Your patient needs more instruction when she says this regarding cervical cancer --
A. I could have cryosurgery B. A pap-smear will diagnose this C. I might have to have a conization, which is cervical removal D. Cn be 100% cured with early detection |
D
|
|
|
Patient least likely to develop UTERINE cancer --
A. Patient who started menopause @39. B. Patient who never had a baby and she's 80. C. Patient who is 54 years old D. A patient who's mother had it |
A
|
|
|
T/F - Your patient can never bleed down there after menopause --
|
F - Can if one has utierine cancer
|
|
|
A CA125 test rules out --
A. Cystic Fibrosis B. Ovarian involvement in cancer C. Pelvic cyst D. Hormonal imbalance |
B
|
|
|
Most definitive Test for uterine cancer (pick all that apply) --
A. CXR B. D&C C. CT D. Liver/Bone Scan E. Endometrial biopsy F> IVP |
B and E
|
|
|
With a total abd. hysterectomy, patients will lose --
A. Uterus B. Ovarie C. Cervix D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
T/F - After radical hysterectomy has pelvic congestion of blood --
|
True
|
|
|
Define Dehiscence: (fill in blank) --
|
Wound margins seperate
|
|
|
Define evisceration: (fill in blank) --
|
Organs come out
|
|
|
Avoid tension on this after hysterectomy --
A. Abdominal suture B. Lower back C. Knees D. Head |
A
|
|
|
Position to avoid with post-radical hysterectomy --
A. Side lying B. Supine C. Low fowler D. High fowler |
D - pressure and blood rush to the area
|
|
|
Okay for a patient with a post-radical hysterectomy --
A. Douching B. Sex C. Showers D. Girdles |
C - no baths
|
|
|
Patient with rad. hysterectomy needs more teaching when she says --
A. I cannot drive for a period of time B. I can strenghten my muscles by lifting weights off the floor C. I should avoid sex for awhile D. It is possible to have hemmorhaging for 10-14 days post-op -- |
B
|
|
|
A patient with a hysterectomy is most concerned with --
A. Pain B. Infection C. Pregnancy D. Reccurance |
B - think of the perineal
|
|
|
Your patient has a whitish vaginal post hysterectomy drainage. You would --
A. Document B. Run a culture C. Call Dr. D. Hide |
A
|
|
|
A patient needs adriamycin. You know she is battling --
A. Cancer B. Infection C. Herpes D. Decreased LOC |
A - it's a form of chemotherapy
|
|
|
A patient needs Cisplatin. You know she is battling --
A. Cancer B. Infection C. Herpes D. Decreased LOC |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is on Tamoxifen (Soltamox). You can expect a decrease in --
A. LDH B. Estrogen C. Platopuera rankoning D. Tetanus |
B
|
|
|
Where is the tail of spence? (fill in the blank) --
|
Outer part of breast that extends into the axilla
|
|
|
You have four women's health patients in your breast oncology clinic. Which one can you assign the LPN --
A. Patient who had her first period at age 9 B. Patient who is 27 and has two children C. The patient who is 42 and has never been pregnant D. The patient who gave birth to her first child at age 39 |
B
|
|
|
You have four women's health patients in your breast oncology clinic. Which one can you assign the LPN --
A. Patient who had her first period at age 9 B. Patient who started menopause at age 59. C. The patient who is 42 and has three kids. D. The patient who gave birth to her first child at age 39 |
C
|
|
|
Your patient had a radical mastectomy on right breast. You owuld tell her after recovery to do all with the right arm except --
A. Squeeze tennis balls B. Check blood pressure on right arm daily C. Wall climb D. Brush hair |
B - No BP, Injections,
|
|
|
Your patient recovered from breast cancer. You would encourage her to do all but ---
A. No nail biting B. Wear gloves in the garden C. Wear a watch on the bad side for a higher self esteem D. Try to flex/extend elbow |
C
|
|
|
You tell your patient with breast cancer surgery to squeeze tennis balls. She asks why. You say --
A. Helps estrogen count B. Helps with oxygen exchange C. Helps restore feeling to extremity D. Helps create alternative circulation |
D
|
|
|
Your patient with Lupron will experience lower ____ levels --
A. Extrogen B. Progesterone C. Luetinizing hormone D. RBC count |
A
|
|
|
Your patient has lung cancer. You would expect to see --
A. Pleuritic pain on expiration B. Non-painful tension on expiration C. Pain on inspiration D. Night sweats |
C
|
|
|
The patient is right when he says this about his bronchoscopy --
A. I will just have a light breakfast before B. It is normal to have some respiratory depression after the exam C. I won't be hoarse after the exam D. I will NPO until the gag reflex reccurs |
D
|
|
|
T/F - Before a sputum specimen, you should have the patient preform oral hygiene before rendering sample --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient with lung issues. You get a sputum sample. This is NOT true --
A. SPecimen gathering is clean technique B. Done in the morning C. Let the cup touch their lips D. Don't let them rinse out mouth done before |
D
|
|
|
For a lobectomy, you would place the patient --
A. Surgical side up B. Surgical side down C. High fowlers D. Prone |
A
|
|
|
For a Pneumenectomy, you would place the patient --
A. Surgical side up B. Surgical side down C. High fowlers D. Prone |
B
|
|
|
T/F - Chest tube placement after a pneumectomy is vital to success --
|
F - no chest tube with pneumectomy
|
|
|
Fill in the blank: don't place patients on too high lateral position after a pneumectomy. Why? --
|
Mediastianal shift
|
|
|
Your patient asks you what early signs of laryngeal cancer are. Youw ould say --
A. Sore throat B. Loss of speech C. Dentures don't fit anymore D. There are no early signs |
D
|
|
|
You suspect your ptient might have laryngeal cancer when he says --
A. I eat allot of ham B. I have pain in just my right ear C. My saliva is thick D. I feel my nostrils are on fire |
B
|
|
|
Post total laryngectomy position --
A. Left lateral B. Prone, head tilted C. Mid-fowlers D. Supine |
C
|
|
|
T/F - Complete TPN is ordered for all post-laryngectomy patients --
|
F - NG feeding
|
|
|
Your patient had a total laryngectomy and the trachea is ulsating. Your first move is to --
A. Call another nurse to help B. Call doctor C. Take vitals D. Stabilize it |
D
|
|
|
Your patient's family member is asking why mouth care with Post-total laryngectomy. You respond by --
A. It will reduce chance for pneumonia B. Stomas can increase oral inflammation C. State regulates this practice D. His mouth stinks |
A
|
|
|
Your patient needs a filter for his tracheostomy. You would reccommend a --
A. Washcloth B. Shammee C. Plastic D. Bib |
D
|
|
|
Not a good idea for a post-total laryngectomy patient --
A. Encouraging patient to write down his words B. Instruct patient to use humidified air C. Practice pursed lip breathing by using a straw D. Teaching a patient exercises he can do besides swimming |
C
|
|
|
YOu are doing trach care. YOu would stop advancing the catheter when --
A. Client coughs B. Resistance is felt C. The Client cirnges D. Both A and B E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
You would assess for this potential complication of trach suctioning --
A. Tachycardia B. Bradycardia C. Asystole D. V-Fib |
B
|
|
|
When you think of liver, think --
A. Nutrition B. Hypertension C. Infection D. Bleeding |
D
|
|
|
Your patient wants to avoid colorectal cancer. You would urge him to have a diet without --
A. Chicken B. Steak C. FIsh D. Veggies |
B
|
|
|
You would allow this before a stool sample --
A. Sandwich with horseradish B. Motrin C. Apple D. Orange |
C - no vitamin C
|
|
|
Age fecal occult blood testing for CRC --
A. 20 B. 30 C. 50 D. 75 |
C
|
|
|
About crc dx --
A. Take sigmososcopy and colonoscopy q 5 yrs B. Sigmoidoscopy 5 yrs, conoloscopy 10 yrs C. Take sigmososcopy and colonoscopy q 10 yrs D. Sigmoidoscopy 10 yrs, colonoscopy 5 yrs |
B
|
|
|
Your patient with a an obstructed visible peristaltic wave has what kind of bowel sounds --
A. Absent B. High pitched C. Low pitched D. Sproadic |
B
|
|
|
You would take a rectal temp on this person --
A. Heart hx B. Thrombocytopneic C. Abdominal-perineal resection D. Immunosuppressed |
A
|
|
|
Greatest risk factor for bladder cancer --
A. Drinking B. Cocaine C. Smoking D. Heroin |
C
|
|
|
Your patient has bladder cancer. You would question this symptom --
A. Painless urination B. Polyuria C. Intermittent gross hematuria D. Microscopic hematuria |
B
|
|
|
Define Ileal conduit (fill in the blank) --
|
Piece of ileum turned into bladder. Ureters placed in one end, the other is brought to the abd. surface as a stoma
|
|
|
After bladder cancer, it is important to --
A. Hourly U/O B. Tell patient impotence is possible C. Mucous-free urine D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
D
|
|
|
T/F - Patient might have mucous in urine after a urostomy --
|
True
|
|
|
Change urostomy appliance in the --
A. Morning B. Mid-day C. Night D. At 3am when REM is highest |
A
|
|
|
True about PSA --
A. Start at age 45 if you have two or more 1st degree relatives with prostate cancer B. Start at age 30 q 3 yrs C. PSA also covers liver issues D. PSA normal is 10ng/ml |
