![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
534 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the anti biotic that cannot be given orally |
Methicillin |
|
|
what is the anti biotic that is effective against Pseudo monas aeruginosa |
Carbanicillin or Ciprofloxacin/ Ticarcyllin |
|
|
what kind of class of bacteria is clindamycin most effective against |
most anaerobic |
|
|
what are the anti cholinesterases irreversible inhibitors |
the Phosphates: isofluorophate/ di isopropyl fluorophate |
|
|
whta is the difference between atropine and the quaternary ammonium derivative of atropine( methyl atropine nitrate) |
Atropine is more potent in oral administration |
|
|
in cholinergic drugs, the quaternary ammonium groupu confers what function |
Direct nicotinic stimulation |
|
|
name some directly acting cholinomimetics |
Carbachol behanechol, Methacholine |
|
|
Methyl paraben as a conservative shows cross sensitivity with what anesthetic |
Paba esters |
|
|
what is the penicillin that is excreted primarily by tubular secretion |
Benzyl penicillin |
|
|
What is the function of Nalidix acid |
a urinary tract antiseptic |
|
|
What is the drug that might cause renal lithiasis because it is not very soluble |
Bactrim |
|
|
What anti biotic we can give to a penicillinase producing staphylococcus |
Oxacillin |
|
|
Name a third generation cephalosporing |
Moxalactam |
|
|
what kind of tetracycline is most slowly secreted by kidney |
Doxycycline; that's why it has a long half life, and can be given once per day not many times a day |
|
|
what is the best treatment for xerostomia |
5 mg pilocarpine |
|
|
what is the drug with which erythromycin interacts to cause cardiovascular events including death |
terfenadine |
|
|
what is the first drug that relieved leukemia |
Aminopterin |
|
|
Name the actions of Phenothiazine ( Zine) : alpha adrenergic drug blockage |
Sedation, anti emetic, potentiate narcotics |
|
|
what pair of anesthetics most likely cause cross allergy |
Lidocaine/ Mepivacaine |
|
|
what causes methemoglobinemia
|
benzocaines. benzenes, nitrites
|
|
|
what is the pathology seen most frequently with chronic temporomandibular joint disorder |
mental depression |
|
|
what is the attitude toward a fracture of the medium root of a tooth with no possibility of treatment of the apical portion |
Extraction and replantation of the coronal portion
|
|
|
What is the injury that results the most in pulpal necrosis |
Avulsion |
|
|
what are the teeth that have the most consistant canal morphology |
mandibular premolars |
|
|
After extraction , the removal of inter radicular bone corresponds to what ? |
removal of labial undercuts |
|
|
the blade type oral implant is suitable for which case |
posterior edentulous area without posterior abutment |
|
|
an occlusal separator is used for which case |
Hemarthrosis |
|
|
What is the most adequate surgical procedure to obtain long term stability for the genioplasty |
Pedicled horizontal sliding osteotomy |
|
|
what is the best procedure to treat chronic recurrent dislocation of the tmj |
articular eminectomy with capsular plication |
|
|
name the advantages of midawolam over diazepam |
Less thrombophlebitis shorter half life no significant active metabolites more rapid and predicatble onset But have the same respiratory depression effect |
|
|
if you inject midazolam intra arterially, what is the first manifestation? |
severe pain in the extremity |
|
|
what are the signs most seen in osteoarthritis |
Crepitus Antegonial notching Flattening of articular surface Apertognathia But : no prognatism |
|
|
what are the two tests to order before general anestheisa |
Blood count and urinalysis If patient is older than 40: EKG |
|
|
What is DHHS, NIH, HRSA, AHRQ |
The Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) is the principal agency of the U.S. government for protecting the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. DHHS includes 11 agencies and more than 300 programs. The other agencies listed are part of the DHHS. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the world’s premier medical research organization. The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) provides access to essential health care services for people with low income, people with no health insurance, and people who live in rural areas or urban neighborhoods where health care is scarce. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) supports research on health care systems, health care quality and cost issues, access to health care, and effectiveness of medical treatments. |
|
|
How do you treat an intruded tooth with closed apex, give time frame |
gradual orthodontic repositioning for 2 to 3 weeks, hydroxyde calcium pulpectomy at 2 weeks after injury, and stabilisation for 2 to 4 weeks |
|
|
what is a case control study? |
In a case-control study, people with a condition (“cases”) are compared with people without the condition (“controls”) but who are similar in other characteristics. Hypothesized causal exposures are sought in the past medical records of the participants. The case-control study could establish a temporal relationship between the exposure and disease of interest, such as a history of alcohol drinking before the appearance of oral cancer. |
|
|
Which statistical test is used to analyze whether or not the means of several groups are equal and generalizes a t test to more than two groups |
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) The χ2 test measures the association between two categorical variables. The correlation coefficient quantifies the relationship between variables (e.g., x and y). If the r value is +1, there is a perfect correlation, with both values increasing in the same direction. A multiple regression analysis provides a mathematical model of linear relationship between a dependent (i.e., an outcome variable) and two or more independent or predictor variables.
|
|
|
why do we use distraction osteogenesis |
when a large advancement is needed |
|
|
The rubber dam is inverted in order to |
provide a complete seal around the teeth |
|
|
What are the gingival technics that increase the attached gingival width |
Free gingival graft, apically displaced full thickness, partial thickness flap |
|
|
What is a critical component in anterior implant placement |
Anterior surgical template |
|
|
Diazepam, epinephrine, and insulin act at ion channel receptors respectively, G-protein–linked receptors, and tyrosine kinase–linked receptors. |
These three receptor types are cell surface receptors. Thyroid hormone and steroid hormones or drugs, such as prednisone, act on nuclear receptors, accounting for much of their action. |
|
|
what are the two benzodiazepines that have the shortest half life |
Midazolam, Triazolam |
|
|
name the three metabolism reaction that local anesthetics undergo |
Hydroxylation Dealkylation Hydrolysis |
|
|
How much is the pka of lidocaine |
7.9 |
|
|
Name a drug that inhibit gasto intestinal glucose absorption |
Acarbose |
|
|
Name two anti epileptics that inhibit calcium channels and are structural analogues of GABA, and have a half life of 3 to 4 hours |
Gabapentin/ Pregabalin.
Phenobarbital enhances chloride channel activity. Carbamazepine is a sodium channel blocker, and ethosuximide is an inhibitor of T-type calcium channels. Valproic acid is also a structural analogue of GABA |
|
|
Name the anesthetic that is used essentially as a topical anesthetic |
Benzocaine |
|
|
Torsades de pointe, or polymmorphic ventricular tachicardia show on the ECG as: |
Longer Q T interval |
|
|
Flumazenil reverse the effect of benzodiazepine: Which benzodiazepine are concerned? |
Diazepam, Zolpidem, Zaleplon ( GABA A receptors) |
|
|
What receptor does Baclofen stimulate |
GABA b |
|
|
What receptor does Buspirone stimulate |
Serotonin 1A receptor |
|
|
Bremstrahlung radiation results from |
interaction of electrons from cathode with tungsten nuclei from anode |
|
|
Name the drug that blocks aldosterone |
spironolactone It is a K+ sparing anti diuritic. It is safe for people taking digoxin , not like thiazide which depletes k+ resulting in more penetration of Digoxin |
|
|
name the odontogenic cyst that rises from the reduced enamel epithelium |
Dentigerous cyst |
|
|
what is the inhalation anesthetic that causes a cardiac arrhythmia when administered with epinephrine |
halothane : it sensitizes the heart to catecholamines Hepatotoxic |
|
|
Name the glucocorticoid that has the most selective activity |
Dexamethasone
Besides: Hydrocortisone has mineralocorticoid activity Aldosterone and Fludrocortisone are mineralocorticoid |
|
|
What is deterministic effect in radiation |
the severity of response is proportional to the dose |
|
|
what organ does faconi syndrome affect |
the kidneys |
|
|
describe the x ray release rythm from the x ray machine |
60 bursts per second, 1/120 second each. So the xrays are produced half of the time |
|
|
what Methicillin resistant staphylococci vulnerable to ; |
Vancomycin |
|
|
Where does localized aggressive periodontitis happen in children and in what ethnicity |
molar area, in African American |
|
|
What position should be chosen to make occlusal adjustement of a prothesis |
Centric Relation |
|
|
describe odontogenic keratocyst hystology |
cystic lining of thin, parakeratinized epithelium with basal cell palisading |
|
|
describe the caracteristics of the palatal seal |
2 mm anterior to fovea shallow in mid palatal area improve retention of the denture, not stability the width compensates for the shrinkage of resin May reduce the gag reflex because it's well sealed
|
|
|
what is Herpetic Whitlow |
a secondary herpes simplex infection that occurs around the nail bed |
|
|
what two drugs can cause lidocaine to stay more in in the blood causing toxicity |
Beta blockers Cimetidine |
|
|
What two drugs cause the lidocaine to be biotransformed rapidly due to hepatic induction |
Barbiturate Phenytoin |
|
|
what can cause the barbiturates to stay more in the blood due to the inhibition of the liver funtion |
Anti fungal |
|
|
o Normal coagulation values • |
Template bleeding time: 1-9min • Prothrombin time: 11-16sec • Incr by warfarin, vit k deficiency, heparin in high doses • Partial thromboplastin time: 32-46sec |
|
|
what are the functions of others ingredients in the anesthetic cartridge |
• NaCl for isotonicity; methylparaben for bacteriostatic; sodium metabisulfate antioxidant |
|
|
Lido+prilo= classe B Mepi+bupi= classe c |
Lido + procaine= skip the exitment phase in overdose and go directly to drowsiness prilo+benzo= Methemoglobinemia |
|
|
o Volatile liquids used for anesthesia sevoflurane (less irritating to airway), desflurane (also requires heading component) • |
CAN use with COPD (unlike nitrous |
|
|
Give 3 anxiolytics to give to an adult patient one hour before procedure( 3 different families of drugst) |
Diazepam: 5 -10 mg Pentobarbital-secobarbital: 50 -100 mg Promethazine: 25 mg. |
|
|
what is the medication that most asmathic and copd patients take, and what antibiotic is contraindicated because of toxicity |
Theophylline: bronchodilator
Never give erythromycine/Clarithromycine because of toxicity |
|
|
What is analeptic |
Nervous system inducer as opposed to depressor |
|
|
Name the full name of Pindborg tumor, and its pathognomonic histologic sign |
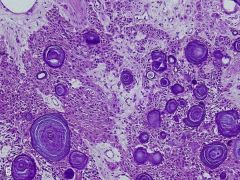
Calcifying epitethelial odontogenic tumor It has Liesengag rings |
|
|
Strength = stiffness x range
• Doubling length →decr strength by ½, 8x less stiff, 4x incr in range • |
Doubling diameter →8x incr in strength, 16x incr in stiffness, working range decr by ½ • |
|
|
o Syndromes manifesting hyper & hypodontia: Clue: Mnemonic: CHOD |
Crouzon’s, Down’s, oro-facial digital syndrome I, Hallermann-STreiff syndrome |
|
|
what is the agency that regulates the transport of waste from the dental office |
EPA |
|
|
