![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
104 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fibrous displasia is defferent from gardener's syndrome osteoma in that |
FD is disfiguring and deforming by expension, while gardener's syndrome is flat and non deforming |
|
|
peripheral giant cell granuloma occurs where |
occurs exclusively in the gingiva like the ossifying fibromas opposite of central giant cell granuloma which occurs in bone. |
|
|
hereditary hemorrhagic telengiectasia is also called |
Rendu Osler Weber Disease |
|
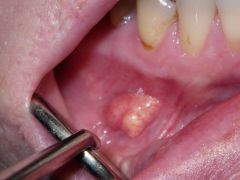
what is this lesion |
verruciform xanthoma |
|
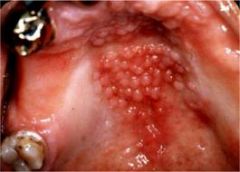
what is this how we treat it |
inflamatory papilary hyperplasia removal of the total prothesis exision if advanced of collegenous cryotherapy curetage |
|
nevoid basal cell carcinoma is also called |
gorlin syndrom autosomal dominant |
|
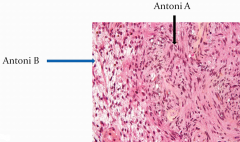
schwannoma has two vriations |
Antoni A and Antoni B occurs mostly in the 8 Nerve |
|
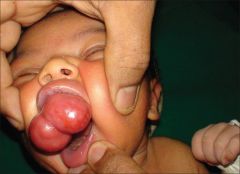
what is this disease called what attitude we should have What kind of histology cells we find To what other pathology is it histologically similar |
congenital epulis of the new born should be resected.dno reccurence Similar to Granular cell myoblastoma in that it contains granular cells. The difference is that GCM has a pseudo epitheliomatous Hyperplasia. GCM occurs in the tongue |
|
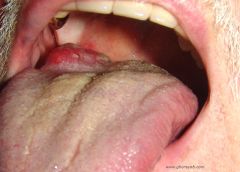
guess what this is It s a slow growing mass painless |
neuro fibroma |
|
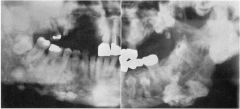
multiple osteoma is called what are the caracteristics |
gardener syndrome males more than females asympto intestinal polyposis always malignant potential accopagned fibroma of sking, epidermal cyst odontoma and impacted teeth |
|
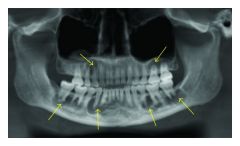
what is this pathology to what type of families it belongs what are the other types of the same pathology what are the other types of the same family |
peri apical cemento ossous displasia, most common in fibro ossous diseases focal: non expansile, edentulous area, mandible,< 2 cm Florid: African american females, > 2 quadrants, no cortical expansion |
|
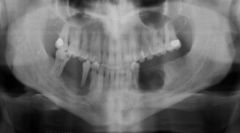
what is this disease, what are the caracteristics what are the others diseases of the same family |
Eosinophilic granuloma: floating teeth cupped out radiolucency like periodontal disease the others are: Letter Siwe: young childern, bones, skin, internal organs hand Schuller: punched out bone lesions |
|
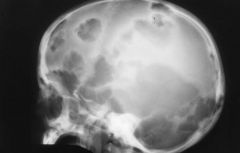
Hand Shuller Christian disease caracteristics |
Punched out bone lesions Exophtalmos Diabetes insipidus Floating teeth |
|
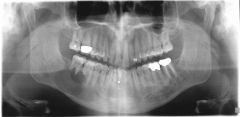