A - normal is <4, protein is only part of the prostate only
|
|
|
Your patient is on being tested for alkaline phosphotase. If increased, you know that --
A. The patient is hypocalcemic B. Bone metassis C. Bone marrow suppression D. Imbalanced PH |
B
|
|
|
Your patient's PSA is 3. You would --
A. Check acid phosphotase B. Check alkaline phosphotase C. Check for metastasis D. Document |
D
|
|
|
T/F - A TURP is done to cure postate cancer --
|
True
|
|
|
Most common complication of a TURP --
A. Hemorrhaging B. Infection C. Pain D. Erectile dysfunction |
A
|
|
|
Belladonna and Opium suppository are given for --
A. Prostate pain B. Bladder spasms C. Urejectomy D. Pancreatic lipase destruction |
B
|
|
|
Good dietary choice for you patient who had a TURP --
A. Bananna B. Cheese C. Multigrain bread D. Chicken |
C - constipation causes bleeding
|
|
|
Good post-TURP activity --
A. Sitting and meditating B. Lifting weights off the ground C. Driving out to the countryside D. Laying down and lifting weights |
D
|
|
|
TX for gastric obstruction --
A. NPO B. NG TUBE C. Monitor further distention D. Both A and C E. A, B and C |
E
|
|
|
Your patient had surgery for stomach cancer. You would assess for this standard complication --
A. Pain B. Anemia C. Infection D. Difficulty eating |
B
|
|
|
Shillings test is used to check for --
A. Vitamin B12 B. Platelets C. Mucous D. RBC's |
A
|
|
|
Your patient had a gastrectomy and there is a NG tube used. You would know to --
A. Realize it's for compression B. Needs to be repositioned q 2 hrs C. SHould never be repositioned bc it can mess up the suture line D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
C
|
|
|
Explain how a gastrectomy can lead to anemia (fill in the blank) --
|
No stomach, parietal cells damaged, no intrinsic factor, no B12 absorbed, no rbc's being made - Anemic
|
|
|
Your patient is about to get a thyroid scan. You would advise --
A. Cut out iodine one week before B. NPO C. Bleeding precautions D. Carotid scan |
A
|
|
|
Tapazole is considered a(n) --
A. Antiuricacid B. Fungus removal C. Thyroid Med D. Anxiety med |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is on PTu. You tell him that these meds will be --
A. Taken for life B. Tapered and restarted in intervals C. Stopped suddenly and never restarted again D. WIll be tapered and discontinued |
D - This will prevent hpothyroidism
|
|
|
Lugols solution is rendered to the patient who has --
A. Hypercalcemia B. Hyperthyroidism C. Hyperkalemia D. Hypernatremia |
B
|
|
|
True about Lugol's solution --
A. Give with milk and use straw B. Increases vascularity of the thyroid gland C. Stops thyroid from making TH's D. It's an iodine supplement |
A
|
|
|
Potassium Iodide and PTU is used for --
A. Hypercalcemia B. Hyperthyroidism C. Hyperkalemia D. Hypernatremia |
B
|
|
|
Not a drug that helps with hyperthyroidism --
A. Beta Blockers B. Radiactive Iodine C. Calcium channel blockers D. Antithyroids |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is on inderal for hyperthyroidism. You woudl worry about --
A. Increased pulse B. Out of control epinepherine C. Increased myocardial contractility D. Decreased cardiac output |
D
|
|
|
This paitent will be administered Inderal; THe patient with --
A. Hyperthyroidism B. Diabetes C. Asthma D. Hypothyroidism |
A
|
|
|
Decreases thyroid vascularity --
A. Inderal B. Radiactive iodine C. PTU D. Lugors solution |
D
|
|
|
Stops thyroid from making th's --
A. Inderal B. Radiactive iodine C. PTU D. Lugors solution |
C
|
|
|
Stops epinepherine --
Decreases thyroid vascularity -- A. Inderal B. Radiactive iodine C. PTU D. Lugors solution |
A
|
|
|
Destroys thryoid cells --
Decreases thyroid vascularity -- A. Inderal B. Radiactive iodine C. PTU D. Lugors solution |
B
|
|
|
Your patient has been prescribed radioactive iodine. This is not true about the drug --
A. Given IV B. Destroys thryoid cells C. Stay away from babies for 24 horus D. Don't kiss anyone for 24 hours |
A - It's a PO
|
|
|
Explain provisions (safety) about radioactive iodine (fill in the blank ) --
|
Stay away from babies and kisisng people for 24 hours
|
|
|
Your patient has a partial thyroidectomy. You would check for bleeding --
A. In the ear B. Anterior neck C. Side of neck that was operated on D. Posterior neck |
D
|
|
|
Explain why a trach set would be nearby for someone who had a thyroidectomy (fill in the blank) --
|
Can hurt parathyroid gland ++ low calcium in blood -- spasms of airway
|
|
|
Your patient had a thyroidectomy and can't close eyelids. You would --
A. Turn off lights B. Tell them to focus on something visually desirable C. Have them lay face down on a pillow D. Use hypallergenic tape for thm |
D
|
|
|
Not a hypothyroid medication --
A. Throglobulin B. Liothyronine C.Lugol's solution D. Levothyroxine |
C
|
|
|
Phoeochromocytoma is located in the --
A. Adrenal gland B. Adrenal Cortex C. Kidneys D. Circle of Odi |
A
|
|
|
Your patient has pheochromocytoma. You would question this reading?
A. BP 188/99 B. Pulse = 129 C. Dry skin D. Flushing |
C
|
|
|
VMA is used to dx problems in the --
A. Adrenal Medulla B. Adrenal Cortex C. Kidneys D. Circle of Odi |
A
|
|
|
VMA assesses --
A. Hgb B.Cardiac enzymes C.Epi and Nor D.Facial cells |
C
|
|
|
(4) Functions of glucocorticoids (Fill in the Blank) --
|
Mood change
Fat/protein breakdown Raised glucose Lowered immunity |
|
|
T/F - Problems withaldosteroneare minieralcorticoid problems --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient with Addison's disease will have which one --
A. Low volume B. Low potassium C. Lowsodium D. Both A and C E. Both A and B |
E
|
|
|
Fkydrocortisone acts as --
A. Potassium B. Aldosterone C. ADH D. Pituitary Hormone |
B
|
|
|
T/F - Your patient isat home taking fludrocortisone. Your patient has an overnight gaine of 7lbs. You shouldhol or reduce --
|
True
|
|
|
Signs of addisonian crisis --
A. LOC decreased B. Vascullar collapse C. Severe hypotension D. Both A and B E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
T/F - An adrenalectomy is used to limit addison's disease --
|
F - cushings
|
|
|
Not a need for a patient with cushing's disease --
A. Increased potassium B. Decreased calcium C.Decreased sodium D.Increased protein |
B - Increase calciumbecause steroids decrease serum calcium making you excrete it through the GI tract
|
|
|
Brittle bones can be found in --
A. Cushing's syndrome B. Addison's syndrome C. Hypocalcemia D. Epstein Barr |
A - steroids take away calcium, borrows from bone to help blood
|
|
|
Bad food choice for patient with cushing's syndrome --
A. Banannas and peaches B. Tuna fish and oranges C. Hotdog and salad D. Boiled chicken andbaked potato |
C
|
|
|
Your patient has sogi phenonomenonYou should offer before bed --
A. Snack B. NPH insulin C. Snack and insulin D. NOthing |
A
|
|
|
T/F - you should eat something before exercise before you exercise --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient had DKA. In addition to hourly glucose checks, also check for --
A. U/O B. Potassium C. Sodium D. Magnesium |
B
|
|
|
With DKA, start with --
A. LR B. D5w C. NS .9 E. NS 3% |
C
|
|
|
When do you add D5W during a DKA event --
A. BG = 50 B. BG = 78 C. BG = 100 D. BG = 300 |
D
|
|
|
Barrier temp for patient with ICP --
A. 99.8 B. 100 C. 100.4 D. 102.1 |
C
|
|
|
Not a sign of autonomic dysreflexia --
A. Headache B. Seeing spots C. Tachycardia D.Hypertension |
C - Bradycardia
|
|
|
For Spinal shock, you would see all but --
A. Bradycardia B. Hypertension C. Flaccid paralysis D. Loss or reflexes |
B- hypotension
|
|
|
First thing to dowith autonomic dysreflexia --
A. Raise hob B. Give O2 C. Call Doctor D. Asessbladder/bowell |
A
|
|
|
Your patient with increased ICP should have this fluid limit --
A. 1000 ml B. 1200 ml C. 1400 ml D. 1500 ml |
D
|
|
|
A VITAL assessment after the administration ofMannitol --
A. Pulse B. Hgb C. Hct D. Lung sounds |
D
|
|
|
Earliest sign of LOC --
A. Pounding headache B. Extreme bradycardia C. LOC decreased D. Absent reflexes |
C
|
|
|
Pick which is worst -- decerbrate or decorticate posturing (FIB) --
|
Decerbrate
|
|
|
Which is "breathe, breathe, breathe, breathe, breathe then apnea" --
A. Cheyne stokes B. Ataxic C. Ligor's pattern D. Apneustic |
B
|
|
|
How do steroids reduce ICP (FIB) --
|
Remove cerebral edema
|
|
|
A good intervention for increased ICP --
A. Play upbeat music on the tv B. Use comfortable restraints C. Lower the protein in diet D. Decrease stimulation toa void seizures |
D
|
|
|
List (4) places you will see bleeding with a skull fracture (FIB) --
|
Eyes, neck, throat, ears
|
|
|
Battle's sign is brusing over the --
A. Temporal region B. Mastoid C. Feet D. Shoulder |
B
|
|
|
Your brother falls and has a cuncussion and is out for a minute. He gets up and starts throwing up. You would --
A. Administer o2 B. Sit in semi-fowlers on couch C. Reduce stimulation D. GO to ED |
D
|
|
|
Explain how Nitroglycerin works (FIB) --
|
Dilation so more oxygen reaches the myocardiaum and releaves pain. Reduced preload and afterload. Causes expansion of arteries and veins.
