![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of connective tissue is found in dental pulp?
|
Loose
|
|
|
What type of cartilage primarily forms the temporomandibular joint?
|
Fibrocartilage
|
|
|
Which layers of the developing tooth is reponsible for the formation of the cervical loop?
|
Inner dental epithelium and outer dental epithelium
|
|
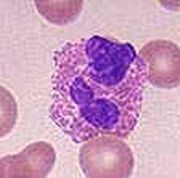
What type of leukocyte is found in the illustration?
|
Eosinophil
|
|
|
What union directly forms the retromandibular vein?
|
Superficial temporal and maxillary veins
|
|
|
The cell type that would have large amount of smooth endoplasmic reticulum throughout its cytoplasm would be a?
a) fibroblast b) leydig cell c) plasma cell d) macrophage e) red blood cell |
Leydig cell
|
|
|
In which organelle does the oxidation of alcohol in beer to acetaldehyde in liver occur?
|
Peroxisomes
|
|
|
What does the epiblast form?
|
Endoderm, Mesoderm, and Ectoderm
|
|
|
How many pairs of ribs directly articulate with the sternum through their own costal cartilage?
|
Seven
|
|
|
Each of the following structures is drained into submandibular lymph nodes Except one?
a) Floor of the mouth b) Tip of the tongue c) Upper lip d) Lower nasal cavity e) Mandibular molar |
Tip of the tongue
|
|
|
General sensory information from the hard palate travels toward the brain on nerves whose cell bodies are located in the?
a) Geniculate ganglion b) Trigeminal ganglion c) Dorsal root ganglion d) Pterygopalatine ganglion e) Otic ganglion |
Trigeminal ganglion
|
|
|
Palatine tonsils is found?
|
Between the palatopharyngeal and palatoglossal folds
|
|
|
Each of the following are characteristic of a patient with Amelogenesis imperfecta Except?
a) Amelogenesis imperfecta disrupts enamel formation b) Amelogenesis imperfecta affects both deciduous and permanent dentition c) Amelogenesis imperfecta affects secretion of cells within the outer epithelium of the dental lamina d) Amelogenesis imperfecta is due to defect in tuftelin, enamelin, ameloblastin, and amelogenin e) Amelogenesis imperfecta can be inherited as X-linked, autosomal dominant, or autosomal recessive |
Amelogenesis imperfecta affects secretion of cells within the outer epithelium of the dental lamina
|
|
|
Innervation of the Erector spinae muscles is from the?
|
Dorsal rami of spinal nerves
|
|
|
What periodontal ligament group runs from the cementum of one tooth to the cementum of an adjacent tooth?
|
Transseptal
|
|
|
What nerves transmit through the cavernous sinus?
|
III, IV, V1, V2, VI
|
|
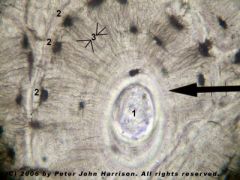
What is at the center of the picture?
|
Haversian Canal
|
|
|
The tentorium cerebelli separates the?
|
Cerebellum and Cerebrum
|
|
|
Which branchial arch forms the arch of the aorta?
|
Left fourth branchial arch
|
|
|
Which of the following is a branch of the splenic artery?
a) Left gastric artery b) Short gastric artery c) Gastroduodenal artery d) Right gastric artery e) Right gastroepiploic artery |
Short gastric artery
|
|
|
Keritinization of cells is commonly found in which of the following oral structures?
a) Lip b) Alveolar mucosa c) Floor of mouth d) Gingiva e) Soft palate |
Gingiva
|
|
|
Which of the following structures is NOT found in the parotid gland?
a) Facial artery b) Retromandibular vein c) External carotid artery d) Temporal branch of the facial nerve e) Zygomatic branch of the facial nerve |
Facial artery
|
|
|
A lesion in which of the following areas would result in a loss of fear and emotion?
a) basal ganglia b) somatosensory cortex c) amygdaloid nuclei d) primary motor cortex e) cerebellum |
Amygdaloid Nuclei
|
|
|
Which of the following are the lateral and medial attachments of the inguinal ligament respectively?