Explain what Sillness and Loe Index means |
a score from 1 to 4 divided by 4 of debris index at the gingival level. 0 : no debris 1: debris revieled by contrast product 2: debris visible at naked eye 3 debris abundant. |
|
|
o More wear occurs on max than mand & on left than right |
Atridox content: 10 percent doxycycline Arestin content: 2 percent minocycline |
|
|
o In gingival CT, most nerve fibers are myelinated |
o Bacterionema & Veillonella have abilty to form intracellular hydroxyapatite crystals |
|
|
name 3 anti hypersensitivity products |
Strontium chloride potassium nitrate sodium citrate |
|
|
o Subgingival root surface roughness doesn’t seem to interfere with healing after SRP |
o gypsum setting time modifyiers:
Retarder=borax, sodium citrate; accelerator=gypsum, potassium sulfate |
|
|
zudovudine as an hiv post exposure prophylaxis reduces the risk by |
81 percent |
|
|
Percussion sensitivity is the hallmark of a tooth that requires a root canal. A fractured cusp or recurrent decay do not necessarily indicate the need for RCT. Pain exacerbated by cold usually means a vital or part vital tooth. |
Pain exacerbated by heat (which this tooth does not exhibit) usually means gas pressure in a devital tooth. An apical lucency on film indicates a tooth that requires a root canal; however, absence of a lucency does not exclude the need for root canal treatment. |
|
|
how many in the population in america suffer from Hypertension |
one in three |
|
|
what type of disorder is fibromyalgia |
Rhumatic desorder |
|
|
what is the anti histaminique that is not contra indicated with cimetidine |
Allegra |
|
|
what happens when the intermediate chain of a local anesthtic gets longer |
potency gets higher |
|
|
what are the advantages of chemical sterilization |
short does not corrode does not damage clothes instruments are dry at the end of the cycle
But : it needs ventilation |
|
|
what is the most dangerous tmj surgery risk to the near by structure |
facial nerve damage |
|
|
what is the method to remove inferior torus |
create groove on the superior aspect of the torus then Use mono beveled chisel to remove the torus |
|
|
What is the best flap for the removal of palatal tori |
Y flap with midline incision |
|
|
post surgical athelectasis usually is a result of what |
Pre operative respiratory infection |
|
|
which area in a child should be avoided when injecting IM |
Gluteal muscles |
|
|
which broad antibiotic has been incriminated in failure of oral contraceptives |
Rifampin |
|
|
what is the sign of Digoxin intoxication |
Ventricular fibrillation |
|
|
individuality of a tooth is caracterised by |
surface texture |
|
|
degree of penetration of light before reflection in the enamel is called |
transluscency |
|
|
what is the dramatic advantage of phenytoin compared to barbiturate |
causes less sedation |
|
|
what is the marketing technique that can be used with reluctant patient |
Optimem |
|
|
when a patient withdraw this anti spychotic, they start having sudden bleeding in the gingival what is the name of this drug |
VAlproic acid |
|
|
what is the drug that causes convulsions when withdrwed suddenly |
Barbiturates |
|
|
what is the sign of back pressure porosity |
Rounded angles |
|
|
is there any anti diabetic drug that acts directly on insulin receptors |
no |
|
|
how much is the casting shrinkage of alloys |
2.2 percent
|
|
|
how much of the americain population does not have dental insurance |
65-70 percent |
|
|
what is the antidote to TCA overdose |
Physiostygmine |
|
|
Benzodiazepines have a mechanism of action in muscle relaxtion close to |
Meprobamate |
|
|
digitalis overdose can cause ventricular arythmia. so we give |
quinidine |
|
|
what is the anxiolytic that gives the most dry mouth
|
Hydroxysine: Atarax
|
|
|
what are the caracteristics of tramadol |
Centrally acting Binds Mu receptors has a serotonin reuptake inhibition funtion transforms in a more active metabolite
But structurally different than morphine |
|
|
what is the analgesic that is given either IM or enteral |
Ketorolac |
|
|
weekly fluoride rinse is 0.2 Naf |
daily fluoride rinse is 0.05 Naf |
|
|
explain what sustain talk means |
when the patient expresses that he does not want to change his habits. like: I can not use the mouth guard because I have so much going on, |
|
|
what is the most effective pit and fissure prevention community measure in school |
sealants, and not rinse of water fluor |
|
|
what size is an aquired nevus compared to a blue nevus |
aquired nevus is less than 6 mm. Blue nevus may be less than 1 cm or more than 2 cm.
The color blue is due to the reflexion of the short wavelengths (blue) : Tyndall effect |
|
|
What is the other name for white sponge nevus |
familial epithelial hyperplasia Cannon's disease |
|
|
how is the lacrimal test called in jogren syndrome |
Schirmer test |
|
|
gingival cysts of the new born are also called? What histology does it have |
Bohn's nodules Epstein's pearls |
|
|
what is the cutanuous counterpart of calcifying odontogenic cyst name |
Malherbe calcibying epithelioma or Pilo matricoma |
|
|
Explain deterministis effect in radiotherapy Explain stochastic effect(chance effect) Give exembples |
Deterministic effect relates the severity of the reaction to the dose: mucositis after radiotherapy Stochastic effect: chance effect: relates the chance of getting a cancer to the dose |
|
|
Learn this |
mucositis appears after two weeks of radiotherapy It's severity follows a deterministic effect healing takes two months to complete |
|
|
Radiation facts: occupational exposure should be less than 50 mSv
0.2 mSv is the dose that workers get in the dental office |
total annual radiation exposure in the USA is : 6.2 mSv half is ubiquitous : Radon Half is man made: 98 percent from radiology CT : 47 percent of man made radiation dental : 0.26 mSv of man made radiation
ALARA: as low as reasonably achievable |
|
|
in an ideal radiograph, the optical density of enamel, dentin and soft tissue should be |
0.4 enamel 1 dentin. 2 soft tissue |
|
|
Herringbone effect or tire track pattern is the result of what when taking the radiograph |
placing the film inversed in the mouth |
|
|
angulation of the radiographic cone directed towards the ceiling is a positive angulation. too little of an angulation gives elongation of tooth |
angulation towards the floor is called negative angulation . too much angulation gives forshortening of the tooth |
|
|
what is the technique that we use when using submento vertex technique in order to view clearly the zygomatic arch and reduce all the other anoatomic parts |
Jug Handle view. it consists of reducing the radition by half which will increase the visibility of the zygomatic arch |
|
|
what is the angulation of the x ray in Towne's radiograph |
30 degrees to Frankfort plane, and film behind the head |
|
|
what is the other name for trombocytopenic purpura |
Werlhof Disease |
|
|
what is the pathology that causes flaring of the teeth |
Thallassemia |
|
|
o Peripheral fibroma and. peripheral odontogenic fibroma are not ulcerated while ..... |
peripheral ossifying fibroma (ulcerated) |
|
|
What is the other name for MEN 2 |
Sipple's syndrome |
|
|
What is the most common odontogenic tumor |
odontoma, then ameloblastoma(painless, resorbs roots and displaces teeth) |
|
|
give the order of occurence of tumors of bone |
Multiple myeloma osteosarcoma(painful) Chondrosarcoma(painless) osteofibroama Ewing sarcome |
|
|
where does sebacous adenoma occur |
Parotide |
|
|
where does pleomorphic adenoma occur the most. how much is the malignancy transformation |
85 in parotide, then the palate 25 % turn malignant |
|
|
what is the difference btw mucous retention cyst and mucocele |
Mucous retention cyst is lined by epithelium while mucocele is not |
|
|
What is the difference between CMOS and CCD |
CMOS is less expensive , more reliable,
but, causes more radiographic noise, and has smaller detector area |
|
|
Fibrous displasia is defferent from gardener's syndrome osteoma in that
|
FD is disfiguring and deforming by expension, while gardener's syndrome is flat and non deforming
|
|
|
peripheral giant cell granuloma occurs where
|
occurs exclusively in the gingiva like the ossifying fibromas opposite of central giant cell granuloma which occurs in bone.
|
|
|
hereditary hemorrhagic telengiectasia is also called
|
Rendu Osler Weber Disease
|
|
|
what is this lesion
|
verruciform xanthoma
|
|
|
what is this how we treat it
|
inflamatory papilary hyperplasia removal of the total prothesis exision if advanced of collegenous cryotherapy curetage
|
|
|
nevoid basal cell carcinoma is also called
|
gorlin syndrom autosomal dominant
|
|
|
schwannoma has two vriations
|
Antoni A and Antoni B occurs mostly in the 8 Nerve
|
|
|
what is this disease called what attitude we should have What kind of histology cells we find To what other pathology is it histologically similar
|
congenital epulis of the new born should be resected.dno reccurence Similar to Granular cell myoblastoma in that it contains granular cells. The difference is that GCM has a pseudo epitheliomatous Hyperplasia. GCM occurs in the tongue
|
|
|
guess what this is It s a slow growing mass painless
|
neuro fibroma
|
|
|
multiple osteoma is called what are the caracteristics
|
gardener syndrome males more than females asympto intestinal polyposis always malignant potential accopagned fibroma of sking, epidermal cyst odontoma and impacted teeth
|
|
|
what is this pathology to what type of families it belongs what are the other types of the same pathology what are the other types of the same family
|
peri apical cemento ossous displasia, most common in fibro ossous diseases focal: non expansile, edentulous area, mandible,< 2 cm Florid: African american females, > 2 quadrants, no cortical expansion
|
|
|
what is this disease, what are the caracteristics what are the others diseases of the same family
|
Eosinophilic granuloma: floating teeth cupped out radiolucency like periodontal disease the others are: Letter Siwe: young childern, bones, skin, internal organs hand Schuller: punched out bone lesions
|
|
|
Hand Shuller Christian disease caracteristics
|
Punched out bone lesions Exophtalmos Diabetes insipidus Floating teeth
|
|
|
what is this lesions in a black male of 54 years
|
multiple myeloma notice the sharp edge of the resobed root cure is : Thalidomide, chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation
|
|
|
what is this disease in a man of 45 years, history of alcohol and smoking
|
Squamous cell carcinoma, comes from: Human Papiloma virus: 16.18.31.33 vitamines deficiency, iron deficiency,and UV light 90 percent in lower lip |
|
|
what is this what is the cause, what is the treatment
|
verrucous carcinoma chewing tobacco excision without radio therapy
|
|
|
what is this occuring in a white child of 5 to 25 years what treatment
|
ewing Sarcoma resection, radiotherapy, and aggressive chemotherapy Signs: Intermittant pain, swelling, fever, anemia, leukocytosis, and onion skinning on radiographs
|
|
|
what is this, what clinic signs
|
Osteosarcoma: painfull swelling, loose teeth, paresthesia, nasale obturation, apistaxis, fractures, ulcerations, mixed rado opacities, Sunburn Appearance, symetrical widening of pdl Elevated alkaline phosphate Treatment: radical resection with chemo or radio
|
|
|
what is this what other pathologies can manifest like this: Well circonscribed, uni or multi locular radiolucency
|
Central Giant cell granuloma other pathologies: Cleidocranial displasia/disostosis Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism
|
|
|
what are the sizes of : acquired nevus common Blue nevus Cellular blue nevus
|
< 6 mm acquired nevus < 1 cm common blue nevus. > 2 cm cellular blue nevus: accurs in 2nd and 4th decade
|
|
|
Neurofibromatosis and Mc Cune Albright both have cafe au lait spots, but there is a big difference in the shape, what is it?