|
|
|
Not a good intervention for heart patient on nitro --
A. Never remove cotton from the container B. Never swallow, put under tongue C. May get a headache D. Keep in a dark glass bottle in a cool place |
A - remove it, it absorbs it. The others are right.
|
|
|
How often should Nitro be renewed --
A. Q30 days B. Q 1 month C. Q 3 months D. Q 6 months |
D
|
|
|
When administering nitro, you should call ems --
A. Before first dose B. After first dose C. Before second dose D. After second dose |
B
|
|
|
List (3) effects of Beta Blockers (FIB) --
|
Reduces C/O
Reduces contractility Lowers bp Lowers HR |
|
|
Doesn't dilate the coronary arteries --
A. Beta blockers B. Calcium channel blockers C. Nitroglycerine D. Morphine |
A
|
|
|
Not a Calcium Channel blocker --
A. Nifedipine (procardia) B. Verapamil (Calan) C. Amlodipine (Norvasc) D. All of the above E. None of the above |
E
|
|
|
Explain why a heart attack could bring on vommiting (FIB) --
|
Pain = vagus nerve stimulation = heart rate decreases = lack of perfusion to the GI tract :)
|
|
|
Why do WBC's go up with a MI (FIB)? --
|
Inflammation
|
|
|
T/F - CK-MB stats go to baseline in 3 days --
|
True
|
|
|
LDH (lactic dehydrogenase) helps determine --
A. Heart output B. Location of tissue damage C. Elevated prostraglandin levels D. WBC creation |
B
|
|
|
Define STEMI and NSTEMI (FIB) --
|
Indicates that the client is having a heart attack. Non-elevation ST secment
|
|
|
Immediately do this for a heart attack victim --
A. Give O2 B. Give digoxin C. Give Aspirin D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
Not a risk for sudden death --
A. V tach B. Asystole C. Vfib D. V. Tack without pulse |
A
|
|
|
Drug to treat vfib (pick all that apply) --
A. Beta Blockers B. Lidocaine C. Inderal D. Amiodorone E. Atropine Sulfate |
B and D
|
|
|
The cardiac drug acronym MONA stands for (FIB) --
|
Morphine
Oxygen Nitroglycerin Asprin |
|
|
First sign of toxicity with Lidocaine --
A. Capillary refill decrease B. Dyspnea C. Afib D. Neuro changes |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is on amiodorone. What should you evaluate for potential side effects --
A. Pulse B. BP C. Cap refill D. LOC |
B - Can cause hypotension
|
|
|
Your patient had a PCI and a stent put in.He says he has chest pain. You should --
A. Call doctor B. Give aspirin C. Give nitro D. Raise head of the bed |
A - This means the occlusion is back
|
|
|
Not a good cardiac rehab exercise --
A. BIcep curls B. Swimming C. Holding freeweights over head for minutes on end D. Runnig |
C - no isometric
|
|
|
Why give colace to a heart patient (FIB) --
|
No straining, straining activates the vagus nerve
|
|
|
Safest time of day for a recovering heart patient --
A. Morning B. Afternoon C. Evening D. Either A or B E. Either A or C |
A
|
|
|
Only approved fibrinolytic for stroke patients --
A. Steptokinase B. Tenecteplase C. Alteplace D. Reteplase |
C
|
|
|
An okay patient to get streptokinase --
A. Intracranial neoplasm B. MI hx C. Intracranial bleed D. Suspected aortic dissection |
C
|
|
|
T/F - Alcohol is part of the bleeding precautions --
|
True - liver think bleeding
|
|
|
T/F - Need a ABG stat when starting streptokinase --
|
F- no abg's
|
|
|
Why give a fibrinolytic at the AC line over central (FIB)? --
|
Need at a compressable site
|
|
|
Eclientifibatide (Integrilin) is administered --
A. IM B. SQ C. Continuous IV D. IV push |
C - helps inhibit platelt ggregration
|
|
|
Your patient is getting a cardiac cath. You would tell them all but --
A. Don't cough whatsoever B. Palpitations are normal C. Will feel hot when dye is inserted D. Have you ever had an allergy to shellfish? |
A - Need to cough to push dye through
|
|
|
List the 5 p's after cardiac cath (FIB) --
|
Pulselessness
Pallor Paralysis Parestesia Pain |
|
|
Not good for a pacemaker patient --
A. PROM to prevent frozen shoulder B. Keep raising arm over head C. Monitor HR D. Have ID card |
B - don't want to loosen electrode
|
|
|
(FIB) Purpose of a swan ganz catheter --
|
Measures heart pressures
Can dx why CO is down |
|
|
Not a complication of a Swan Ganz catheter --
A. Pulmonary embolism B. Increased CVP C. Pulmonary Infarction D. Thrombophlebitis |
D
|
|
|
(FIB) Function of a A-Line --
|
Monitors BP continueously
|
|
|
Not part of Allen's test --
A. Apply pressure to ulnar vein B. Release pressure while continuing to compress the radial artery C. Assess color in extremities D. Color should return within 6 seconds |
A - Ulnar/radial arteries
|
|
|
T/F - You cn give meds via the A-line, but you cannot draw blood --
|
F - Other way around
|
|
|
List different ways to dx heart failure (FIB) --
|
Scwan ganz to measure pressure
A-line to mesure bp constantly Echocardiogram CXR BN Peptide |
|
|
(FIB) - List four things assessed by an echocardiogram --
|
Rear pressure
Picture of the heart Ejection fraction Pumping action |
|
|
Your patient is going to get an echocardiogram. This is used to dx --
A. Pulmonary edema B. Triponin levels C. Pumping pressure D. AFib |
C
|
|
|
You need to check a patient's heart for pounding pressure and rear pressure. You would go with a --
A. CXR B. Angiocatheter C. BNP D. Echo |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is showing signs of hf when the bnp reaches --
A. 100 B. 150 C. 200 D. 250 |
A
|
|
|
Your patient has taken digoxin and has vision changes, nausea and arrythmia. You would suspect --
A. Sodium = 11.8 B. Potassium = 3.1 C. Magnesium = 1.0 D. Calcium = 10.5 |
B
|
|
|
Late sign of dig toxicity --
A. Nausea B. Vision changes C. Anorexia D. Vomiting |
B
|
|
|
Your patient had heart failure and takes Ms. Dash. You would then monitor the patient's --
A. Sodium B. Nitrogen C. Potassium D. Albumin |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is taking enalapril. You would monitor for --
A. Sodium B. Nitrogen C. Potassium D. Albumin |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is on a ARB medication. You would use this for --
A. HTN B. MI C. Heart failure D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
E
|
|
|
Not used for MI --
A. Morphine B. Enalapril C. Aspirin D. Nitroglycerine |
B
|
|
|
FIB - Why should your patient on ACE inhibitors worry about potassium? --
|
The patient is decreasing the angiotensin cycle. Lower sodium/water = more potassium
|
|
|
Your client is on a baloon pump , you advise to --
A. Drink more fluids B. Keep legs straight C. Lay supine D. Raise arm above heart level |
B
|
|
|
Your patient hs pulmonary edema. This is not a drug you would give --
A. Lassix B. Natercore C. Beta Blockers D. Dobutamine |
D
|
|
|
T/F - Natacore should only be executed for 48 hours --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient has cardiac tamponade. You would see all but --
A. Increased CVP B. Incerased Bp C. Decreased cardiac output D. Pressures in all four chambers the same |
B - Only stuff in heart will increase, the normal bp runs through the rteries and veins
|
|
|
Define paradoxical pulse (FIB) --
|
When the systolic pressure falls > 10mm during insipiration
|
|
|
Paradoxical pulse occurs during --
A. Inspiration B. Expiration C. Both D. Niether |
A
|
|
|
A maximum narrowed ulse pressure pulse pressure is considered --
A. Less than ten B. Less than 20 C. Less than 30 D. Less than 40 |
D
|
|
|
T/F - Atherosclerosis is generalized location-wise --
|
F - it's everywhere
|
|
|
T/F - We elevaate veins and we dangle arteries --
|
True
|
|
|
Which is true about beurger's and raynauds --
A. Both are venous B. Raynauds - venous, Beurgers -- arterial C. Both are arterial D. Raynauds - arterial, Beurgers -- venous |
C
|
|
|
Progression of color on a raynaud's chick's fingers --
A. Red, white, blue B. White, blue, red C. Blue, red, white D. White, red, blue |
B
|
|
|
Buerger's disease usually affect --
A. Fingers B. Feet C. Head D. Shoulders |
B
|
|
|
Test for heparin --
A. Att B. PT C. INR D. Aptt |
D
|
|
|
Range for appt --
A. 20-36 B. 30-40 C. 40-54 D. 55-100 |
A
|
|
|
Normal PT range --
A. 8.8 B. 9.0 C. 10 D. 11.9 |
C 9.6 - 11.8
|
|
|
Your patient has a chest tube and there is fluctuation in the water seal tube. You would --
A. Document B. Assess dressing C. Check drainage D. Call Doctor |
A - that's what it should be doing
|
|
|
List (3) reasons why the fluctuation in a chest tube has stopped (FIB) --
|
1. Lung re-expanded
2. Kinks in the tubing 3. Suction not working properly |
|
|
Your patient should call the MD if chest tube drainage is --