what is this lesions in a black male of 54 years |
multiple myeloma notice the sharp edge of the resobed root cure is : Thalidomide, chemotherapy, stem cell transplantation |
|
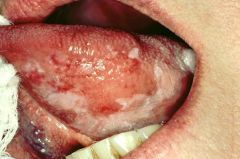
what is this disease in a man of 45 years, history of alcohol and smoking |
Squamous cell carcinoma, comes from: Human Papiloma virus: 16.18.31.33 vitamines deficiency, iron deficiency,and UV light 90 percent in lower lip |
|
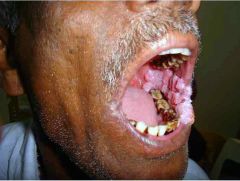
what is this what is the cause, what is the treatment |
verrucous carcinoma chewing tobacco excision without radio therapy |
|
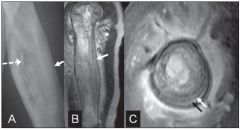
what is this occuring in a white child of 5 to 25 years what treatment |
ewing Sarcoma resection, radiotherapy, and aggressive chemotherapy Signs: Intermittant pain, swelling, fever, anemia, leukocytosis, and onion skinning on radiographs |
|
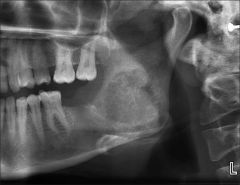
what is this, what clinic signs |
Osteosarcoma: painfull swelling, loose teeth, paresthesia, nasale obturation, apistaxis, fractures, ulcerations, mixed rado opacities, Sunburn Appearance, symetrical widening of pdl Elevated alkaline phosphate Treatment: radical resection with chemo or radio |
|
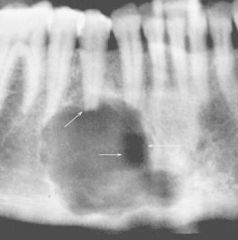
what is this what other pathologies can manifest like this: Well circonscribed, uni or multi locular radiolucency |
Central Giant cell granuloma other pathologies: Cleidocranial displasia/disostosis Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism |
|
|
what are the sizes of : acquired nevus common Blue nevus Cellular blue nevus |
< 6 mm acquired nevus < 1 cm common blue nevus. > 2 cm cellular blue nevus: accurs in 2nd and 4th decade |
|
|
Neurofibromatosis and Mc Cune Albright both have cafe au lait spots, but there is a big difference in the shape, what is it? |
Mc Cune Albright is shap irregular edges, while neurofibromatosis is smooth |
|
|
what are the other names for white sponge nevus |
familial epithelial hyperplasia Canon's disease hereditary Bilateral+ keratin genes 4 and 13 |
|
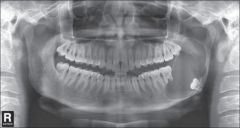
what is this: what are the caracteristics of it |
the radiograph is not diagnostic of this pathology: Dentigerous cyst notice the resorption of the adjacent teeth it might transform into ameloblastoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and intraossous mucoepidermoid carcinoma |
|
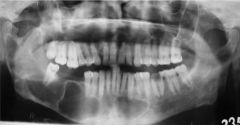
what is this pathology in a patient who has falx cerebri calcified, hyperkertinized pitted hands and feets.
cysts and fibromas on the skin?
|
OKC: odontogenic Keratocyst. Can be multiple in the Nevoid Basal cell carcinoma, which is Gorlin syndrome high recurence rate
the keratocyst is lined by parakeratinized epithelium.
The variation that is orthokeratinized is less agressive and less recurent.