|
Mc Cune Albright is shap irregular edges, while neurofibromatosis is smooth
|
|
|
what are the other names for white sponge nevus
|
familial epithelial hyperplasia Canon's disease hereditary Bilateral+ keratin genes 4 and 13
|
|
|
what is this: what are the caracteristics of it
|
the radiograph is not diagnostic of this pathology: Dentigerous cyst notice the resorption of the adjacent teeth it might transform into ameloblastoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and intraossous mucoepidermoid carcinoma
|
|
|
what is this pathology in a patient who has falx cerebri calcified, hyperkertinized pitted hands and feets. cysts and fibromas on the skin?
|
OKC: odontogenic Keratocyst. Can be multiple in the Nevoid Basal cell carcinoma, which is Gorlin syndrome high recurence rate the keratocyst is lined by parakeratinized epithelium. The variation that is orthokeratinized is less agressive and less recurent.
|
|
|
what is this pathology? who are the candidates? are are the caracteristics? what is the treatment?
|
Ossigying Fibroma women from 30 to 40 years well circonscribed, mixed density asymptomatic Treatment: enucleation without recurrence
|
|
|
what is this disease? what are the caracteristics what is the main difference with fibrous displasia
|
Fibrous displasia, family of the fibro ossous diseases Ground glass appearance can be mono ostotic, polyostotic, mac cune albright (poly + endocrine disease), Cranio facial Less clear borders than ossifying fibroma More maxillary than mandib like ossifying fibroma
|
|
|
what is the name of this lesion happening in young individual? what is the main caracteristic of this lesion What are the other pathologies of odontogenic source
|
ameloblastoma well demarcated borders the other odontogenic tumors: Odontogenic myxoma: honey comb appearance Odontogenic Fibroma: more females maxillary anterior Cementoblastoma: benign, mixed radio appearance.
|
|
|
the difference between men1 , men 2(sipple syndrome ) , and men 3 is.....
|
men 3 has mucosal neuroma. So a patient with mucosal neuroma also might develop a medullary carcinoma of Thyroid
|
|
|
what are the two pathologies that cause an enlargement of the pdl
|
Sclerodermaosteosarcoma
|
|
|
cleft palate occurs when, what gender cleft lip occurs when , what gender, where?
|
Cleft palate: 8 to 10 weeks, in females Cleft lip: left unilateral is 80 of cases. 6 to 7 weeks in males mostly Van Der Woude Syndrome: lip pits autosomal dominant with 90% penetrance
|
|
|
high alkaline phosphatase is found in Low alkaline phosphatase is found in
|
Paget disease of bone Hypophosphatasia
|
|
|
what is this pathology
|
Ectodermal displasia:patient looks older than normal, no salivary, nor sweat glands. x linked recessive the cone teeth are a differential diagnosis with cleidocranial dysplasia, which also has a bossing forehead
|
|
|
what are the caracteristics of Pierre Robin Syndrome
|
Micrognathie, Cleft lip Glosso ptosis High arched palate
|
|
|
what is this lesion what are the caracteristics
|
Cherubism Caracteristics are: multiple radiolucencies, peri vascular collagen cuffing, eyes stare in the space Multi nucleated Giant cells in histology
|
|
|
Hypo para thyroidism is caracterised by
|
Blunt apices, hypoplastic enamel, Delayed eruption of teeth
|
|
|
Muscular distropy is caracterised by
|
loss of force to bite, so open mouth breathing. increased caries
|
|
|
what are the signs of hypothyroidism
|
Crenetism in children, myxedema in adults Underdevelopped mandible Over developped maxilla macrodontia, so teeth malposition
|
|
|
Hyper parathyroidism= Von recklinghousen = Brown tumor
|
Multi cystic radiolucencies, Giant cell in histology Extravasation of red cells+Hemosiderin= that's why it is a Brown tumor
|
|
|
what is the incubatin period of Hepatitis B
|
6 to 8 weeks
|
|
|
What is the incubation period of Hepatitis A
|
4 to 6 weeks
|
|
|
the most serious complication of Ludwig's Angina is
|
oedema of the Glottis
|
|
|
What is the toxic dose of fluoride for adults and children
|
Adults: 2 gram of fluoride Children: 5 to 10 mg/kg, very toxic if it reaches 16mg/kg 1 ppm of fluoride supplementation adds 1 to 2 mg in the diet. no toxic manifestation below 5 mg daily diet.
|
|
|
what is the main cause of xerostomia:
|
Medication Jogren syndrome is the main pathology that causes it. Radio therapy most toxic effect is xerostomia Other pathologies are: RA, Scleroderma, SLE.
|
|
|
what is this pathology
|
malignant melanoma, Sites of predilection: palate and maxillary gingiva uncommon pathology of the oral cavity
|
|
|
how to distinguish between basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
|
basal cell carcinoma is bullous like and does crust and ulcerate, Squamous does not manifest as bullous. Basal carcinoma very rarely metasatizes. MOHS is the best resection technique
|
|
|
what is the difference between hodking lymphoma and non hodkin lymphoma
|
see picture. Hodkin lymphoma is 85% B cell lymphoma
|
|
|
what are the caracteristics of oral cancers
|
basal cell carcinoma is most common, than, squamous, than malignant melanoma.
|
|
|
malignant melanoma types
|
Horizontal: superficial spreading(most common) Lentigo Maligna melanoma Lentigenous melanoma: sun exposed areas in elderly Vertical: Nodular melanoma, poorest prognosis
|
|
|
ewing sarcoma , osteosarcoma, and burkitt lymphoma(non hodkinian lymphoma) share radiographically the same appearence
|
Moth eaten radiolucency one variation of ewing sarcoma in the radio is inion skinning both cancers come to children: Bukitt: 3 years african and 11 years american ewing sarcoma: 5 to 30 years
|
|
|
Ramsay Hunt syndrome is the result of post herpetic neuralgia Involvment of of facial nerve and geniculate ganglion
|
ossifying fibroma and fibrous displasia share the same radiographic appearance. The only difference is that ossifying fibroma has weel circonscribed borders while fibrous displasia does not
|
|
|
Sturge-Weber disease (encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis) which consists of a facial lesion. known as
|
the port-wine stain
|
|
|
What is this pathology in a black woman of of 45 years old, non painful and not expensile
|
Peri apical cemento ossous displasia
|
|
|
What is this diseasewhat are the three caracteristics of it
|
Regional odonto displasia/Ghost teethShort rootsextra large pulpopen apexPermanent teeth more affected
|
|
|
What might be this lesion
|
granular cell myoblastoma Is similar histologically to the congenital epulis of the new born, but has pseudoepitheliomatous layer
|
|
|
what is the name of the osteo myelitis that occurs in children
|
Garre osteomyelitis
|
|
|
what are the diseases that cause enlarged pulp chambers
|
dentin dysplasia type 2 in permanent teethHypo phosphatasiadentinogenesis imperfecta Type 3
|
|
|
what are the main caracteristics of Hypo phosphatasia
|
Premature loss of teethHypo calcification of teeth and bones in generallarge pulp chambers
|
|
|
what is the disease that causes hypercementosis and hear loss?
|
Paget disease
|
|
|
whta is this organisation fo collagen around vessels called?where does it appear most frequently
|
It is called perivascular cuffing. It is pathognomonic of Cherubism.
|
|
|
What are the mandibular signs of Hypothyroidism?
|
Macroglossyunderdevelopment of mandibleOver development of maxillaretained temporary teeth
|
|
|
a child has fever and those marks opposite to the molars, what is this pathology
|
those are koplik spots .They occur in Meales
|
|
|
what are the pathologies that cause xerostomia What is it's treatment
|
Jogren RA Scleroderma SLE Treatment: Hydroxymethyl Cellulose/Carboxymetyl cellulose
|
|
|
name the order of ossous malignancies
|
1 osteosarcoma2 chondro sarcoma3 fibro sarcoma4 Ewing sarcoma (a distinguishing feature is that Ewing sarcoma has glycogen laden cells)
|
|
|
what is the name and caracteristics of a sarcoma that accompanies HIV positive patients
|
Kaposi Sarcoma: a form of angio sarcoma.Palate is the most frequent intraoral site.Herpes 8 has an etiologic factor
|
|
|
What is this lesion?What is the site of predilection?
|
Oral Lymphoepithelial cyst. Floor of the mouth, It is yellow pink, while lipona is more yellow This is a congenital cyst that is the counterpart of the branchial cyst that occurs anterior to the sterno cleido mastoid muscle
|
|
|
What is this stain name?what is it usefull for?what are the signs and causes of the pathology
|
Immuno peroxidase stain.Useful to diagnose metastatic carinoma of bonesigns are: moth eaten radiolucencies, painfull expension of angle of mandible in 56 year old patient.Prognosis is 10 percent after 5 years
|
|
|
Post herpetic neuralgia causes what syndrome
|
Ramsey Hunt syndrome, which is a an itchy and hyperesthesic sensation of the facial nerve
|
|
|
what is the difference between central giant cell granuloma, and giant cell tumor(brown tumor of the hyperparthyroid)
|
Both are radiologically and histologically the same.But central giant cell granuloma occurs exclusively in the jaws while giant cell tumor occurs mostly in long bones.also, in blood test, we find elevated calcium and alkaline phosphatase in Giant cell tumor
|
|
|
what is the other name to mono ostotic fibrous displasia
|
jaffe Lichtendtien syndrome
|
|
|
lateral periodontal cyst occurs exclusively in ?