A. Bright red B. Greater than 50 ml/hr C. Greater than 100/ml/hr D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
E
|
|
|
If the chest tube unit breaks, you FIRST --
A. Call MD B. Check vitals C. Place tube in saline or whatever cup of water on hand D. Call another nurse to hel |
C
|
|
|
Your patient has continuous bubbling on his chest tube system. You would first --
A. Assess the tubing for leakage B. Assess the patient for connectionn C. Call the doctor D. Call the manufacturer |
B
|
|
|
Not a risk for Pulmonary embolism --
A. Overhydration B. Venous stasis C. High cholesterol D. Birth control pills |
A - dehydration can cause this
|
|
|
Your patient has a small pulmonary embolism. You would --
A. COntinue to monitor B. Immediately raise the bed, adminster o2 C. Call MD D. Call crash cart |
A
|
|
|
A VQ scan helps detect --
A. Radiation B. Pulmonary perfusion C. Embolus activity D. Arterial stridor |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is about to have a vq scan. You ask patient to remove jewelry, she asks why. You would tell her --
A. Takes away pulse ox-readings B. Can give false readings C. Can give off metallic, allergic reaction D. None of the above |
B
|
|
|
Not true about a D-Dimer --
A. Will tell clot location B. Increased with pulmonary embolous C. It's a blood test D. Will show how bv's are reacting to clots |
D
|
|
|
T/F - With a vq scan, a dye is used --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient has hypoxia leading to pulmonary hypertension. You would start looking for --
A. Dyspnea B. Blood-tinged sputum C. Distended neck veins D. Tight chest |
C - Right heart failure can happen
|
|
|
(FIB) Why would wbc's go up with a pulmonary embolous? --
|
Inflammation
|
|
|
T/F - Ambulation and dehydration are the best ways to prevent a pulmonary embolous --
|
F - ambulate and hydrate
|
|
|
Priority intervention tx for pulmonary emboolous --
A. ABG's B. Prevention C. Oxygen D. C. Venous pressure monitoring |
B
|
|
|
Not S/S of pneumothorax --
A. Labored breathing B.Wet lung sounds C. Increased respiration D. Subq emphysema |
B - abscent
|
|
|
Largest complication to look out for with pneumothorax --
A. Increased RR B. Decreased BP C. P. Embolism D. Decreased C/O |
D
|
|
|
Valsalva would help the patient with --
A. Open pneumothorax B. Closed pneumothorax C. Tension pneumothorax D. Tension hemothorax |
A - Increases the intrathoracic pressure so no more air
|
|
|
If the patient has chest trauma, place --
A. High fowlers B. Semi fowlers C. Flat D. Prone |
C
|
|
|
Type of breathing seen with a sternal fracture --
A. Shallow B. Deep C. Intermittent D. Quick and deep |
A
|
|
|
The best to give to a patient who is having chest trauma with shallow breaths --
A. Morphine B. Darvocett C. Acetaminophen D. Dilaudid |
C
|
|
|
T/F - With CPAP and Bipap, all breathing is done by the patient --
|
F - CPAP, yes, BIpap, no
|
|
|
Your patient has montelukast prescribed. Your patient needs more teaching when he says --
A. This will help an accute exacerbation B. Nobody under 12 should get this C. Monitor the liver frequently D. This can help in a prophyllactic capacity |
A - NEVER ACCUTE
|
|
|
Your patient has alberterol prescribed. Your patient needs further education when he says --
A. This will help my accute asthma attacks B. This will help relieve bronchospasm C. This can help prevent future attacks D. This will help with my Chronic airway issues |
C - never prophyllactic
|
|
|
Only drug that's used for non-accute asthma --
A. Albuterol B. Atrovent C. Salmetrol D. Terbuteline sulfate |
B
|
|
|
Your patient is wrong when he says he's going to buy OTC drugs while taking this --
A. Albuterol B. Atrovent C. Salmetrol D. Terbuteline sulfate |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is on atrovent. You don't suspect this s/s --
A. Dry mouth B. Diarrhea C. Urinary retention D. Unable to form tears |
B - it's an anticholinergic
|
|
|
You would expect to see dry mouth and urinary retention with this drug --
A. Atrovent B. Albuterol C. Salmetrol D. Terbuteline sulfate |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is on theophyline. You would question this lunch --
A. Pizza and a chocolate donut B. Water and tossed salad C. Steak and baked potato D. Mushroom sauce and linguini with a side of prunes |
A - no caffeine
|
|
|
(FIB) - Healthy pheothyline levels --
|
10-20
|
|
|
You should monitor for sugar rise with --
A. Prednisone B. Flucatosone C. Methoprednisone (Solumedrol) D. Both A and C E. A, B and C |
D
|
|
|
Your patient had an accute asthma attack. You would prescribe --
A. Atrovent B. Prednisone C. Flucatosone D. Budnisone |
B
|
|
|
Your patient has an accute asthmatic eppisode. You would prescribe --
A. Atrovent B. Budnisone C. Flucatosone D. Methopridnisolone |
D
|
|
|
You would give this to your patient with an accute attack --
A. Flucatosone B. Atrovent C. ALbuterol D. Butdnisone |
C
|
|
|
This is an asthmatic prophyllactic --
A. Flucatisone B. Albuterol C. Prednisone D. Solmedrol |
A
|
|
|
Which can cause delayed growth --
A. Inhaled steroids B. Systemic steroids C. Anticholinergics D. Antiterbuclin |
B
|
|
|
You would contraindicate alchol with this class --
A. Inhaled steroids B. Systemic steroids C. Anticholinergics D. Antiterbuclin |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is on INH and riframpin and you assess for all but --
A. Smoking B. Alcohol consumption C. Vitamin B6 status D. Red, brown sweat/urine |
A
|
|
|
T/F - Atrovent can help with long term COPD --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient has been prescribed viagra. You would watch for this when used wth antibiotics --
A. Tachycardia B. Tachypnea C. Hypotension D. Fluid volume excess |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is on AVODART> You would know this patient has --
A. Increased ICP B. BPH C. Raynauds D. Decreased C/O |
B
|
|
|
You would minitor for all but with proscar/avodart --
A. PSH B. Impotence (can cause) C. Monitor urine for possible residual D. Watch for inflammation |
D
|
|
|
Your patient on testosterone should be watched for all but --
A. Extreme clotting B. Decrease insuline needs C. Sodium/water retention D. Edema |
A - Bleeding precautions
|
|
|
Yoru patient is on acetasol and coritic. This will help with ear infections by destryoing --
A. Bacteria B. Viruses C. Fungus D. Protozoa |
C
|
|
|
A good med for ear pain --
A. Cipro B. Acetasol C. Auralgon D. Coritic |
C
|
|
|
T/F - When doing ear meds, Pull pinna back on adults and then down/back on kids --
|
F - Up and back on adults
|
|
|
List four sequences of stump toughening (FIB) --
|
Into a soft pillow
Into a firm pillow Into a bed Into a chair |
|
|
Your patient had an amputation. You would first --
A. Elevate it on pillow B. Elevate it on sling C. Keep below level of the waist D. Rotate it daily |
A
|
|
|
Your amputee states pain 8 out of 10. You would go and --
A. Administer morphine B. Perform percussion movements on limb C. Elevate limb D. Encourage distraction |
D
|
|
|
List (3) good reasons to use traction (FIB) --
|
1. Realigns bone (reduction)
2. Reduces spasms Immobilizes |
|
|
Your patient is on traction. The weights should hang --
A. On a chair B. At the foot of the bed C. Freely in air D. On a weight rack |
C
|
|
|
T/F - High top tennis shoes can prevent foot drop
|
True
|
|
|
Types of traction to use with hip factures --
A. Bucks B. Russell's C. Halo D. Crutchfield |
A
|
|
|
Best to use with a femoral injury --
A. Bucks B. Russell's C. Halo D. Crutchfield |
B
|
|
|
Best choice for prolonged traction --
A. Bucks B. Russel's C. Halo D. Both A and B E. Both B and C |
C
|
|
|
Your patient has some serous drainage from his halo pin. you would --
A. Remove pin and sterilize B. Elevate HOB C. Call Dr. D. Document |
D
|
|
|
T/F - Russell's traction is used pre-op for a hip replacement --
|
F
|
|
|
Trochanter roll prohibits --
A. External rotation B. Flexion C. Medial rotation D. Ipsolateral flexion |
A
|
|
|
Not a good clothing piece for a person one day after hip replacement --
A. Gown B. Loose pants C. Blouse and skirt D. Loose shirt |
C - no leg crossing
|
|
|
Good for a hip replacement --
A. Long-term sitting B. Low chairs C. Stair climbing D. Swimming |
D
|
|
|
(FIB) - Explain compartment syndrome --
|
Squeezing of a fracture that has not had ice or has been elevated. Fluid accumulates in the tissues and impirs tissue perfusion.