|
|
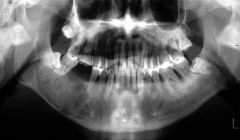
what is this pathology? who are the candidates? are are the caracteristics? what is the treatment? |
Ossigying Fibroma women from 30 to 40 years well circonscribed, mixed density asymptomatic Treatment: enucleation without recurrence |
|
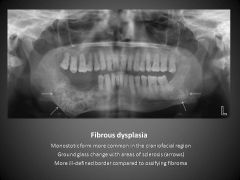
what is this disease? what are the caracteristics what is the main difference with fibrous displasia |
Fibrous displasia, family of the fibro ossous diseases Ground glass appearance can be mono ostotic, polyostotic, mac cune albright (poly + endocrine disease), Cranio facial Less clear borders than ossifying fibroma More maxillary than mandib like ossifying fibroma |
|
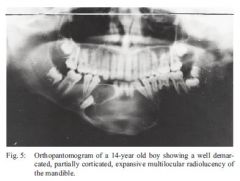
what is the name of this lesion happening in young individual? what is the main caracteristic of this lesion What are the other pathologies of odontogenic source |
ameloblastoma well demarcated borders the other odontogenic tumors: Odontogenic myxoma: honey comb appearance Odontogenic Fibroma: more females maxillary anterior Cementoblastoma: benign, mixed radio appearance. |
|
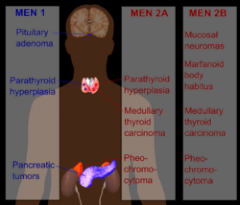
the difference between men1 , men 2(sipple syndrome ) , and men 3 is..... |
men 3 has mucosal neuroma. So a patient with mucosal neuroma also might develop a medullary carcinoma of Thyroid |
|
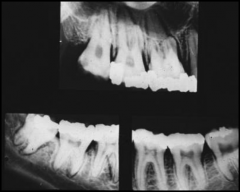
what are the two pathologies that cause an enlargement of the pdl |
Scleroderma |
|
|
cleft palate occurs when, what gender cleft lip occurs when , what gender, where? |
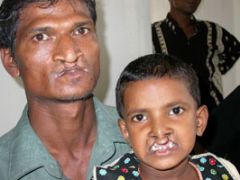
Cleft palate: 8 to 10 weeks, in females Cleft lip: left unilateral is 80 of cases. 6 to 7 weeks in males mostly Van Der Woude Syndrome: lip pits autosomal dominant with 90% penetrance |
|
|
high alkaline phosphatase is found in Low alkaline phosphatase is found in |
Paget disease of bone Hypophosphatasia |
|
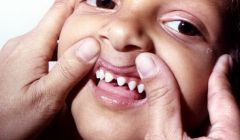
what is this pathology |
Ectodermal displasia:patient looks older than normal, no salivary, nor sweat glands. x linked recessive the cone teeth are a differential diagnosis with cleidocranial dysplasia, which also has a bossing forehead |
|
|
what are the caracteristics of Pierre Robin Syndrome |
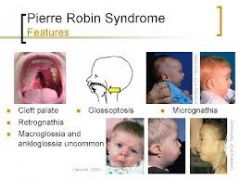
Micrognathie, Cleft lip Glosso ptosis High arched palate |
|
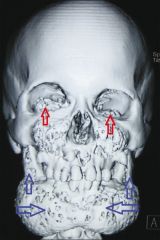
what is this lesion what are the caracteristics |
Cherubism Caracteristics are: multiple radiolucencies, peri vascular collagen cuffing, eyes stare in the space Multi nucleated Giant cells in histology |
|
|
Hypo para thyroidism is caracterised by |
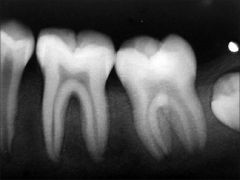
Blunt apices, hypoplastic enamel, Delayed eruption of teeth |
|
|
Muscular distropy is caracterised by |
loss of force to bite, so open mouth breathing. increased caries |
|
|
what are the signs of hypothyroidism |
Crenetism in children, myxedema in adults Underdevelopped mandible Over developped maxilla macrodontia, so teeth malposition |
|
|
Hyper parathyroidism= Von recklinghousen = Brown tumor |
Multi cystic radiolucencies, Giant cell in histology Extravasation of red cells+Hemosiderin= that's why it is a Brown tumor |
|
|
what is the incubatin period of Hepatitis B |
6 to 8 weeks |
|
|
What is the incubation period of Hepatitis A |
4 to 6 weeks |
|
|
the most serious complication of Ludwig's Angina is |
oedema of the Glottis |
|
|
What is the toxic dose of fluoride for adults and children |
Adults: 2 gram of fluoride Children: 5 to 10 mg/kg, very toxic if it reaches 16mg/kg 1 ppm of fluoride supplementation adds 1 to 2 mg in the diet. no toxic manifestation below 5 mg daily diet. |
|
|