a) Iliac crest and ischial spine b) Pubic symphysis and anterior superior iliac spine c) Pubic tubercle and pubic symphysis d) Anterior superior iliac spine and pubic tubercle e) Iliac crest and pubic symphysis |
Anterior superior iliac spine and pubic tubercle
|
|
|
What stage during fetal life does the formation of the tooth germ initiate?
|
6th week
|
|
|
The most common type of stroke is found in which of the following arteries?
a) Anterior cerebral b) Lenticulostriate c) Posterior cerebral d) Posterior cerebellar e) Basilar |
Lenticulostriate
|
|
|
A lesion to the facial nerve at the stylomastoid foramen would lead to which of the following signs and symptoms?
a) Decreased taste in the anterior 2/3 of the tongue b) Decreased salivation in the mouth c) Decreased lacrimation d) Paralysis of the stapedius muscle e) Inability to close the eye |
Inability to close the eye
|
|
|
Hinge movement of the temporomandibular ligament occurs between the?
|
Articular disc and Condyle
|
|
|
Gliding movement of the temporomandibular ligament occurs between?
|
Articular eminence and Articular disc
|
|
|
Which periodontal fibers runs from the alveolar bone apically to the root cementum?
|
Oblique
|
|
|
Which of the following cells are NOT normally found in the periodontal ligament?
a) Macrophages b) Epithelial cells c) Fibroblasts d) Endothelial cells e) Cementocytes |
Cementocytes
|
|
|
Juxtaglomerular cells are found in the?
|
Afferent Arteriole
|
|
|
Which two nerves normally emerge between the superior and inferior heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle?
|
buccal and anterior deep temporal nerves
|
|
|
The canal of Schlemm carries?
|
Aqueous humor
|
|
|
Which layer of cells in the adrenal cortex is primarily responsible for production of androgens?
|
Zona Reticularis
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT found in the anterior triangle of the neck?
a) Common carotid artery b) Vagus nerve c) Superior thyroid artery d) Greater auricular nerve e) Internal jugular vein |
Greater auricular nerve
|
|
|
Which of the following structures is NOT found in the right atrium of the heart?
a) Crista terminalis b) Fossa ovalis c) Trabeculae carneae d) Coronary sinus e) Musculi pectinati |
Trabeculae carneae
|
|
|
What limits lateral movement of the mandibular condyle?
|
Medial wall of articular fossa
|
|
|
What is the best approximation of the organic mineral content volume found in dentin?
|
20%
|
|
|
Patient presents to the dentist with a decreased function in his right arm after being stabbed in the right chest. Examination reals a winged right scapula and an inability to raise the right arm above the horizontal. Which nerve was affected?
|
Long Thoracic
|
|
|
Which muscle allows the patient to adduct and elevate the scapula?
|
Rhomboideus Major
|
|
|
When asked to protrude her tongue, the patient's tongue deviates to the left side. Which muscle is paralyzed?
|
Left genioglossus
|
|
|
What type of epithelium composes striated ducts of the parotid gland?
|
Simple columnar cells
|
|
|
A 59 year old female patient visits the dentist to determine why she has been suffering from a lack of saliva and lack of tears. she also complains of loss of taste in the foods that she enjoys. The dentist performs a cranial nerve exam to elucidate the underlying cause of the clinical manifestation.
Which of the following is the correct association between cranial nerves, parasympathetic ganglion, and target structures? a) Nerve VII, pterygopalatine ganglion, lacrimal gland b) Nerve V, pterygopalatine ganglion, lacrimal gland c) Nerve VII submandibular ganglion, parotid gland d) Nerve X, otic ganglion, submandibular and sublingual glands e) Nerve IX, submandibular ganglion, parotid gland |
Nerve VII pterygopalatine ganglion lacrimal gland
|
|
|
Stensen's duct passes through the buccinator and opens into the oral vestibule usually opposite to which tooth?
|
Maxillary 2nd Molar
|
|
|
What does the lesser petrosal nerve innervate?
|
Parotid gland
|
|
|
The intrinsic muscles of the patient's tongue is derived from the?
|
Occipital Myotomes
|