|
|
|
T/F - Never loosen a cast even when compartmental syndrome is occuring --
|
False - losen the cast
|
|
|
First 24 hours of a patient's cast, use --
A. Fingertips B. Palms C. Forearms D. Feet |
B
|
|
|
With cast the first 24 hours --
A. Keep covered and wet B. Keep uncovered and wet C. Keep covered and dry D. Keep uncovered and dry |
D
|
|
|
Not a good place to rest a cast --
A. TV tray B. Pillow C. Bed D. Egg crate |
A - no hard surfaces
|
|
|
(FIB) --Your patient had pain with a cast. You give pain. What is the MOST important reason to reassess pain --
|
We want to see if there's a possibility for compartmental syndrome.
|
|
|
Patient most likely to endure a fat embolism --
A. 10 year old female B. 14 year old male C. 22 year old male D. 39 year old female |
B - young boys do weird crap like that.
|
|
|
When you see a snowstorm on a CXR, you can expect --
A. DVT B. Pulmonary embolism C. EKG distorition D. Fat embolism |
D
|
|
|
You have a patient with a fat embolism. You would look for a rash on the --
A. Chest B. Arm C. Umbillicus D. Neck |
A
|
|
|
Your patient had a fracture and he is bleeding from his eye. You would assess for --
A. Shock B. Compartment syndrome C. Neurological crisis D. Fat embolism |
D
|
|
|
Your patient suffers depression. Your best response in the AM --
A. Are you hungry? B. Do you still want to sleep? C. Do you want to go and eat or do you feel like showering first? D. DO you want to take a shower first? |
C - Give options. NO simple questions
|
|
|
You ask your patient if he's reading for breakfast. He just sits there for five seconds. You --
A. Ask him again B. Ask "yes or no?" C. Say "I notice that you're being silent" D. Wait |
D - They are slow responders
|
|
|
Your patient has delusions of granduer. You would use this nursing DX --
A. Risk for low self esteem B. Risk for injury C. Risk for urinary retention D. Disturbed thought process |
A
|
|
|
Most important attribute in dealing with a manic patient --
A. Convince them their delusions are false B. Consistant approach C. Talk about delusions and explore reasonings with client D. Teach them constructive ways to use their manipulative skills |
B
|
|
|
Your patient is a manic. Your worst intervention --
A. Decrease stimuli in the room B. Provide PURPOSEFUL activity C. Encourage to attend group support D. Don't argue or reason with them |
C
|
|
|
T/F - You should walk with a manic during meals --
|
True
|
|
|
Great activity for a manic --
A. Paint by numbers B. Crossword puzzle C. Study for a test D. Writing |
D
|
|
|
Best way to help your manic patients through a shift --
A. Assemble all together and allow them to voice concerns B. Treat them with a one-on-one basis C. Allow them to help become trustees of the ward D. Encourage healthier displays of sexuality |
B
|
|
|
Your schizo patient says "Wild birds yonder dotsen niglo pool chud." A therapeutic response --
A. "Niglo pool chud?" B. "Can you please clarify?" C. "Well, I like me some Niglo pool chud" D. "Does expressing yourself in nonsensical words make you feel safe? |
B - don't explore or give attention to the words
|
|
|
Your in a psych ward and you have four new admits. You would instinctively watch this one for suicide precautions --
A. High school graduate B. Female charge nurse C. Elderly decorated war veteran D. Grandmother of twoq |
C - Elderly men are a big risk grouip
|
|
|
You approach your schizo patient in the morning. Your least therapeutic response --
A. You want breakfast? B. What made you stay up all night? C. Are you feeling queesy? D. Did you sleep okay last night? |
B - lcosed ended questions
|
|
|
Your schizo patient is angry. You try to rechannel anger by offering --
A. The patient to practice karate kicks at the wall B. Listen to soothing music C. Talk witht he patient about his childhood D. Call the patient's rabbi |
A
|
|
|
Not a good activity for a paranoid patient --
A. Writing B. Painting C. Chess D. Swimming |
C
|
|
|
Least desireable type nurse for a paranoid patient --
A. Bubbly B. FIrm C. Realistic D. Direct and humorless |
A
|
|
|
Not a good idea for post-traumatic-stress patients --
A. Support Groups B. Medication C. Talk about issues, but don't push D. Seclusion |
D
|
|
|
Best implementation for a OCD patient --
A. Free schedule B. Time delay techniques C. Not verbalizing disapproval D. Allow patient to perform ritual |
A - Needs structure
|
|
|
T/F - With alcoholism withdrawal we walk and talk and reorientate vs. the first 3 stages --
|
F - just during I and II
|
|
|
Not a finding in a stage II alcohol withdrawal --
A. Hypoactive B. Increased BP C. Increased pulse D. Disorientation |
A
|
|
|
Your patient has stage III (Delerium tremens) for withdrawal. Yo ushould --
A. Keep light on B. Give antidepressant C. Turn lights off D. Have patient sleep it off |
A
|
|
|
Korsokoff's syndrome is a --
A. Emotional labile state B. Inability to speak C. Disorientation to time D. Disoritentation to space |
C
|
|
|
Normal for an alcoholic (pick 2) --
A. Mg = .05 B. Na = 199 C. Ca = 9.9 D. K+ = 2.9 |
A and D
|
|
|
Antabuse is a deterant to --
A. Overeating B.Alchohol C. Heroin D. Qualudes |
B
|
|
|
Why do alcoholics suffer impotence? (FIB) --
|
Nerve damage
|
|
|
The alcholic upon discharge has to avoid all but --
A. Cough Syrup B. Cologne C. Deodorant D. Aftershave |
C
|
|
|
T/F - Anxiolytics are cool for alchol detox --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient is a bulemic. You should sit and observe post meal for --
A. 1 hr B. 2 hr C. 3 hr D. 4hr |
A
|
|
|
Client most likely to believe that any relationship is better than no relationship --
A. Schizo B. Bipolar C. Manic D. Personality disorder |
D
|
|
|
Patient most likely to need rules enforced --
A. Schizo B. Bipolar C. Personality disorder D. Manic |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is hallucinating and say that angry people are chasing him? You would say --
A. What do they look like? B. Why are they chasing you? C. Do you wanna talk about this? D. The people are angry? |
C
|
|
|
T/F - People hallucinating need to be involved in activities --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient will be under watch for _____ with kidney stones --
A. Arrythmias B. Hemorrhaging C. High blood pressure D. Gout |
A
|
|
|
What to look for in urine with patients with kidney stones (FIB) --
A. RBC B. Platelets C. WBC D. BOth A and B E. Both A and C |
E
|
|
|
List what will happen to each with glomerulnephritis --
BP Facial area UO USG HGB BuN/Creatinine |
BP = Up
UO = Down USG = Up HGB = Down BUN = Up |
|
|
T/F - Strep causes glomeralnephritis
|
True
|
|
|
What causes a headache in glomerunephritis (FIB) --
|
Toxins not being excreted
|
|
|
List the 4 C's of communication (FIB) --
|
Clear
Concise Correct Complete |
|
|
Your patient has a central line to be inserted. You would remember all but --
A. Consent form must be signed B. Bring a 10ml flush with you for the triple lumen catheter C. Physician will verify blood return from each lumen D. You will have to flush each lumen with 10 mL NS. |
B
|
|
|
Your patient needs blood drawn out out of the central line. You would make sure to --
A. Keep previous infusions running B. Do not flush lumen before drawing blood. C. First draw 10 ml of waste blood, then draw the blood to be used for a lab test D. Flush again after blood draw |
C
|
|
|
Your patient has a central line. It is most important to --
A. Let lumen air out to avoid waste B. Put running infusions on hold before drawing blood C. Confirm blood return on lumens after instillation D. Lumen must be clamped befoe disconnecting any iv tubing |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is at risk for air embolous from central line. You would turn patient on --
A. Left side B. Right side D. Supine E. Prone |
A - air travels upward