what is the main cause of xerostomia: |
Medication Jogren syndrome is the main pathology that causes it. Radio therapy most toxic effect is xerostomia Other pathologies are: RA, Scleroderma, SLE. |
|
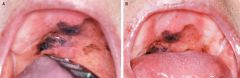
what is this pathology |
malignant melanoma, Sites of predilection: palate and maxillary gingiva uncommon pathology of the oral cavity |
|
|
how to distinguish between basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma |
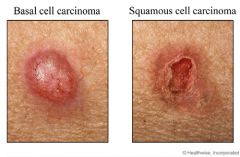
basal cell carcinoma is bullous like and does crust and ulcerate, Squamous does not manifest as bullous. Basal carcinoma very rarely metasatizes. MOHS is the best resection technique |
|
|
what is the difference between hodking lymphoma and non hodkin lymphoma |
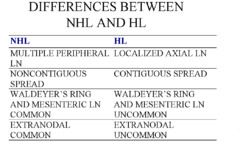
see picture. Hodkin lymphoma is 85% B cell lymphoma |
|
|
what are the caracteristics of oral cancers |
basal cell carcinoma is most common, than, squamous, than malignant melanoma. |
|
|
malignant melanoma types |
Horizontal: superficial spreading(most common) Lentigo Maligna melanoma Lentigenous melanoma: sun exposed areas in elderly Vertical: Nodular melanoma, poorest prognosis |
|
|
ewing sarcoma , osteosarcoma, and burkitt lymphoma(non hodkinian lymphoma) share radiographically the same appearence |
Moth eaten radiolucency one variation of ewing sarcoma in the radio is inion skinning both cancers come to children: Bukitt: 3 years african and 11 years american ewing sarcoma: 5 to 30 years |
|
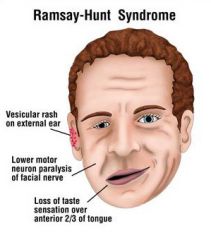
Ramsay Hunt syndrome is the result of post herpetic neuralgia Involvment of of facial nerve and geniculate ganglion |
ossifying fibroma and fibrous displasia share the same radiographic appearance. The only difference is that ossifying fibroma has weel circonscribed borders while fibrous displasia does not |
|
|
Sturge-Weber disease (encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis) which consists of a facial lesion. known as |
the port-wine stain |
|
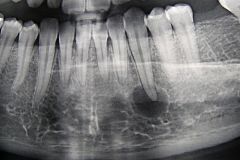
What is this pathology in a black woman of of 45 years old, non painful and not expensile |
Peri apical cemento ossous displasia |
|
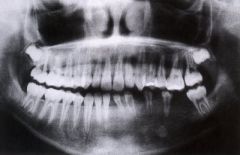
What is this disease |
Regional odonto displasia/Ghost teeth |
|
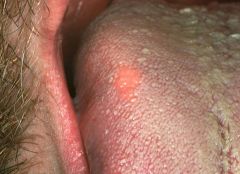
What might be this lesion |
granular cell myoblastoma
Is similar histologically to the congenital epulis of the new born, but has pseudoepitheliomatous layer
|
|
|
what is the name of the osteo myelitis that occurs in children |
Garre osteomyelitis |
|
|
what are the diseases that cause enlarged pulp chambers |
dentin dysplasia type 2 in permanent teeth |
|
|
what are the main caracteristics of Hypo phosphatasia |
Premature loss of teeth |
|
|
what is the disease that causes hypercementosis and hear loss? |
Paget disease |
|
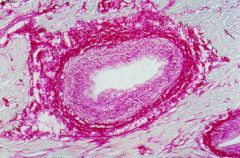
whta is this organisation fo collagen around vessels called? |
It is called perivascular cuffing.
It is pathognomonic of Cherubism.
|
|
|
What are the mandibular signs of Hypothyroidism? |
Macroglossy |
|
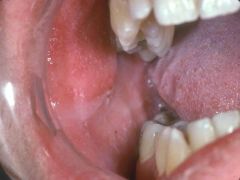
a child has fever and those marks opposite to the molars, what is this pathology |
those are koplik spots . |
|
|
what are the pathologies that cause xerostomia
What is it's treatment
|
Jogren
RA
Scleroderma
SLE
Treatment: Hydroxymethyl Cellulose/Carboxymetyl cellulose
|
|
|
name the order of ossous malignancies |
1 osteosarcoma |
|
|
what is the name and caracteristics of a sarcoma that accompanies HIV positive patients |
Kaposi Sarcoma: a form of angio sarcoma. |
|
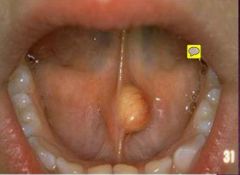
What is this lesion? |
Oral Lymphoepithelial cyst.
