![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
227 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Subsidence
|
Nearly vertical downward movement of Earth's surface
|
|
|
Causes of subsidence
|
Dissolution of limestone,
thawing of frozen ground, compaction of sediment, shrinking of expansive soil, earthquakes, collapse of volcano |
|
|
Karst
|
An irregular landscape containing many depressions
Results from the dissolution of rock Evident in areas of limestone |
|
|
Chemical reactions leading to limestone dissolution
|
Water + carbon dioxide = carbonic acid
Carbonic acid + limestone = calcium carbonate |
|
|
limestone dissolution can lead to continous voids, which may produce:
|
Caves or sinkholes
|
|
|
Karst plane
|
Surface containing many sinkholes
|
|
|
Sinkholes, two basic types:
|
solution sinkholes: formed by acidic groundwater
Collapse sinkholes: formed by collapse of surface |
|
|
Flowstone
|
General term for accumulation of calcium carbonate precipitated from water in a cave
|
|
|
Stalactite
|
Deposit of calcium carbonate that extends downward from the roof of a cave
|
|
|
Stalagmite
|
Deposit of calcium carbonate on the floor of a cave
|
|
|
Tower karst
|
Large rock pillars remnant of highly eroded landscapes
|
|
|
Disappearing streams
|
Stream on the surface that disappears into a cave
|
|
|
Springs
|
Groundwater discharges at the surface
|
|
|
Thermokarst
|
Irregular surface produced by thawing permafrost
|
|
|
Piping
|
Groundwater percolating through loose sediment, creating underground tunnels that could collapse to form depressions/ravines
|
|
|
Fine sediment
|
Land may slowly compact over time as water in the soil pores decreases - typically balanced by new sediment deposited from the river
|
|
|
Collapsible Sediment
|
Large amount of pore space, soil grains loosely bound together - infiltrating water can dissolve minerals holding soil together
|
|
|
Organic sediments
|
Contains large amount of water, if water is lost, great reduction in thickness
|
|
|
Expansive soils
|
Clay-rich soil
Easily expand and shrink during wet/dry |
|
|
Levees along the Mississippi River
|
Restrict natural flooding events, preventing wetlands from being replenished with new sediment
|
|
|
Groundwater mining
|
Removing groundwater to use for drinking water, enhance existing subsidence
|
|
|
Drainage basin
|
For lakes, it is the area of land that drains into that lake
|
|
|
Divide
|
Ridge of higher land that separates which way rivers flow
|
|
|
Continental divide
|
Located along the spine of the Rocky Mountains, separates which ocean the streams and rivers will eventually drain into
|
|
|
River Gradient
|
Change in elevation over the distance a river flows - steep in higher elevations
|
|
|
Bed Load
|
Materials that roll, slide or bounce along the bottom
|
|
|
Suspended Load
|
Silt and clay particles carried in the water - accounts for 90% of the total load of most rivers
|
|
|
Dissolved Load
|
Material derived from chemical weathering of rock and sediment within the drainage basin
|
|
|
Discharge
|
The volume of water flowing past a point in a river of a specific period of time
|
|
|
Discharge Formula
|
Q(Discharge) = V (velocity) x A (cross-sectional area)
|
|
|
Alluvia fan
|
Deposited by the river on land at the river mouth
|
|
|
Delta
|
Deposited by the river in water at the river mouth
|
|
|
Braided channel pattern
|
Large number of channels are evident, abundant bed load from melting glaciers - channels wider and more shallow, lack vegetation on islands
|
|
|
Anastomosing channel pattern
|
2 or more channels, intervening islands with temporary sediment. Islands more stable than braided patterns, may support vegetation
|
|
|
Meandering channel pattern
|
Single channel that is shaped like a snake
|
|
|
Meandering velocity changes
|
Greatest on the outside of the curve causing erosion, slower on the inside causing deposition
|
|
|
Cutbank
|
Erosion on the outside of a meandering curve
|
|
|
Point bar
|
Deposition on the inside of a meandering curve
|
|
|
Riffle
|
Shallow section of a river where water moves rapidly over a gravel bed
|
|
|
Pool
|
Deep section of a river where water moves slowly
|
|
|
Floodplain
|
Area of flat land adjacent to a channel that is subject to natural flooding
|
|
|
Avulse
|
Water leaves meandering river during flood, cutting a new channel that forms a shorter route
|
|
|
Oxbow lake
|
Abandoned section from an avulsion
|
|
|
Bankfull discharge
|
Discharge at which point water first flows out of the channel - when the flood officially begins