|
|
|
For dressing care of a Central line, you must wear --
A. Gloves B. Gloves and mask C. Gloves, mask and gown D. Gloves mask, gown and respirator |
B
|
|
|
Which is true about central line care --
A. Gauze dressing should be changed every 24 hours B. Wear mask and gown to avoid contamination C. If transparent tegaderm dressing is used, must be changed every 36 hours D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
A
|
|
|
Explain three point gait (FIB) --
|
Two crutches forward, no wieght on bad leg, bring other leg forward
|
|
|
Your patient has a cane. He is to go up the staris. He should put what up first --
A. Good B. Bad C. Cane D. Both A and C E. Both Be and C |
D
|
|
|
List your order is supposed to go down stairs with cane --
Cane good leg Injured leg |
Cane
Injured leg Good leg |
|
|
Not a good intervention for a patient in anaphylactic shock --
A. Epinepherine B. Morphine C. Dopamine D. Elevate legs |
B
|
|
|
Not true about septic shock --
A. of infectious nature B. Massive vasodilation caused byinflammatory response C. Sepsis with hypotension and bad volume replacement D. Surgical drains can help |
C - Despite adaquate fluid replacment, this is still going on
|
|
|
Cullen's sign is found around --
A. Flank area B. Chest C. Umbilical D. Near perineum |
C
|
|
|
Gray turners sign is found at --
A. Flank area B. Chest C. Umbilical D. Near perineum |
A
|
|
|
FIB - How would hypotension occur from pancreatitis --
|
Shunting
|
|
|
Normal AST range --
A. 0-25 B. 8-40 C. 10-30 D. 10-20 |
B
|
|
|
Normal ALT --
A. 0-25 B. 8-40 C. 10-30 D. 10-20 |
C
|
|
|
Normal amylase number --
A. 10 B. 25 C. 39 D. 49 |
D - 45-200
|
|
|
Normal Lipase count --
A. 100 B. 120 C. 145 D. 199 |
A
|
|
|
Why bedrest for pancreatitis? --
A. Decreased stomach secretions B. Pain residing C. To heal the Circle of Odi D. to regenerate healthy ast levels |
A
|
|
|
Your patient has pancreatitis. What side effects does cogentin have --
A. Drooling B. Urinary retention C. Pain in the eyes D. Sweating |
B
|
|
|
Atropine (Lonox) has what kind of effect --
A. Proteinurea B. Reduced inflammation C. Dry mouth D. Shoulder pain |
C
|
|
|
FIB - How can cirrhosis cause anemia? --
|
Bleeding internally
|
|
|
You would question this order for a person with cirrhosis --
A. Vitamin C powder in milk B. Vitamin B12 IM C. Vitamin D tablet D. Vitamin B6 Sublinguial |
B - Bleeding precautions
|
|
|
FIB - Protein breaks down into _____ and the liver converts this to -____ --
|
Amonia, urea
|
|
|
To assess for asterixes, you would look at the --
A. Eyes B. Sclera C. Mucous membranes D. Hands |
D
|
|
|
Fetor is described as --
A. Declining hepatocytes B. Acetone breathing C. Iron breakdown D. RBC elevation |
B
|
|
|
Neomycin sulfate helps reduce the ______ bacteria --
A. Amonia B. Sugar C. Acid D. Lactose |
A
|
|
|
T/F - We would give O2 to someone with esophageal varices --
|
True
|
|
|
How does sandostatin help in the liver --
A. Lowers BP B. Elevates portal pulse C. Reduces bleeding D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
Not a s/s of chron's --
A. Bloody stool B. Anemic C. Constipation D. vomiting |
C
|
|
|
Not a s/s of chron's --
A. Bloody stool B. Fluid volume excess C. Diarrhea D. vomiting |
B - Dehydration
|
|
|
Good diet choice for chron's patient --
A. Cheese B. Whole grain bread C. Apple D. Lettuce |
A - Need low fiber diet.
|
|
|
T/F - Kock's pouch is a form of an ileostomy --
|
F - no bag, just a valve
|
|
|
How do we irrigate an iliostomy --
A. 20 cc's of water B. Revolving between ice cold and tepid water C. 100 CC's at once, keep bucket nearby D. We don't |
D - it's all liquid non need to do that.
|
|
|
What's a big nursing dx for a patient with ileostomy --
A. FVE B. FVD C. Risk for injury D. Disturbed sleep pattern |
B
|
|
|
FIB - why would a patient with an ileostomy develop kidney stones --
|
Dehydrated
|
|
|
We would not irrigate the patient that has a cholostomy at --
A. Ascending colon B. Transverse part 1 C. Transvers part 2 D. Descending |
A
|
|
|
Best time to irrigate a colostomy --
A. First thing in the morning B. Before a meal C. After a meal D. Before bed |
C
|
|
|
Positioning for a appendecitis patient --
A. Sit them up B. Lie them on side C. Prone D. Right side, hand behind head |
A
|
|
|
Positioning for patient with intermittent tube feeding --
A. SUpine B. Prone C. Right sidelying, elevated D. Left sidelying, elevated |
C
|
|
|
Why would we take liquid over tablets for an ulcer? --
A. Quicker absorption B. Coating C. Less s/e D. Less pain |
B
|
|
|
When do we take antacids for Peptic ulcers? --
A. Bedtime B. Morning C. Stomach is empty D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
E
|
|
|
Not part of a GI cocktal --
A. Donnatel B. Viscous lidocaine C. Golytely D. Mylanta II |
C
|
|
|
Helps forma barrier over an ulcer --
A. Carafate B. Viscous lidocaine C. Golytely D. Mylanta II |
A
|
|
|
Position to lie patient who has dumping syndrome --
A. Side-lying left B. Side-lying right C. Prone D. Supine |
A
|
|
|
A patient with dumping syndrome should drink --
A. Before meal B. During meal C. Right after meal D. Between meals |
D
|
|
|
You would lower this in the patient with dumping syndrome's diet --
A. Protein B. Fats C. Carbs D. Salt |
C - carbs empty much quicker
|
|
|
Your patient needs a central line for hyperalimentation. Why? (FIB) --
|
Particles eat up peripheral veins
|
|
|
We are discontinuing the tpn. We would check this as we ween --
A. BP B. Pulse C. BG D. RR |
C
|
|
|
t/F - We would make sure not to mix tpn ahead of time --
|
True
|
|
|
PPN is --
A. Central line, 50% glucose B. Peripheral line, 50% glucose C. PICC Line, 20% glucose D. Central line, 20 % glucose |
D
|
|
|
Positiong for a central line insertion --
A. Prone B. Sidelying C. Semi-Fowler D. Trendleberg |
D
|
|
|
Position if air gets in central line --
Positiong for a central line insertion -- A. Prone B. Left trendleberg C. Right trendleberg D. Trendleberg |
B
|
|
|
Your patient is about to have the central line put in. They should --
A. Quickly breathe in and out B. Ask them to take a deep breath and quickly exhale three times C. Two exhales - one quick inhale pattern D. Deeep breath and hummmmmm |
D
|
|
|
For peds, we assess for nutrition by runing all but which test? --
A. BUN B. Albumen C. BG D. Nitrogen |
C
|
|
|
How many cups of milk should a 14 month consume daily? --
A. 1 cup B. 2 cups C. 4 cups D. 8 cups |
B - 2-3
|
|
|
Avg calories a day for a school age chidl --
A. 1100 B. 1200 C. 1400 D. 1600 |
D
|
|
|
FIB What does pain assessment stand for with (FLACC) --
|
Face
Legs Crying Consolibility Actions |
|
|
Wong baker scale shoudl be given at age --
A. 6 months B. 1 C. 2 D. 3 |
D
|
|
|
FIrst age where kids use the numerical pain scale --
A. 5 B. 6 C. 9 D. 18 |
A
|
|
|
Affected part of the RSV --
A. Arterioles B. Bronchioles C. Alveoli D. Sternum |
B
|
|
|
T/F - With asthma, episodes of wheezing are done on inspiration --
|
F - End expiration
|
|
|
If you percuss the chest with an asthma patient, what would you experience --
A. Hyperresonance B. Hyporesonance C. resonance D. None of the above |
A
|
|
|
PEFR measures --
A. Forced inhalation B. Relaxed inhalation C. Forced exhalation D. Both and C E. Both B and C |
C
|
|
|
Your patient should have all but this in the cystic fibrosis diet --
A. Low fat B. Low protein C. High Calorie D. Use of pancreatic enzymes |
B - high protein
|
|
|
T/F - Never have pancreatic enzymes touch lips --
|
True
|
|
|
Your cystic fibrosis patient is eating fried chicken. You then say --
A. You can't be eating that B. DO you want to tell me why you feel compelled to eat that? C. "Why are you doing this?" D. You might want to add some more pancreatic enzymes to that |
D
|
|
|
Baby with CF is prone to --
A. Hypernatreia B. Hypocalcemia C. Hypermagnesemia D. Hyponatremia |