Floor of the mouth,
It is yellow pink, while lipona is more yellow
This is a congenital cyst that is the counterpart of the branchial cyst that occurs anterior to the sterno cleido mastoid muscle
|
|
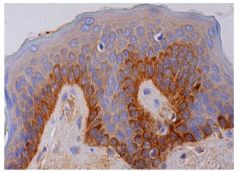
What is this stain name? |
Immuno peroxidase stain. |
|
|
Post herpetic neuralgia causes what syndrome |
Ramsey Hunt syndrome, which is a an itchy and hyperesthesic sensation of the facial nerve |
|
|
what is the difference between central giant cell granuloma, and giant cell tumor(brown tumor of the hyperparthyroid) |
Both are radiologically and histologically the same. |
|
|
what is the other name to mono ostotic fibrous displasia |
jaffe Lichtendtien syndrome |
|
|
lateral periodontal cyst occurs exclusively in ? |
Mandibular canine premolar region.
It is tear drop shaped
|
|
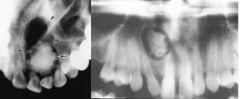
what is this pathology |
Calcifying odontogenic cyst.(Gorlin cyst)
Microscopically has Gost cells
|
|
|
what is the other name for central epithelial odontogenic tumor ( CEOT) |
Pindborg tumor.
Painless swelling, almost exclusively central intra ossous than peripheral.
|
|
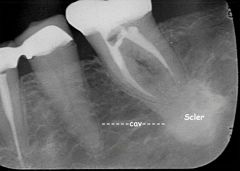
what is the difference between cemento blastoma and condensing osteitis |
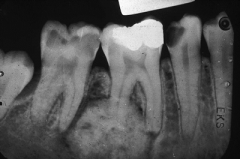
The cemento blastoma obscures the root, while the condensing osteitis doesnt |
|
|
Wegener Granulomatosis presentation |
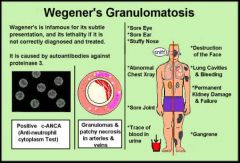
Granulomatous inflamation necrosis vasculitis |
|
|
Peripheral Giant cell granuloma is very similar to the Pyogenic granuloma, the two main differences are radiologic and histologic |
Radio: Peripheral Giant cell granuloma tends to have a radiolucency underneath while pyogenic granuloma not.
Histological analysis is also important |
|
|
Begning lympho epithelial lesion is also called |
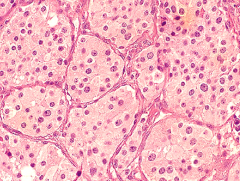
Mickuliz syndrome, auto immune disease like Jogren syndrome can manifest as the inflammation of both parotide glands
The pathognomic sign is Histological: Epimyoepithelial islands |
|
|
What are the two main causes of parotide enlargement |
pleomorphic adenoma Warthin's tumor: papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum (PCL) |
|
|
What is the main order of occurence of minor salivary gland malignancies |
Muco epidermoid carcinoma Poly morphous low grade adeno carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the parotide order of malignancies |
Muco epidermoid carcinoma acinic cell carcinoma Adeno carcinoma: this tumor is rare but agressive with 25% pain or facial weakness presentation. Malignant mixed tumor: 3types:Carcinoma ex mixed tumor: most frequent malignant mixed tumor deriving form the pleomorphic adenoma
|
|
|
Stevens Johnson syndrome( erythema multiforme) etiologies in : Adults children |
Adults: drugs and malignancies Children: infection |
|
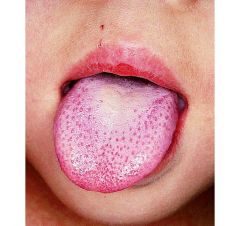
what is this disease called strawberry tongue in a child with a rash his body |
Scarlett fever Caused by strep Pyogen |
|
|
what is the cause of proliferative verrucous leukoplakia |
HPV 16 and 18 |
|
|
what is the cause of candyloma accuminatum |
HPV 6 and 11
|
|
|
What is the most High risk HPV |
16, 18, 31,33 |
|