|
Mandibular canine premolar region. It is tear drop shaped
|
|
|
what is this pathology
|
Calcifying odontogenic cyst.(Gorlin cyst) Microscopically has Gost cells
|
|
|
what is the other name for central epithelial odontogenic tumor ( CEOT)
|
Pindborg tumor. Painless swelling, almost exclusively central intra ossous than peripheral.
|
|
|
what is the difference between cemento blastoma and condensing osteitis
|
The cemento blastoma obscures the root, while the condensing osteitis doesnt
|
|
|
Wegener Granulomatosis presentation
|
Granulomatous inflamationnecrosisvasculitis
|
|
|
Peripheral Giant cell granuloma is very similar to the Pyogenic granuloma, the two main differences are radiologic and histologic
|
Radio: Peripheral Giant cell granuloma tends to have a radiolucency underneath while pyogenic granuloma not. Histological analysis is also important
|
|
|
Begning lympho epithelial lesion is also called
|
Mickuliz syndrome, auto immune disease like Jogren syndromecan manifest as the inflammation of both parotide glands The pathognomic sign is Histological:Epimyoepithelial islands
|
|
|
What are the two main causes of parotide enlargement
|
pleomorphic adenomaWarthin's tumor: papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum (PCL)
|
|
|
What is the main order of occurence of minor salivary gland malignancies
|
Muco epidermoid carcinomaPoly morphous low grade adeno carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the parotide order of malignancies
|
Muco epidermoid carcinomaacinic cell carcinomaAdeno carcinoma: this tumor is rare but agressive with 25% pain or facial weakness presentation.Malignant mixed tumor: 3types:Carcinoma ex mixed tumor: most frequent malignant mixed tumor deriving form the pleomorphic adenoma
|
|
|
Stevens Johnson syndrome( erythema multiforme) etiologies in :Adultschildren
|
Adults: drugs and malignanciesChildren: infection
|
|
|
what is this disease called strawberry tongue in a child with a rash his body
|
Scarlett feverCaused by strep Pyogen
|
|
|
what is the cause of proliferative verrucous leukoplakia
|
HPV 16 and 18
|
|
|
what is the cause of candyloma accuminatum
|
HPV 6 and 11
|
|
|
What is the most High risk HPV
|
16, 18, 31,33
|
|
|
what is the cause of focal epithelial hyperplasiaHeck's disease
|
HPV 13 and 32
|
|
|
What is this pathology?What are the caracteristics?
|
Ascher syndromeCaracteristic:Blepharochalasisdouble lipenlargement of thyroid
|
|
|
What does Mucicarmine stain reveal?
|
Cryptococcus neoformans
|
|
|
all these drugs cause gingival hyperplasia
|
Sodium valproate: for epilepsyNefidipine/Verapamil: calcium channel blockercyclosporine: immuno suppressant
|
|
|
Asher syndrome: triad: double lip, eye, and thyroid enlargement.Apert syndrome: premature fusion of suture: deformation of skull and retardation
|
papillon Lefevre syndrome: hyperkeratosis of palms and soles/ periodontitis extreme Nevoid basal cell carcinoma: hyperkeratosis/cysts/fibromas of skin/ calcification of falx cerebri
|
|
|
What can this pathology be in a patient who accidently bit his upper lip
|
Canalicular mono morphic adenoma: begnin tumor of minor salivary glands almost exclusively of upper lip. Attention: mucocele ressembles this pathology but occurs only in lower lip.
|
|
|
What is the contenance of OKC
|
Keratin: white substance cheese like in aspirationTreatment is marsupialisation and enucleation
|
|
|
what is the type of biopsy that we should perform for ulcers and bullous dieseases
|
incisional biopsy of both normal and lesional tissue.We must leave some of the lesion in order to be able to evaluate it in the future
|
|
|
what is this pathology?
|
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
|
|
|
What is this disease?What are the caracteristics?
|
Tuberous sclerosis.Mental retardationseizure disorderangio fibroma of the skin
|
|
|
Exanthema subitum is another name for
|
Roseola in children.caused by herpes 6
|
|
|
what is Zoster sine Herpete?
|
non rash zoster manifestation
|
|
|
What is this disease?what is the bacteria related to ti?
|
Cat scratch diseaseBartonella Hansalea is the bacteria related to it
|
|
|
Pyognic granuloma, peripheral giant cell granuloma and peripheral ossifying fibroma look clinically the same, but histologically, guess the diference
|
Pyogenic granuloma: vascular proliferationPGCG: giant cell multi nucleated.Peripheral ossifying fibroma: contains calcification
|
|
|
Granulocytic sarcoma is a cancer related to ?
|
Leukemia
|
|
|
Multiple Myeloma has histologically and amourphous glassy pink material. Yes or NO
|
Yes
|
|
|
in herpes zoster infection in elderly, especially when the patients are elderly and immune depressive, they may have a nose involvement , which mean that the naso ciliary nerve( of the trigeminal) is affected. It is mandatory in this case to refer the patient to ?
|
and ophtalmologist.We must also give a systemic anti viral drug.
|
|
|
where does ameloblastoma originate from
|
rest of Mallasezdentigerous cystenamel organ
|
|
|
where does OKC originate from
|
Dental Lamina
|
|
|
Where does dentigerous cyst originate from
|
reduced enamel epithelium
|
|
|
What are the maximum dose of epinephrine for a healthy person and caradio vascular diseased person?
|
healthy: 0.2 mgcardiovascular disease: 0.04mgRemember: 1/100 000 epi anesthetic contains 0.01 mg/ml of epi.1/200 000 epi anesthetic contains 0.005 mg/ml of epi
|
|
|
What is the antibiotic that concentrates mostly in bones? and gingival fluid
|
Bone: clindamycin.Gingival fluid: tetracycline
|
|
|
What type of Erythromycine causes allergic cholestatic hepatitis
|
Erythromycine estolate
|
|
|
what sulfonamides can be prescribed with what orther antibiotic
|
trimethoprimbecause they act sequently in the folic acid synthesis process
|
|
|
how does probenecid affect penicillin in the body
|
It reduces the excretion of penicillin in the kidney
|
|
|
Erythromycine should be avoided when a patient is taking what drug?
|
Seldan(anti histaminic), because it causes arythmia due to the blockage of matabolism of seldan
|
|
|
First drug to give in mild hypertension
|
Thiazide: diuritique
|
|
|
Calcium channel blockers:
|
nefidipineverapamil: also indicated in atrial fibrillationcause gingival enlargementBut:Amlodipine does not cause gingival enlargement
|
|
|
Beta blockers:
|
Propanolol: non selective Beta blockerAtenolol, metoprolol: selective beta blocker
|
|
|
direct acting vasodilator
|
HydralasineIndicated in first intention in a preganant patient with eclampsia
|
|
|
Ace in hibitors:
|
captoprilCan cause swelling(hypertrophy) in the tongue
|
|
|
Angiotensin1 inhibitor
|
Lasilactone
|
|
|
Angiotonsin 2 inhibitor
|
Lasartan (Cosaar)
|
|
|
Severe blood pressure
|
Clonidine
|
|
|
Calcium channel blockers cause what side effect in the oral cavity
|
Gingival enlargement
|
|
|
Blood pressure medication cause what in the oral cavity
|
Xerostomia and sometimes disgeusia
|
|
|
Heart failure( decrease in CO) drug
|
Digitalis (Digoxin): increase the contractility force of the heart.Indicated in the three things that cause failure:MI / Valvular disease / cardiac arrythmiaInteresting: Digitalis causes decrease in Heart rate: incicated in atrial flutter and atrial fibrillationSide effect: GAG reflex
|
|
|
what are the cardiac arrythima drugs
|
Quinidine: Atrial/supraventricular arrythmiaIt increases the refractory periodLidocaine: decreases the exitability of the ventricule
|
|
|
what is the class of nitro glycerinWhat disease does it treatwhat is the side effect of it
|
Vaso dilatorAngina pectorisside effect: xerostomiaContra indicated when usind phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors(Seldanaphil:Viagra): both are vaso dilators
|
|
|
methyldopa, is the drug with central action- it alters CNS control of blood pressure by acting on cardioregulatory and vasomotor systems of the brain by stimulating alpha2 receptors in the brain stem.metropolol is a selectively blocks beta-1 receptors in the heart to reduce cardiac output.
|
hydralazine has a direct action onvascular smooth muscle to reduce hypertension via vasodilation.propranolol blocks beta receptors in the heart,while guanethidine prevents the release and causes depletion of catecholamines taken up into storage vesicles . It does not cross the bloodbrain barrier.
|
|
|
Clonidine is one form of Methyl dopa which is a hypertension drug that acts where?
|
centrally.clonidine and methyldopa stimulate alpha 2 receptors of the brain thus reducing the hypertension
|
|
|
what is the anti hypertensive drug that causes oto toxicity and deafness?
|
High ceiling/loop diuretic: Furosemide
|
|
|
Symptoms of digitalis toxicity include all of the followinga. Extrasystolesb. Nausea and vomitingc. Yellow-green visiond. A-V conduction block
|
Chlorothiazide is a diuretic which causes potassium loss orhypokalemia. This results in greater penetration of digitalis intothe myocardium, and thus potential toxicity.
|
|
|
name two opiate analgesics that are mixed agonist antagonist
|
pentazocinenalbuphinenalorphine
|
|
|
What other opoid can we use for heroin dependancy
|
Methadone.Because the withdrawal reactions are less stressfull than heroin
|
|
|
succinylcholine treats what kind of spasmand why ? I promise, it is very interesting
|
laryngo spasmsuccinyl choline is actually two acetylcholine fused together.Acetyl cholinesterase cannot break it down.So when it fixes to the muscarinic cholinergic receptors, it is not broken down, causing the the muscle to relax instead of contracting repeatedly.. THAT IS INTERSTING, ISN'T IT?But: plasma esterase can break it, so patient with plasma esterase deficiency experience longer action time
|
|
|
atropine and scopolamine bind to Ach receptors drying up the salivary glands.What is the less common molecule that does that ?