D
|
|
|
Early sign of Cystic Fibrosis in newborn --
A. Failure to swallow B. Thinned secretions C. Failure to pass meconium D. Extreme thirst |
C
|
|
|
Not good for a GERD patient --
A. Upright position for feedings B. Elevated prone positioning C. Putting child in car seat D. Avoiding chocolate |
C
|
|
|
Nursing dx for baby with pyloric stenosis --
A. Nutrition: less than caloric provision B. Pain C. Risk for injury D. Disturbed sensory processes |
A
|
|
|
Known as "megacolon" --
A. Intusseption B. Hirschprungs C. Cystic Fibrosis D. Pyloric stenosis |
B
|
|
|
You would ***** this for hirschsprungs --
A. Nerves B. BP C. BG D. HIV status |
A
|
|
|
Area affected by hirshsprungs --
A. Ascending B. Rectum C. Sigmoid D. Anus |
C
|
|
|
Biggest worry about cleft palate/lip? --
A. Pain B. Self image C. Nutrition D. Infection |
C
|
|
|
With a cleft palate baby, we place the rubber typed syringe --
A. Middle B. Upward toward the roof C. Drop onto tongue D. DOwn the side of teh mouth |
D
|
|
|
T/F - Clefte palate will be worked on before cleft lip --
|
F
|
|
|
FIB - how can burping a baby prevent aspiration --
|
If you swallow air == abdominal distention -- pressure == vommiting == aspiration
|
|
|
Not a position for cleft palate surgery baby --
A. Pone B. Supine C. Sidelying D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
A
|
|
|
Your patient asks when is the best time for cleft palate surgery to be done for her baby. You would say --
A. When the baby turns two B. Before speech develops C. WHen the baby can read D. When the baby passes meconium |
B
|
|
|
Avoid putting this in a child's mouth who had cleft palate/lip surgery --
A. Straw B. Metal spoon C. Pacifier D. Both A and B E. Both A and C |
E
|
|
|
For celiac disease, BROW stands for -- (FIB)
|
Barley
Rye Oats Wheat |
|
|
Best choice for celiac patient --
A. Rice and pork B. Ham and cheese on rye C. Oatmeal and egg whites D. Lunchmeat and wheat thins |
A
|
|
|
Not a good choice for your celiac client --
A. Corn chowder B. Boca Burgers C. Rice cakes D. Pizza |
D
|
|
|
Jelly stool will be expected with --
A. Meconium ileus B. Celiac disease C. Intussecepution D. Esophageal atresia |
C
|
|
|
T/F - A baby with intussusception can heal naturally --
|
True
|
|
|
Your patient's baby has esophageal atrisia. You could tell because --
A. The baby is inconsolable B. No meconium has passed C. No urine flow D. Swollen airway |
B
|
|
|
With trachesophageal fistula, we check the 3 C's. Those are all but --
A. Cough B. Choke C. Cyanisois D. Colorectal fusion |
D
|
|
|
What position would you place a baby with trachesophageal fistula --
A. On back flat B. On back , shoulders elevated C. Prone D. Sidelying |
B
|
|
|
Number one prevention for sickle cell disease --
A. Bedrest B. Hydraton C. Antibiotics D. Analgesics |
B - hydration stops sickling
|
|
|
Wilm's tumor is found in --
A. Heart B. Lungs C. Kidney D. Spleen |
C
|
|
|
Not a sign of wilm's tumor --
A. Swelling B. Tough to palpate C. Bilateral abdominal mass D. None of the above |
C - only on onesside
|
|
|
Your patient has kawasaki disease. You owuld know that this attacks the --
A. Intestinal flora B. Coronary arteries and vessels C. Lung D. Parenchyma |
B
|
|
|
Early sign of kawaski disease --
A. Baby throwing up B. Baby can't keep feeding C. Baby sleeping too little D. Baby spitting up blood |
B
|
|
|
Not a good intervention to release workload on heart --
A. Decrease stimuli B. Controled room temp C. Sitting up D. Warm and humidified O2 |
D
|
|
|
Your patient's baby is sucking his fists. you would assess for --
A. Decreased LOC B. Hunger C. Pain D. Paresthesia |
B
|
|
|
How long should it take for an infant feeding --
A. 30 min B. 1 hr C. 2hr D. 4 hr |
A
|
|
|
How often should a baby be fed --
A. 30 min B. 1 hr C. 2hr D. 3 hr |
D
|
|
|
Your infant is scheduled for digoxin. HR is 99. You would --
A. Hold B. Administer C. Give booster D. Give w/ beta blocker |
A - Babies 110 and up
|
|
|
Therapeutic digoxin range for child --
A. 55 B. 60 C. 72 D. None of the above |
C
|
|
|
Your 2 year old is digoxin. You would --
A. Give one hour before feeding B. Mix with appleasauce C. Mix in orange juice D. Increase dosage if 2 doses were missed |
A
|
|
|
Maximum dose for kids --
A. .5cc B. .75 cc C. 1 cc D. 1.5 cc |
C
|
|
|
Your child patient had digoxin and vommits. You would --
A. Call doctor B. Give next dose C. Reduce next dosage D. Hold next dose |
D
|
|
|
Your child patient missed two dig doses in a row. you would --
A. Call doctor B. Give next dose C. Reduce next dosage D. Hold next dose |
A
|
|
|
Your patient is four hours past due on the dose. YO uwould --
A. Call doctor B. Give next dose C. Reduce next dosage D. Hold next dose and give next time |
D
|
|
|
Good time to give your dig to your child patient --
A. 1 hour before breakfast B. During breakfast C. 2 hours after breakfas D. Both A and C E. Both B and C |
D
|
|
|
Your patient is on enalapril. You would watch for --
A. Increased bp B. A cough C. Headache D. Increased ICP |
B
|
|
|
Important assessment for ace inhibitor patient --
A. Mg B. C C. K+ D. Na |
C
|
|
|
How do we administer O2 to a baby --
A. N. Cannula B. Venturi mask C. Blow by face |
C
|
|
|
Necessary Intervention to combat polycythemia --
A. Hydration B. Sedation C. Ambulation D. Gate theory |
A
|
|
|
Not an Acyanotic defect --
A. Ventricular septum B. Atrial septal defect C. Transposition of gret vessels D. Atrial flutter |
C
|
|
|
Ventricular septal defect can cause --
A. Pulmonary htn B. Left hf C. Right hf D. Necrosis |
C
|
|
|
With an atrial septal defect, you can expect all but --
A. Ventricular dysrhythmias B. HF C. Atrial fib D. Murmu sounds |
A
|
|
|
A potentially bad thing with pateent ductus arteriosus --
A. Pulmonary htn B. Left hf C. Right hf D. Necrosis |
B
|
|
|
FIB - Name drug that closes the patent ductus arteriosus --
|
Indomethacin
|
|
|
Patient with coarctation of the aorta might wind up with --
A. Pulmonary htn B. Left hf C. Right hf D. Necrosis |
B
|
|
|
T/F - With coarction of aorta, one would notice a big difference in the pulses of the upper and lower extremities --
|
True
|
|
|
NOt part of tetrology of fallot --
A. Overriding aorta B. Right ventricular hypotrophy C. Pulmonary stenosis D. Ventricular septal disorder |
B - hypertrophy
|
|
|
Not involved in transposition of great vessels --
A. Aorta B. Pulmonary artery C. Pulmonary vein |
C
|
|
|
For otitis media, you would lie on the ____ side --
A. Affected B. unaffected C. Prone D. Supine |
A
|
|
|
T/F - For otitis media, we use heat only --
|
F - alternating hot and cold
|
|
|
Mitral sounds --
A. 2nd right intercostal space. B. 2nd left intercostal space. C. 4th intercostal space, at lower left sternal border. D.5th left intercostal space, 1 cm |
D
|
|
|
Aortic sounds --
A. 2nd right intercostal space. B. 2nd left intercostal space. C. 4th intercostal space, at lower left sternal border. D.5th left intercostal space, 1 cm medial to mid-clavicular line |
A
|
|
|
Tricuspid --
A. 2nd right intercostal space. B. 2nd left intercostal space. C. 4th intercostal space, at lower left sternal border. D.5th left intercostal space, 1 cm |
C
|
|
|
Pulmonic --
A. 2nd right intercostal space. B. 2nd left intercostal space. C. 4th intercostal space, at lower left sternal border. D.5th left intercostal space, 1 cm |
B
|
|
|
Define paradoxical pulse (FIB) --
|
It is when systolic falls 10 during INSPIRATION
|
|
|
BNP is used to assess --
A. MI B. CHF C. Anuerism D. Fatigue |
B
|
|
|
Your patient is about to have BNP done. This patient is on natrecore. You would --
A. Take BNP B. Cancel C. Wait for 2 hrs after Natrecor is turned off D. Call doctor |
C
|
|
|
Your patient is on an INTRA AORTIC BALLOON PUMP. You would do all but --
A. Have patient flex legs B. Check distal pulses C. Assess LOC D. Keep legs straight |