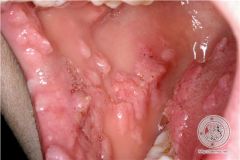
what is the cause of focal epithelial hyperplasia Heck's disease |
HPV 13 and 32 |
|
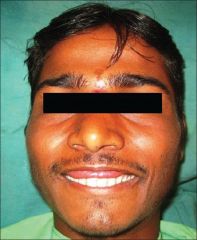
What is this pathology? What are the caracteristics? |
Ascher syndrome Caracteristic: Blepharochalasis double lip enlargement of thyroid
|
|
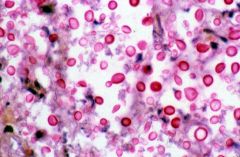
What does Mucicarmine stain reveal? |
Cryptococcus neoformans |
|
|
all these drugs cause gingival hyperplasia |
Sodium valproate: for epilepsy Nefidipine/Verapamil: calcium channel blocker cyclosporine: immuno suppressant |
|
|
Asher syndrome: triad: double lip, eye, and thyroid enlargement. Apert syndrome: premature fusion of suture: deformation of skull and retardation |
papillon Lefevre syndrome: hyperkeratosis of palms and soles/ periodontitis extreme
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma: hyperkeratosis/cysts/fibromas of skin/ calcification of falx cerebri |
|
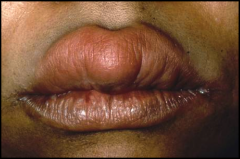
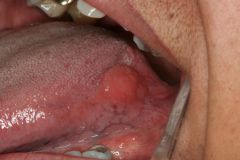
What can this pathology be in a patient who accidently bit his upper lip |
Canalicular mono morphic adenoma: begnin tumor of minor salivary glands almost exclusively of upper lip.
Attention: mucocele ressembles this pathology but occurs only in lower lip. |
|
|
What is the contenance of OKC |
Keratin: white substance cheese like in aspiration Treatment is marsupialisation and enucleation |
|
|
what is the type of biopsy that we should perform for ulcers and bullous dieseases |
incisional biopsy of both normal and lesional tissue. We must leave some of the lesion in order to be able to evaluate it in the future |
|
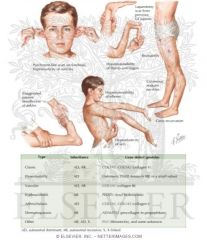
what is this pathology? |
Ehlers Danlos Syndrome |
|
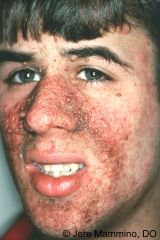
What is this disease? What are the caracteristics? |
Tuberous sclerosis. Mental retardation seizure disorder angio fibroma of the skin
|
|
|
Exanthema subitum is another name for |
Roseola in children. caused by herpes 6 |
|
|
what is Zoster sine Herpete? |
non rash zoster manifestation |
|
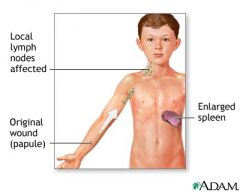
What is this disease? what is the bacteria related to ti? |
Cat scratch disease Bartonella Hansalea is the bacteria related to it |
|
|
Pyognic granuloma, peripheral giant cell granuloma and peripheral ossifying fibroma look clinically the same, but histologically, guess the diference |
Pyogenic granuloma: vascular proliferation PGCG: giant cell multi nucleated. Peripheral ossifying fibroma: contains calcification |
|
|
Granulocytic sarcoma is a cancer related to ? |
Leukemia |
|
|
Multiple Myeloma has histologically and amourphous glassy pink material. Yes or NO |
Yes |
|
|
in herpes zoster infection in elderly, especially when the patients are elderly and immune depressive, they may have a nose involvement , which mean that the naso ciliary nerve( of the trigeminal) is affected. It is mandatory in this case to refer the patient to ? |
and ophtalmologist. We must also give a systemic anti viral drug. |
|
|
where does ameloblastoma originate from |
rest of Mallasez dentigerous cyst enamel organ |
|
|
where does OKC originate from |
Dental Lamina |
|
|
Where does dentigerous cyst originate from |
reduced enamel epithelium |