|
Propantheline: which is a pro banthine, a synthetic atropineMetantheline is also a pro banthine
|
|
|
Remember this:
|
TCAs, H1 antihistamines, opioid analgesics cause xerostomia
|
|
|
Beta adrenergic blocking factores act in two ways:
|
They limit the formation of Renin, thus reducing the blood pressure.They block Beta 1 receptors, thus inhibiting the fixation of norepinephrine
|
|
|
What is the major side effect of the anti depressant phenitoin
|
Gingival hyperplasia
|
|
|
Are these all NSAID:IbuprofenIndomethacinPhenylbutazoneAcetylsalicylic acid
|
Yes
|
|
|
any intoxication coming from cholinergic blockers like atropine , propontheline, or scopolamine can be treated with
|
Primarily Physostigmine,But also other cholinergic agonists like neostigmine or
|
|
|
intoxication by insecticides and organo phosphates are treated with
|
enzyme generator like pralidoxime.
|
|
|
learn this:Curare is a non depolirizing Ach receptor blocker
|
While Succinylcholine is a depolarizing blocker
|
|
|
In the treatment of Parkinson, we give a sympathomimetic and another substance to protect it from degradation. What are they?
|
Levodopa.and Carbidopa is going to inhibit levodopa decarboxylase.
|
|
|
The barbituric are classified depending on their lasting effect to two classes. What are they?
|
Thiopental: ultra short actingPheno barbital: long acting
|
|
|
Name two anti psychotics?What is their mode of action?
|
Phenothiazine/ChlorpromazineHaloperidol(Haldol): more recentThey block the dopamineThey block the dopaminergic sites in the brain
|
|
|
what do you give for allergic skin reactions
|
Chlorpheniramine
|
|
|
What do you give for sedation before surgery as an anti histaminic
|
Prometazine.
|
|
|
What do you give for Parkinsonism?
|
diphenhydramine
|
|
|
What do you give for hurt burn (gastric acid treatment) or ulcer
|
cimetedine
|
|
|
what is the emergency treatement for Addison's crises(hypoaldosteronism)
|
2ml , 100 mg of Hydrocortisone Hemisuccinate
|
|
|
All of the benzodiazepines are metabolized in actives metabolites, which prolongs the action of the drug, but here are three expetions, what are they?
|
Oxazepam,Midazolam,Lorazepam
|
|
|
A patient with a cardio vascular problem should not be given in term of epinephrine more than:
|
2.2 carpule of 1/100 000 epi.Or0.04mg of epinephrine maximum. Remember:1 cc of 1/ 100 000 xilocaine contains 0.01 mg of epi.
|
|
|
Propranolol is a non selective beta blocker. This is, you know very well, humm. But it has also another cute action on the kidney, what is it?
|
It decreases the release of renin
|
|
|
What is one effect of narcotic opiates like codeine on the coughing?
|
it supresses the cough reflex
|
|
|
what is the effect of edrophonium?
|
anti cholinesterase, like physiostygmine or neostygmine but is used to treat Myasthnia Gravis
|
|
|
What is Phentolamine?
|
An alpha blocker
|
|
|
What is iso proterenol ( iso prenaline usefull for)
|
is a beta 2 agonist, used to facilitate breating during surgery because it causes bronchodilation.
|
|
|
to avoid mast cell degranulation in histamine reactions , you can can inject before it happens? But now that you have an anaphylactic choc, you have to inject?
|
Cromalyn: anti histaminic. Epinephrine: Physiologic antagonist of histamine
|
|
|
What are the advantages of Midazolam conpared to diazepam?
|
Midazolam is not dissolved in propylen glycol, thus there is no risk of thrombophlebite.It does not generate active metabolites, thus has a short half life .more rapid and predictable onset.
|
|
|
what do you inject to stop the effect of benzodiazepine?
|
Flumazoline
|
|
|
what are the main causes of gingival enlargement
|
Calcium channel blockers: Nefedipine/VerapamilPhenitoin and cyclosporine
|
|
|
Side effects of ACE inhibitors are: CAPTOPRIL
|
Cough, ;angioedema(swelling of the tongue), potassium excess, taste changes, orthostatic hypotension, pregnancy contra indication, rash, indomethacin inhibition, liver toxicity
|
|
|
An asmathic patient to whom we need to give a beta blocker, which one sould we give?
|
Metaprolol, because it is selective to beta 1 and does not cause side effects of beta2 blockage.
|
|
|
If we need to give a beta blocker to a pregnant woman, what should we give?
|
Labetalol, because it has an alpha 1 blocker, so it reduces the hypertension that a pregnant woman can have.And it has a beta1 blocker function as well
|
|
|
What is the maxium recommanded dose of lidocaine in a child, depending on the weight in pound and kilos? Good Luck!`
|
2-3.2 mg / Pound Or4.5-7 mg /kilo
|
|
|
What are the causes for an antibio prophylaxy in cardiac problems
|
Congenital heart disease.artificial valve.antecedant of endocarditiscardiac transplantation with valvulopathies.
|
|
|
Metronidazole is contraindicated when the patient takes alcohol, and being treated by?
|
disulfiram( which is the treatment for chronic alcoholism)
|
|
|
Celecoxib is a NSAID that is different from other NSAID like ibuprofene because it?
|
Does not cause gastro intestinal ulcer, simply because it inhibits COX 2( which is responsible for inflammation and pain ) and not CoX 1 like other NSAID ( which is responsible for the protection of the GI)
|
|
|
Codeine is a pro product that is tranformed to morphine by a liver enzyme.It 's conversion can be inhibited by the selective serotonine reuptake inhibitors like
|
FluoxetineParoxetineSertraline
|
|
|
What is MonteLucka useful for?
|
It is a cortico steroid tha is useful to reduce inflammation
|
|
|
the class of anesthetic that cause the most allergic reactions are?
|
Ester anesthetics: Because of the excipient that is para amino benzoic Acid.Propoxicaine.Procaine.Cocaine.Tetracaine
|
|
|
Sulfonylurea increase insulin secretion,It contains these two variants
|
GlipizideGlyburide
|
|
|
what is ERYC?
|
Erythromycin delayed release.It is coated so it has a delayed release.
|
|
|
what are the medications that you can give to treat pseudomonas aeruginosa Clue: the mnemonic is PCT
|
PiperacillingCarbanicillingeTicarcilline.
|
|
|
what is the maximum dose of Articaine that we can give to either an adult or a child in one appointment, knowing that it is related to the weight
|
7mg/kg
|
|
|
azole" = azole-type antifungal drugs (e.9., clotrimazole). "coxib" = COX-2 inhibitors fe&, celecoxib). "dipine" = dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (e.g., nicardipine). "olol" = beta-adrenergic receptor blockers (e.g., naclolol ). "ilol" or "alol" = beta-adrenergic receptor blocker that also blocks alphal-adrenergic receptors(e.g., canedilol or labetalol)
|
"osin" = alphar-adrenergic reccptor blockers (e.g., terazosin). "pril" - ACE inhibitors (e.g., enalapril). "sartan": angiotensin II receptor blockerc (e.9., olmesartan). "statin" = HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (e.9., atoflastatin)"onium" or "urium" : quatemary ammonium compounds, usually competitive peripheral actingskeletal muscle relaxers (e.9., pancuronium)
|
|
|
Acid stable penicilhns (may be used orally) include:. Penicillin VK. Amoxicillin. Ampicillin. Nafcillin. Oxacillin. Cloxacillin. DicloxacillinExtended spectrum penicillins include:. The aminopenicillins - Ampicillin and Amoxicillin
|
Broad spectrum penicillins include:. Piperacillin. Ticarcillin*** These two penicillins have the widest spectrum ofall the penicillinsPenicillinase-resistant penicillins include:. Nafcillin. Oxacillin. Cloxacillin. Dicloxacillin
|
|
|
NSAIDs can inhibit the antihypertensive effect of?
|
ACE inhibitors, betablockers.and diuretics.
|
|
|
what two drugs would you give to a patient who has arthritis
|
Piroxycam(Feldene).Prednisone.
|
|
|
name three anti cholinesterase inhibitors that are prescribed for Alzeihmer's disease? Hint: Mnemonic for the initials : DRuG
|
DonepezilRivastigmineGalantamine
|
|
|
What is Amyl Nitrite?What is its orginal function?As a second function, how does it neutrilize cyanide?
|
it is a nitroglycerinvaso dilator in the treatment of Angina PectorisIt neutralizes cyanide by oxidizing hemoglobin into Methemoglobin wich binds cyanide tightly prenventing it from going to tissues
|
|
|
Verapamil is a calcium channel blocker, but has also an anti arythmic function by treating......
|
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachicardia. Only Verapamil and Diltiazem are calcium channel blockers that have anti arythmic functions
|
|
|
How we call hair loss in chemathrapy treatment
|
Alopecia
|
|
|
What treatment would you give to reduce the symptoms of altitude sickness. Hint: it is a cabonic anhydrase inhibitor
|
Acetazolamide
|
|
|
You cannot give the anti fungic and triazolam(aid for sleep) together to the patient because
|
the anti fungal drugs inhibit the enzyme that metabolizes triazolam, thus making its levels higher in blood.
|
|
|
Name three medications for Gout disease
|
ProbenecidAllopurinolcholchicine
|
|
|
Name three medications used in treatment of mercury poisoning
|
DimecaprolPenicillinamineBritish Anti-Lewisite (BAL)
|
|
|
When drugs end in mum like pimecrolimum , it is what kind of drugs
|
Immuno supressant
|
|
|
When drugs end in mab, like adalimumab, it is what kind of drugs
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
|
|
Alcohol is synergistic with....Name 4 categories of drugs
|
diazepam (Valium), narcotics, barbiturates and phenothiazines.