A
|
|
|
T/F - Coughing increases HR --
|
True
|
|
|
Integrilin is used for --
A. Pain B. Platelet aggregation C. Dopamine reuptake D. Downs syndrome |
B
|
|
|
FIB - Venous or arterial insufficiency --
Decreased pulses |
Arterial
|
|
|
FIB - Venous or arterial insufficiency --
Pale when elevated, red when lowering leg -- |
Arterial
|
|
|
FIB - Venous or arterial insufficiency --
Absent Edema |
Arterial
|
|
|
FIB - Venous or arterial insufficiency --
Normal pulses |
Venous
|
|
|
FIB - Venous or arterial insufficiency --
Gnagrene |
Arterial
|
|
|
FIB - Venous or arterial insufficiency --
Compression used |
Venous
|
|
|
FIB - Venous or arterial insufficiency --
Loss of hair over foot -- |
Arterial
|
|
|
FIB - Venous or arterial insufficiency --
Ulcers on ankles |
Venous
|
|
|
t/F - Vomiting is known with kidney failure due to toxin retention --
|
True
|
|
|
t/F - Fluid challenge bolus is done with chronic kidney failure --
|
F - acute
|
|
|
Not true about glomerunephritis --
A. Decrease carbs B. Fluid replacement, take lossess and add 500 mL C. Tell client blood and protein can be in urine for months D. Reduce sodium in the diet |
A
Reduce sodium because of fluid volume excess |
|
|
Not true about nephrotic syndrome --
A. Increase protein in diet B. DIuretics help C. No bed rest - constant ambulation D. Steroids will help |
C - need bedrest for diuresis
|
|
|
If heparin doesn't work for hemodialysis due to allergy --
A. Rocephin B. Lovenox C. Ateplase D. Cingring |
C
|
|
|
FIB - name 4 hemodialysis ports --
|
Shunt
Graft Asch catheter Fistula |
|
|
T/F - We feel a bruit and hear for thrills --
|
F - other way around
|
|
|
Fluid amount for dwell time --
A. 2000-2500 B. 2500-3000 C. 3000-3500 D. 3500-4000 |
A
|
|
|
We warm diasylate due to avoiding --
A. Hypotension B. Vasoconstriction C. Infection D. Fat embolism |
B
|
|
|
What if all the diasylate fluid doesn't come out --
A. Elevate hob B. Lie supine C. Turn to side to side D. Ambulate |
C
|
|
|
Not true about CAPD --
A. Done at night B. Risk for infection C. Can get arthritis with this D. Need a teachable client |
A - 4 x a day, 7 days a week
|
|
|
#1 complicaiton of peritoneal dialysis --
A. Pain B. Peritonitis C. Hernia D. Altered body image |
B
|
|
|
T/F - Patients on peritoneal dialysis can have a constant sweet taste --
|
True
|
|
|
INcrease these (2) items in the diet for a peritoneal dialysis client --
A. Fiber B. Protein C. Fats D. Carbs |
A and B
|
|
|
T/F - Accumulated abdominal fluid can decrease peristalsis --
|
True
|
|
|
A softening of the cervix --
A. Goodells B. Chadwick's B. Hegar's C. Listers |
A
|
|
|
Godeel's starts showing at week --
A. 3 B. 4 C. 8 D. 10 |
C
|
|
|
T/F - Fetoscope for baby at 17-20 weeks --
|
True
|
|
|
Calorie increase after first trimester per day --
A. 100 B. 300 C. 500 D. 1000 |
B
|
|
|
T/F - Avg daily dose of f. acid is 900 mg --
|
F - 400 mcg
|
|
|
Worst activity for pregnant woman --
A. Sitting by air conditioner B. Swimming C. Meditation D. Chilling in the hot tub -- |
NO heat
|
|
|
Visit once a month for the hospital until week --
A. 8 B. 19 C. 28 D. 49 |
C
|
|
|
T/F- Ultrasound prior to a procedure, the pregnant mom will drink --
|
F
|
|
|
Urinary frequency cycle for pregnant woman --
A. 1st - yes, 2nd - yes, 3rd - yes B. 1st - no, 2nd - yes, 3rd - yes C. No for all D. 1st - yes, 2nd - no, 3rd - yes |
D
|
|
|
T/F - NV should stop by second semester --
|
True
|
|
|
True about weight gain in preggers --
A. 4 lbs first and second semester B. 0 lbs first sem, 1 pound per month in second and third C. 4 lbs first semester, 1 lb per week in second and third D. None of the above |
C
|
|
|
With lightening, you will find all but --
A. Difficulty breathing B. Increased urination C. Head at station 0 D. This occurs 2 weeks before term |
A
|
|
|
t/F - Come to hospital when contractions are 10 minutes apart or membrane rupture --
|
F - 5 minutes
|
|
|
Each fetal accelleration should last for --
A. 5 sec B. 10 sec C. 15 sec D. 20 sec |
C
|
|
|
T/F - We want to see a positive test for an oxytocin stress test --
|
F - we want a negative
|
|
|
A stress test for a baby is true for all except --
A. 3 contractions, 40 seconds, 10 min B. 3 contractions, 10 seconds, 30 min C. 1 contraction, 30 seconds, 10 min |
A
|
|
|
Caused by hypoxia from head compression --
A. Early B. Late C. Variable D. Distended |
A
|
|
|
Umbilical cord compression --
A. Early B. Late C. Variable D. Distended |
C
|
|
|
true labor pain starts in --
A. Abdomen B. Flank C. Back D. Head |
C
|
|
|
Positining for epidural --
A. Right side B. Left C. Prone D. High fowlers |
B
|
|
|
Major complication of Epidural anestesia --
A. Raised pulse B. Decreased respirations C. Hypotension D. Headaches |
C
|
|
|
T/F - Women who have vaginal birth after c-section are at risk for uterine rupture --
|
True
|
|
|
T/F - With complete uterine rupture, pain my stop but contractions won't --
|
False - contractions will
|
|
|
Danger with Uterine rupture --
A. Decreased respirations B. Hypovolemic shock C. Neutrogenic shock D. Hypervolemic reaction |
A
|
|
|
Position for oxytocin --
A. Right sidelying B. Prone C. Left sidelying D. Supine |
C
|
|
|
T/F - During emergency delivery, we place hand on fetal head and apply gentle pressure --
|
True
|
|
|
We keep baby's head down to avoid --
A. Pain B. Aspiration C. Neural tube defects D. Growth |
B
|
|
|
Why would we dry babies at birth --
A. Avoid infection B. Enhance diuresis C. Avoid shock D. Thermoregulation |
D
|
|
|
Temp may increase to ____ during first four hours --
A. 90.9 B. 99.5 C. 100.4 D. 101.1 |
C
|
|
|
T/F - HR goes down for about 6 to ten days (50-70) range after birth --
|
True
|
|
|
Uterus IMMEDIATELY after birth --
A. One finger above sternum B. One finger above pelvis C. Two finger below umbilicus D. Between sternum and umbilicus |
C
|
|
|
A FEW HOURS after birth, the fundus rises to --
A. One finger above sternum B. One finger above pelvis C. One finger above umbilicus D. Between sternum and umbilicus |
C
|
|
|
T/F - Rubra - 3-4 days and colored dark red --
|
True
|
|
|
T/F - Cabbage leaves are good for non-breast feeding women only --
|
True
|
|
|
ML in the first 24 hrs notes postpartum hemmorhage --
A. 100 B. 200 C. 300 D. 500 |
D
|
|
|
T/F - Binding and cabbage leaves help breastfeeders with mastitis --
|
F - only with non-breastfeeding
|
|
|
For penecillin with breastfeeding ____ first --
A. Feed baby B. Administer penecillin C. Niether D. Either or |
A
|
|
|
FIB - Which brest do we offer first with mastitis --
|
Affected
|
|
|
Apgar (FIB) -- list all 5 --
|
Muscle tone
Color HR R Reflex irritability |
|
|
Erythromyacin fights --
A. Ghonnrhea B. Syphilus C. Chlymidia D. Epinepherine |
C
|
|
|
T/F - Pathologic jaundice is due to Rh/ABO incompatability --
|
True
|
|
|
T/F - No problem exists if mother is Rh+ and fetus is Rh- --
|
True
|
|
|
T/F - Hydatiform mole is dx with cxr --
|
F
|
|
|
First sign of ectopic pregnancy --
A. Bleeding B. Pain C. Pallor D. Involution |
B
|
|
|
Methotrexate ends up --
A. Expanding lung capacity B. Stops nosebleeds C. Halts pregnancy D. Prevents HIV |
C
|
|
|
T/F - A laprotomy is done of a tube has ruptured with ectoic pregnancy --
|
True
|
|
|
Thiamine SQ shot helps with the defecit of --
A. B1 B. B2 C. B6 D. B12 |
A
|
|
|
Not true about preeclampsia --
A. Sudden weight gain B. Decresaed DTRS C. Increased BP D. Proteinera |
B - increased
|
|
|
T/F - With m. sulfate, needs to be augmented with pitocin to keep labor going --
|
T
|
|
|
Celestone, a steroid, helps with --
A. Infection fighting B. Hemophaliea C. Sickle cell anemia D. Fetal lung maturation |
D
|
|
|
T/F - Asthmatics should breath through mouth in cold air --
|
F - Breathe through nose
|
|
|
Worst drink idea for an asthmatic --
A. Hot tea B. Milk C. Tap water (tepid) D. Coffee |
B - NOthing cold
|