|
|
|
* Aspirin/Acetaminophen/NSAIDso NSAIDS-block cox/ prostaglanding synthesis, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic; ie ASA, ibuprofen, naproxen
|
Cox 2 selective inhibitors will reduce pain & inflammation without risk of GI ulcers (ie celecoxib (Celebrex))* NSAIDs can inhibit antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors, B blockers and diuretics
|
|
|
Name two sympatomimetics with indirect action
|
Amphetamine and methylphenidatemosby's page298
|
|
|
how does digitalis work, and what ion does it increase in the heart cells
|
inhibits Na, k ATPaseIncreases calcium ions in the heart cells
|
|
|
name each generation of cephalosporin
|
1/ cefalexin2/ cefaclor3/ ceftriaxone4/ cefepim5/ cetaroline
|
|
|
name some SSRI |
Fluoxetine Paroxetine Sertraline Fluvoxamine Citalopram |
|
|
Name MAO inhibitors |
Tranylcypromine Phenelzine Selegiline |
|
|
How does nitroglycerin exert its action molecularly
|
increase the level of cGMP
|
|
|
What is the molecule that penicillines inhibit in the cell wall synthesis
|
Transpeptidase
|
|
|
What enzyme does methotrexate inhibit
|
Dihydropholate
|
|
|
how does glipizide enhance insulin synthesis
|
it closes ATP sensitive potassium channels |
|
|
how does Zalephon as a sedative act molecularly
|
inhibits selectively benzodiazepine receptors |
|
|
read page 424 in
|
mosby's
|
|
|
what part of the brain do the anti psychotic drugs like phenothiazine target |
Nigrostriatal pathway |
|
|
what ion do benzodiazepines drugs target in the cell |
chloride
|
|
|
what antibiotic lacks amine group and is only used as a cream
|
benzocaine
|
|
|
90 percent of penicillin is eliminated through what path
|
tubular excretion.non metabolisedin half an hour
|
|
|
____ has an antibacterial spectrum that is limited to anaerobes.A:AmoxicillinB:ClarithromycinC:ClindamycinD:GentamicinE:Metronidazole
|
Amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and clindamycin are effective against some anaerobes, but their spectrum is not limited to anaerobic bacteria. Aminoglycosides are effective only against aerobes. The action of metronidazole requires a reduced environment. Its antibacterial spectrum is limited to anaerobes. Metronidazole is also effective against many parasites. |
|
|
Flumazenil blocks the receptors stimulated by which of the following drugs? (Choose all that apply.)A:BaclofenB:Buspirone C:Diazepam D:Zolpidem E:Zaleplon
|
Flumazenil blocks both types of benzodiazepine receptors associated with γ-aminobutyric acid A (GABAA) channels, blocking the effects of diazepam, zaleplon, and zolpidem, the latter two being selective for the Bz1 receptor. Baclofen stimulates GABA B receptors, and buspirone is a partial agonist at serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptors.
|
|
|
what are the nerves that contain parasympathic fibers
|
3, 7, 9, 10
|
|
|
The use of vasoconstrictors in anesthesia should be avoided when the patient is using : Give two types of drug
|
Non selective beta blockers.TCA drugs
|
|
|
Hyperyentilation in an anxious dental patient leads to
|
carpopedal spasm(a spasm ofthe hand, thumbs, foot, or toes).
|
|
|
Patient treated by Ketamine can develop Laryngospasm,We can treat them with two things, what are they?
|
OxygenSuccinylcholine
|
|
|
Patients having COPD and being treated with theophylline cannot receive what kind of antibiotics, and why
|
Erythromycin, or clarithromycineBecause Erythromycin increases the metabolism of theophylline and may cause toxicity.
|
|
|
Hyper esthesia has 3 sub categories, what are they?
|
Hyper algesia: pain provoked by a naturally painful stimulus.Allodynia: pain provoked by a stimulus that is usually non painfulHyper pathia: subjective pain retalive to no stimulus
|
|
|
what Cyst comes from dental lamina
|
OKC
|
|
|
where does the ameloblastoma come from
|
Rests of Mallassez,Dentigerous CystEnamel organ
|
|
|
where does dentigerous cyst come from
|
reduced enamel epithelium
|
|
|
if the diabetic patient is going to receive dental anesthesia and sedation , what attitude should he have
|
reduce the insulin intake that day, and no eating before sedation
|
|
|
What is the first thing to give to a patient who has an osteoradionecrosis manifestation without secondary infection |
Just saline rinses, and recommand good nutrition |
|
|
What is the yearly occupational and non occupational dose in terms of REM |
0.5 REM in non occupational 5 Rem in occupational |
|
|
When developping a film, what does cracked reticulation of the emultion mean? |
big difference in temperature between baths |
|
|
What do branching lines mean in a radiograph |
Static charges when opening the film rapidly |
|
|
What is the main difference between Pemphigus Vulgaris and Pemphigoid in terms of distribution |
Pemphigoid does not usually happen on the skin, but only in the oral cavity and yhe eyes |
|
|
When are thee systemic or topical antiviral only effective in herpes simplex |
in the prodromal phase |
|
|
How does Pleomorphic adenoma manifest extrabuccaly |
as a freely movable mass peri auricularly Asymptomatic |
|
|
When we have a giant cell tumor or Brown Tumor in histology, what is the next exam that we should do |
Assess calcium level to know if it's brown tumor(initiate treatment only after calcium balance re establishment)
Or a Tumor( initiation enucleation) |
|
|
What is the pathogen that lives in pigeon excrements, and has a polysaccharide capsule that stains positive in musicarmine stain, and that affects Hiv positive patients |
Criptococcus Neoformans |
|
|
Multiple Myeloma is a painful pathology that affects 65 year old patients and manifests histologically as |
Glassy pink amorphous material |
|
|
What is the most two clear manifestation of Plumbism poisoning( Lead) |
Gingival lead line Burton's line. Tremor of tongue and hypersialy |
|
|
What is acrodynia, and how does it manifest? |
mercury poisoning. manifests like: Metallic taste, enlargement of salivary glands and tongue |
|
|
What is the other name for monomorphic adenoma |
canalicular adenoma |
|
|
suspected malignancies should have what kind of biopsy |
incisional biopsy, to be able to evaluate the rest in the future |
|
|
When patients have breast or prostate cancer, metastasis to the bone are frequent, so we have to expect what when we treat them in the oral cavity |
We have to expect that they had biphosphonate therapy to avoid having bone metastasis, so they are prone to osteonecrosis |
|
|
For the last time:
|
Pemphigus is supra basilar Pemphigoid is subepithelial |
|
|
Hemophila is X linked recessif, this mean that .... |
only a mother carrier of hemophiliac can transmit the disease |
|
|
Herpes Zoster is treated by systemic antivirals, but when the tip of the tongue is affected, this means that the naso ciliary mucles is affected, so the attitude would be to ..... |
refer the patient to an ophtalmologist |
|
|
What is the most frequent manifestation of squamous cell carcinoma
|
non healing ulcer |
|
|
name the three pathologies that are auto immune and create ulcers in the oral cavity |
Celiac Sprue Behcet Crohn |
|
|
Explain what Christensen's phenomenon is |
the intermaxillary space created after the protrusion of the mandibule, refers to the movement of the condyles downward and forward |
|
|
what are the three indications of labial bars |
absence of canines periodontal health problem Unfavorable teeth to soft tissue contour |
|
|
What is the function of beading or scribing(tracage) in the maxillary rpd |
increases strength and avoid food impaction under the rpd |
|
|
What kind of clasp do you use in classe one and two Kennedy |
RPI and RPA(rest, proximal plate,Ackers) |
|
|
What is the main use of wrought wire system in clasps |
reducing the torque of periodontally compromised teeth or endodontically treated. Also used if the the retention is opposite to the fulcrum line |
|
|
What kind of clasp do you use in classe three |
circonferential |
|
|
what is the order of preference in a distal extension RDP |
RPI RPC Wrought wire |
|
|
describe the dimensions of guiding planes |
one third of the bucco lingual width 2 to 3 millimeters from the marginal ridge |
|
|
In fixed prothesis, what occlusal scheme would you choose for class 1 and 2 malocclusion |
classe 1: cusp ridge classe 2 malocclusion: cusp fossa |
|
|
what is the compound that allows resin to bind to dentin |
4 MTA |
|
|
What are the furfacesa incriminated inthe non working side interference |
internal surfaces of the facial cusps of the mandibular molars |
|
|
When casting alloys, we have to use crucibles that are not contaminated by other alloys, |
Crucibles are not related to the gypsum type, but need to process only one type of alloy |
|
|
When pooring the cast for a complete prothesis, what is the width of the bead? What is the thickness of the cast |
Bead: 3/8th Thickness of cast : 16mm |
|
|
What is REALEFF |
Resiliency and like effect:
The resiliency of soft tissue compensate for limitations of the articulator |
|
|
when designing the RPD, that does the term surveying mean |
locating the height of contours on abutment teeth |
|
|
What is the indication of indirect retainer |
Classe 1 to prevent the movement of the denture in an occlusal direction
|
|
|
Learn this |
under pressure, teeth move by 0.2 mm. Tissues move by 1 mm |
|
|
How much should Wrought wire and cast metal width be
|
Wrought wire : 0.02 inch
cast metal : 0.01 inch |
|
|
Finish line in RDP are the smooth lines between resin and metal. What is the angulation for external finish line and internal finish line |
external: less than 90 internal = 90 |
|
|
what is the modification of teeth order in RPD design: |
Parallel guiding planes heights of contour Retentive contours rests |
|
|
In dental porcelain, What is the function of Feldspar Quartz/silica Kaolin |
Feldspar: matrix Quartz/Silica: form the skeleton and give strength Kaolin : binder |
|
|
Describe the two main reaction when glass ionomer as a luting agent is setting |
calcium binds to 2 cooH to form a soluble gel Aluminium binds 3 cooh to for an insoluble cement |
|
|
o If pt complains that their “s” sound sounds more like “th” |
→incisors to far palatally or palate too thick |
|
|
What are the names of the refractory products that allow thermal expension of phosphate investement |
Quartz Cristoballite |
|
|
give the ways we can make dental plaster Dental stone Die stone |
Dental plaster( Paris, Beta, type 2): heat the gypsum in 150 -160 dry.
Dental stone(type 3): heat in autoclave with steam at 120-130
Die stone: boil in 30 % cacl, or mgcl |
|
|
o Acrylic resins: explain the components |
Powder=PMMA polymer, benzoyl peroxide initiator, pigments
Liquid=MMA monomer, hydroquinone inhibitor, cross-linking agents, chemical activator (dimethyl-p-toluidine0—if self curing( reducing the shrinkage from 7 to 0.2) |
|
|
• Forward slide can be corrected by grinding mesial inclines of max teeth & distal inclines of mand teeth |
Protrusive interferences occur bt distal inclines of facial cusps of max & mesial inclines of facial cusps of mand |
|
|
o 4 theoretical determinants for restoring functional occlusal surfaces: |
amt of vertical overlap, contour of articular eminence, lateral shift in working condyle, position of the tooth in the arch |
|
|
o Balanced occlusion—occlusion of teeth which presents a harmonious relation of the occluding surfaces in centric & eccentric positions within the functional range •
What are it's determinants? |
5 factors: condylar guidance (dictated by pt), incisal guidance, occlusal plane, compensating curve, angle/height of cusps |
|
|
o Porcelain attaches to metal via mechanical & chemical bonding (oxide layers) |
Fe is key in PFM bonding to gold based alloys; Cr is key in PFM bonding to gold-substitute alloys |
|
|
o Classification based on fusion (vitrification) temp: |
• High fusing—for denture teeth • Medium fusing—for all ceramic & porcelain jacket crowns • Low fusing—for PFM |
|
|
o Pickling of the metal when fabricating a pfm. What is that? |
process of removing surface oxides from a casting prior to polishing; placed in an acidic soln |
|
|
if we want to gain more strength in the ceramic, we have to substitue quartz by |
Silica |
|
|
what is the main reason for fracture of the occlusal seat |
Inadequate rest seat preparation |
|
|
Balanced occlusion is more important during occlusion or swallowing |
Swallowing |
|
|
What is the other name for resin modified glass ionomer |
Compomer: it can be used as a liner, or as a secondary base after caoh2 |
|
|
What is the minimum distance between the major connector and the free gingiva in the maxilla |
6 mm |
|
|
When checking the occlusion, what are the three things related to the shim lock that need to be verified |
the restoration holds to shim lock the other teeth hold the shim lock multiple spots appear when try the shim lock on occlusal surface |
|
|
When there is a problem sitting the FDP, what are the two things that are suspected first, and what are the two things that we should not suspect |
Suspected: proximal contacts and marginal integrity.
Not suspected: axial contours and occlusion |
|
|
What is the thing that allow us to conserve the anterior guidance when restoring anterior teeth |
Custom incisal guide table |
|
|
Define Metamerism |
a color difference between two objects under different lighting conditions |
|
|
What are the two main signs of a crack in the tooth |
pain while shewing. Pain in cold sometimes discoloraiton of the cusp that contains the crack |
|
|
What is the requirement in reduction for a zirconia crown |
same as a metal crown: 1.5 in holding cusps and 1 in non holding cusps
Amalgam restoration and ceramo-metallic have same depth: 1.5 and 2 for holding |
|
|
What is the the main difference between cast ceramic and feldspthic porcelain in indirect restoration of teeth |
Feldspathic restoration causes more wear than cast ceramic to opposite teeth |
|
|
Name the two features that are considered primary retention in amalgam preparation |
Grooves and locks |
|
|
describe bur 245 |
3 mm long. 0,8 mm width inverted cone , rounded angles |
|
|
discuss the different approaches of restoration depending on the depth of the excavation |
more than 2 mm left to the pulp: Gluma desensitizer. btw 0.5 and 2 mm left: RMGI to obtain 2 mm thickness then, gluma desensitiser. Pulp exposed: 0.5 caoh2 plus RMGI plus Gluma |
|
|
Hoe deep can the composite restoration go without any liner |
as deep as 0.5 mm of dentin remaining
If deeper than 0.5 mm, Caoh2 plus RMGI Plus resin |
|
|
What is the protocol for indirect restoration concerning the protection of the pulp |
more than 2 mm of dentin: nothing, not even liner like the amalgam. 0.5 to 2: RMGi less than 0.5 mm: caoh2 plus RMGI |
|
|
what is Hollenbeck carver used for? How about amalgam knife |
Hollenck: facial and lingual amalgam exess amalgam knife: proximal exess |
|
|
• Indium—decr surface tension, decr Hg, reduce creep, incr strength, MUST BE USED IN ADMIXED (bc they need admixed more Hg) |
• Spherical alloys—need less Hg;
admixed alloys—require more Hg |
|
|
o Dimensional compensation via setting expansion & thermal expansion |
• Incr water→decreases expansion • Longer spatulation→more expansion • Longer time bt mixing & immersion in a water bath, the less it will expand |
|
|
o Ingredients of wax = |
paraffin wax (main ingredient), gum dammar (improves smoothness), carnauba wax (hard and decr flow of wax) |
|
|
• Hoe— |
cutting edge perpendicular to axis of the hand; used for Class II and V preps for direct gold • |
|
|
Angle former— |
used for sharpening line angles & useful to form convenience points for gold foil preps • |
|
|
Ordinary hatchet— |
cutting edge directed in same plane of the handle; bibeveled; used to prepare retentive areas • |
|
|
Spoon— |
remove caries, carve amalgam |
|
|
o Enamel hatchet |
is only instrument that allows you to have proper access to margins & that will impart proper cavosurface angle to the margins |
|
|
The chisel family named their son CHAD |
Chisel Hoes Angle Former Discoid and Cleoid |
|
|
The Hatchet family named their son HEG |
Hatchet Excavator Gingival marginal trimmer |
|
|
HIgh copper alloys contain 10 t 30 percent Cu by weight. Copper reduces creep and increase strenght by what means |
reduce gamma 2 phase of amalgame |
|
|
Slots, pins and grooves, as secondary retention features have similar retentiveness |
denting bonding is still instable depending of the nature of dentin(sclerotic, .....), but it is not shown to be stronger than enamel |
|
|
A beveled shoulder design around a capped cusp of a gold onlay preparation is termed a |
a collar |
|
|
What are the requirements for dental core |
Circonference and vertical walls both more than 3 mm |
|
|
What is the most important indications of labial bars |
incisive and promolar inclunation absence of canines |
|
|
describe the finish line for gold inlay proximal metal metallo ceramic porcelain/full ceramic |
gold inlay proximal: shoulder bevel metal: chamfer metallo ceramic: chamfer porcelain/full ceramic: shoulder |
|
|
What is the protocol for BRONJ |
if patient is taking oral biphosphonate more less than 3 years: no adjustement, you can proceed with implants
More than three years: 3 Months of drug vacation are required prior to surgery
IV biphosphonate is an absolute contra indication for implants, but not oral Biphos. |
|
|
What are the nerves anesthetised by the Gaw gates technique |
inferior alveolar auriculo temporal mylohyoid Lingual long buccal: 75 % of time |
|
|
Explain the Thumb technique |
the hub of the seringe in alveolar nerve bloc should stop between first and second molar |
|
|
if you don't want to calculate the pediatric dose of anesthetic by Young's or Clark's rules you can.... |
give one cartridge per 20 pounds of weight |
|
|
what would you inject if the patient turns chocolate colored because of methemoglobinemia |
IV injection of methyl blue 1-2mg/Kg over 5 minutes |
|
|
In emergency room , what does P 3 E mean |
P3: severe systemic disease + E= emergency
P4 : servere systemic disease with constant threat to life
Only P1(normal) and P2(mild systemic disease) patients are candidate for in office sedation
|
|
|
Drugs with decreased blood solubility have what caracteristic? |
increased onset of action |
|
|
Drugs with increase lipid solubility have what caracteristic? |
more potent because it binds rapidly the lipid membrane receptors |
|
|
drugs with increase blood gaz partition coefficient have what caracteristic |
higher solubility and passage from lung to blood |
|
|
What is the approach that we can use to pop the fractured zygoma |
Gillies approach |
|
|
What are the causes of metabolic alcalosis |
Steroid Cushing syndrome Conn's syndrome Vomiting Diuritics |
|
|
What are the products that increase in kidney disease |
Potassium Creatinine Phosphorus |
|
|
What are the product that decreasse in metabolic alkalosis |
calmium potassium
|
|
|
what is the least invasive tmj surgical procedure |
Arthroscopy
NOte: arthrocentesis, which is even less invasive is not a surgical procedure |
|
|
During local anesthetic administration, the patient should be placed in a ____ position. A: Trendelenburg B: Supine C: Reclined D: Semisupine |
The supine position is correct. This position prevents fainting during or immediately after the injection of local anesthetic. Reclined or semisupine is not back far enough, and Trendelenburg is too far back. |
|
|
According to Malamed, slow injection is defined as the deposition of 1 mL of local anesthetic solution in not less than ____. A: 15 seconds B: 30 seconds C: 60 seconds D: 2 minutes |
Malamed recommended that one cartridge of local anesthetic be delivered over not less than 1 minute; 1 mL (one half cartridge) should be delivered over not less than ½ minute (30 seconds). |
|
|
In an adult of normal size, penetration to a depth of ____ mm places the needle tip in the immediate vicinity of the foramina, through which the posterior superior alveolar nerves enter the posterior surface of the maxilla. A: 10 B: 16 C: 20 D: 30 |
The proper depth of penetration for the posterior superior alveolar nerve is half the length (16 mm) of a long needle or three fourths the length (15 mm) of a short dental needle. Penetration beyond 16 mm has a significantly higher incidence of positive aspiration and hematoma formation. |
|
|
According to Malamed, the maximum local anesthetic dose of lidocaine (with or without vasoconstrictor) A: 1.5 mg/kg B: 2.0 mg/kg C: 4.4 mg/kg D: 7.0 mg/kg |
Malamed recommended that a maximum of 4.4 mg/kg (2.0 mg/lb) of lidocaine be administered regardless of whether vasoconstrictor is in the formulation. The package insert for lidocaine allows up to 7 mg/kg when lidocaine is packaged with vasoconstrictor. |
|
|
Which local anesthetic is most hydrophobic and has the highest degree of protein binding? A: Mepivacaine B: Lidocaine C: Bupivacaine D: Procaine |
Lipid solubility (hydrophobicity) and protein binding are the most important factors in determining duration of action of a local anesthetic. Bupivacaine has the longest duration of action of the local anesthetics listed and has the highest hydrophobicity; it is bound 95% to protein. The other agents have lower hydrophobic qualities and are bound 75% or less to protein. |
|
|
Which class of dental anesthetics have the shortest half life |
the esters because they are metabolised i the blood.
Note articaine which is an amide has an ester bond, which makes it have a short half life |
|
|
What is the effect of local anesthetics on the heart |
Deacrease the maximum rate of depolarization of Purkinje fibers and nyocardium |
|
|
What is the innervation of tensor veli palatini |
nerve 5
|
|
|
What is the innervation of levator veli palatini |
nerve 10 |
|
|
What is the action of the cervical branch of the facial nerve |
retraction and depression of the angle of the mouth |
|
|
In what space do you find Stenson's duct |
the buccal space |
|
|
Does a patient with mitral valve prolase with regurgitation require antibioprophylaxy |
no. The new guide lines don't require it |
|
|
in case of implantology in a penicillin allergic patient |
600 mg one hour before is enough. don't add anything after that |
|
|
How to calculate the maining oxygen in an E cylinder |
pressure remaining* 0.3/10. Exemple: pressure remaining: 1000 psi. so oxygen remaining: 1000*0.3/10 = 30 minutes.
if the cylinder attains 1000 psi, it has to be replaced |
|
|
What is the first treatement of the tmj when non surgical tretments fail |
arthrocentesis: which is not a surgical treatement |
|
|
Mepivacain is the only anesthetic that is packaged in both 2 and 3 % concentrations
Mepivacain has also the lowest PKa of 7.7 |
Lido: 2 % Bupi: 0.5 Arti: 4 %
Articaine has the highest concentration of anesthtic : 4 % |
|
|
• Coronal root fracture—poor prognosis, splint 6-12wks |
• Midroot fracture—splint 3wks |
|
|
During Root canal treatment , what is transportation |
exessive removal of the outside curve of the apical half of the canal |
|
|
Explain the process of fabrication of reamer, K file and Hedstrom |
Reamer: twisting stainless steel: triangular, square K file: grinding stainless: diamond, triangular, square: can be used as reaming or push pull Hedstrom: cutting the spiral flutes |
|
|
What are the group of pathogens that first infect the root canals. What are the group of pathogen that is found after the debridement of the canal |
First: Gram negative bacteria Second: Gram positive facultative anaerobes |
|
|
What is J hook head gear |
it is a sort of high pull head gear that is mostly used for anterior arrangement rather than for orthopedic purposes |
|
|
What are the two appliances that are considered fixed rather than removable for patient who are not compliant |
Pendulum appliance Forsus Fatigue resistant device |
|
|
In total prothesis, what is the cause of occlusion shunt |
the occlusal plane is lower in molar region |
|
|
calcification times for permanent teeth |
first molar: birth All anterior teeth beside lateral: 6 months maxillary lateral : 12 months first premolar: 18 monhts second premolar: 24 months second molar: 30 months Third molar: 8-9 years |
|
|
how long does it take for a perament crown to complete formation |
4 to 5 years for all teeth, exept first molar(3 years), and canine 6 years
10 years total for the teeth to form , exept , canine 13 years |
|
|
What are the pathologies that have microdontia |
CHED , just lear this mnemonic |
|
|
What are the pathologies that have macrodontia: Hint: 2 pathologies only : Mnemonic: HO |
Hemihypertrophy otodental syndrome |
|
|
Dilaceration is a very common finding in what pathology |
Congenital Ichthyosis |
|
|
What is the role of functional inquiry in dealing with children |
evaluate main concern evaluate the cooperative ability |
|
|
what are the indicaitions and contra indicaitons of aversive techniques |
indications: momentary uncontrolled and defiant
Contra indicaitons: timid, tense cooperative |
|
|
What is the innervation of the maxillary molars |
middle superior alveolar nerve for maxillary temporary first molar, not the PSAN, and infiltration is enough. PSAN innervates the max temp second molar: we need to anethetize it plus infiltration
In the mandibule, always do a nerve block for deep caries, RCT and extraction, because infiltration is reserved for minor caries |
|
|
What are the four plateaus of stage 1 anesthesia(analgesia) |
Paresthesia: tingling Vasomotor: warm sensation Drifting: euphoria, pupils fixed, sensation of floating Dream: eye close but react to speech |
|
|
Fixed Kiddie partials is intended for which age, and what wire diameter we use? |
less than 3 years old. 0.036 -0.040 |
|
|
What is the indication of a lower lingual holding arch with a spur |
loss of unilateral mandibular temporary canines .
The spur function is to prevent the drift of the lateral incisive. So it is only indicated when the drift didn't happen yet. |
|
|
Extrusion of primary teeth . What do you do if it's more than 3 mm. If the blood clot didn't form yet? |
if it's more than 3 mm: extraction if the blood clot didn't form yet: reposition, splint 7 to 14 days, endo. |
|
|
What is the wire size in splinting one tooth. and many teeth |
one tooth: 0.016-0.022 if orthodontic wire. or 0.018 mm if round wire
Many teeth: 0.028mm |
|
|
Late mesial shifl of mandibular first molar can correct an end to end molar relationship to a class 1 relationship, but we increase the crowding of the buccal teeth by how much |
1.7mm |
|
|
What is the Tanaka Johnoson analysis: It calculates the the buccal segment lenght of permanent teeth(canine , 1st premolar, 2nd premolar) based on the inferior permanent incisives What is the formulation for the lower? what is the fomulation for the upper |
L/2 + 10.5 mm in lower.
L/2 + 11 mm in upper.
Exemple: length of lower permanent incisives is 22 mm. Estimated lower buccal segment: 22.5. Estimated upper buccal segement : 23mm |
|
|
Pit an fissure sealant result in the formation of an enamel hibrid layer of how large?
it reduces the caries of how much |
40 um
reduces the caries by 60 % |
|
|
What is the most common temporary congenitally missing tooth? |
maxillary lateral |
|
|
o Largest primary tooth is mand 2nd molar; mand lateral is smallest primary tooth |
syndromes having both Hypo and hyperdontia: ChOD microdontia: CHED Macro dontia: HO Hyperdontia: CGDSCH Taurodontism: TODEKA |
|
|
What is the most common impacted tooth |
maxillary canine |
|
|
crenetism causes enlarged tongue and delayed eruption |
Rickets causes delayed eruption
|
|
|
in edgewise brackets, the magnetude of the forces generated depends of the bracket size |
Twin bracket and single wing bracket both are used to gain more rotaitonal control |
|
|
What are the reasons the orthodontist uses non rigid archwire at the beginning of treatment |
Because the rigid wire may fracture the appliance. the rigid wire may be permanently deformed a non rigid wire is more pliable , thus more appropriate for the beginning of the treatment |
|
|
In orthodontia, what does an open coil spring help do |
upright teeth when it expends |
|
|
What is tipping of a tooth, and what is the difference with rotation |
tipping is the movement of tooth crown and rooth in opposite direction.
Rotation is the movement of a tooth around the long axis of the tooth |
|
|
What is the observable in the dark zone of orthodontic heavy and light forces within 4 hours |
Heavy forces: cell death. Light forces: cAMP |
|
|
what, among translation and intrusion require more force |
translation |
|
|
The left molar is in class 2 wheras the right molar is in a classe 1. What is the relationship named? |
Classe2 div 1 subdiv left |
|
|
What is the difference between the edgewise and the Begg appliance |
Edgewise has horizontal slots while the Begg has vertical slotsa
Straight wire appliane has a slots that have prescription in them |
|
|
Name 4 analysis used in cephalometric radiographs |
Steiner. Wits Downs Cogs |
|
|
What is Bolton's discrepency |
difference in size between maxillary and mandibular teeth |
|
|
Is the anterior cross bite correction maintained thanks to the overjet or the over bite created |
the overbite created |
|
|
Is condylar cartilage concidered a critical growth center of the mandibule or not |
no. The mandibule can grow even if the condyle is injured |
|
|
What is the single most importrantn idicator of joint function |
the amount of maximum opening |
|
|
what are the general TMD classifications |
Internal joint pathology and myofacial pain |
|
|
Never replant a primary avulsed tooth
|
gemination gives two crown on a single root.
Fusion gives fused rooths but still two seperate canals |
|
|
the shape of a tooth is determined in what stage? |
Cap: proliferation |
|
|
What are the materials that are indicated in high carious risk patient |
Gi, compomer, stainless steel crown Not resin |
|
|
in intruded permanent teeth, the puppectomy after traction should be done with CAOH2 |
in natal or neonatal teeht, extraction shouldn't be done systematically |
|
|
What is the biologic width of around the implant. what is the distance between the epithelium and the crestal bone. |
o Epithelium forms apically to approx 1-1.5mm from crestal bone around the implant |
|
|
o Phases of periodontal treatment plan: |
• Preliminary phase—emergencies • Phase I—caries control, ext hopeless teeth, mouth preparation (SRP), plaque control, OHI, occlusal adjustment, night guards, splinting, re-examination • Phase II—perio surgery • Phase III—restorative • Phase IV—maintenance |
|
|
what is the nature of the sulcular epithelium |
non keratinized squamous epithelium WITHOUT RETE Pegs.
RETE PEGS appear when there is inflammation |
|
|
• Chisel scalers—for proximal surfaces too closely spaced to permit use of other scalers esp ant part of mouth |
• Hoe scalers—for scaling ledges or rings of calculus |
|
|
Junctional epithelium is made of internal basal lamina, and external basal lamina. The internal basal lamina is facing the tooth and also called epithelial attachment.
What are the three components of the epithelial attachment |
Hemi demosomes, then lamina densa, then lamina lucida |
|
|
learn these medications that cause gingival hyperplasia |
immunosuppressive mycohenolate. antidepressant sertraline. the antipsychotic pimozide the interferon alpha 2 beta |
|
|
Give the two nomenclature for the gingival inflammation |
Initial/Transient/incipient: PMN dominant early /developping: lymphocytes dominant Chronic/ established: plasma cell dominant. |
|
|
Cells involved in acute ainlammation include basophils, tissue mast cells and platelets |
these three cells are the only ones that secrete histamines |
|
|
explain the severity of the periodontitis related to the clinical attachment loss mesures |
Slight periodontitis: 1-2mm Moderate : 3-4mm Severe: equal or more than 5mm |
|
|
Explain what is the rule of thumb when performing crown lengthening. |
we need 3mm from the alveolar crest to the margin of the preparation we need 2 mm of sound tooth to be retentive. Total: 5 mm |
|
|
name the three kinds of healing mechanisms after periodontal treatment |
Regeneration(of bone, cementum, pdl) Repair (by scar) New attachment(embedding of new pdl) |
|
|
What is the acyclovir posology |
15 mg/kg 5 times daily for 7 days |
|
|
What is the cellular source of the final tissue of the free gingival graft |
the connective tissue , and specifically the underlying lamina propria which is 0.75 mm deep |
|
|
What is the dose of nitroglycerin given to an anginal crisis |
0.3 mg nitroglycerin every 5 minutes |
|
|
A patient presents with exactly 30 percent of 5 mm CAL, is this periodontitis generalized or localized |
Generalized. Anything that is 30 % or more should be classified as generalized |
|
|
What is the radiographic appearance of calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor(Pindborg) |
Snow driven flackes in radiolucency |
|
|
what is the difference between radiographic mottle and contrast |
contrast is the range of densities on a radiograph, and radiographic mottle is an uneven density on a radiograph |
|
|
Name four techniques to reduce the gingival pocket |
Ossous surgery. Gingivectomy. Apically positioned flap. Guided tissue regeneration
But: connective tissue graft is used for root coverage not pocket reduction |