|
|
|
Stage
|
The level of the river surface
|
|
|
Flood stage
|
The level of the river surface must reach in order for it to cause property damage
|
|
|
Hydrograph
|
A graph showing changes in discharge or changes in stage over time
|
|
|
Recurrence interval
|
The average time between floods of a certain size
|
|
|
Upstream floods
|
Occur in the upper part of the drainage basin, produced by heavy rainfall of short duration over a relatively small area
|
|
|
Flash floods
|
Sudden and involve a large increase in discharge, occur in areas of steep typography and little vegetation
|
|
|
Downstream floods
|
Cover relatively large areas, produced by rain of long duration of by rapid melting of snowpack
Slow but substantial rise in discharge |
|
|
The Red River
|
Flows through the city of Winnipeg, frequently floods from melting snowpacks at the north end of the river and impermeable soil
|
|
|
Natural service functions of floods
|
Fertile lands, depositing of nutrients
Flush out debris Sustain wetlands by adding sediment |
|
|
Physical barriers to floods
|
Earthen and concrete levees, flood ways, storm-water retention basins
|
|
|
Channelization
|
Straightening, deepening or widening existing river channels - control floods, generally negative impact on fish
|
|
|
Riprap
|
Control channels in a more environmentally friendly way
|
|
|
Flood drainage reduction program
|
Disaster assistance will not be provided for a development built in a designated flood-risk area
Provinces and territories will ensure that municipalities cone on the basis of flood risk |
|
|
Ozone layer is found in the:
|
Stratosphere
|
|
|
All weather is confined to the
|
Troposphere
|
|
|
Cirro
|
High cloud
|
|
|
Alto
|
Mid-level cloud
|
|
|
Strato
|
Low cloud
|
|
|
Cumulus
|
Puffy cloud
|
|
|
Stratus
|
Flat cloud
|
|
|
High puffy cloud
|
Cirrocumulus
|
|
|
Mid level puffy cloud
|
Altocumulus
|
|
|
Low level puffy cloud
|
Stratocumulus
|
|
|
High level flat cloud
|
Cirrostratus
|
|
|
Mid level flat cloud
|
Altostratus
|
|
|
Low level flat cloud
|
Stratostratus
|
|
|
Northern hemisphere areas of low pressure
|
Air circulates counter-clockwise and rises, the result is clouds and precipitation
|
|
|
Northern hemisphere areas of high pressure
|
Air circulates clockwise and sinks, the result is clear skies
|
|
|
Front
|
Boundary between two air masses - the name describes the type of air behind the front
|
|
|
Cold front
|
Dense cold air undercuts warm air
|
|
|
Warm front
|
Less dense warm air overrides cold air
|
|
|
Thunderstorm development requires:
|
An unstable environment (steep vertical temperature gradient)
hot air near the ground Water vapour Rising air (lifting mechanism, front) |
|
|
3 stages of thunderstorms
|
Cumulus, mature, dissipative
|
|
|
Hail
|
Formed during thunderstorms in very tall clouds - forms a ring of ice each time it enters the cold part of the cloud
|
|
|
Lightning
|
A spark of electricity occurring in a cloud - heats air causing the air to expand, creating a shockwave
|
|
|
What is the main requirement for lightning?
|
A cumulonimbus cloud containing a region of opposite charges
|
|
|
Tornado
|
A rotating column of air touching the ground that formed within a supercell thunderstorm
|
|
|
Funnel cloud
|
Funnel that does not touch the ground, turns counter clockwise in northern hemisphere
|
|
|
Organizational stage of tornado
|
Wind shear causes rotation to develop, funnel cloud protrudes from abode, dust and debris rotates underneath
|
|
|
Mature stage of tornado
|
Most severe damage occurs at this stage, may only last 10-15 minutes
|
|
|
Rope stage of tornado
|
Stretches out and weakens
|
|
|
Wind shear
|
A change in wind speed or wind direction over a horizontal or vertical distance
|
|
|
The only cloud that can house a tornado
|
Cumulonimbus cloud
|
|
|
Tornadoes are classified on the:
|
Enhanced Fujita Scale, from EF0 to EF5 (322km/hr)
|
|
|
Tornado alley (US)
|
Oklahoma/Kansas, cold air comes down from the Rockies and meets warm air from mexico
|
|
|
Super Outbreak
|
148 tornadoes touched down between Ontario and Alabama
|
|
|
Joplin Tornado
|
EF5 tornado killed 162 people, 2.2 B in damage
|
|
|
Goderich Tornado
|
2011, killed one person, EF3
|
|
|
Fog
|
Reduced visibility to less than 1km, occurs at night when air cools to the dew point
|
|
|
Blizzard conditions
|
At least 40km/hr winds
Snow falling or blowing snow Reduce visibility to less than 1km Wind chill less than -25C Must occur for 3 hours |
|
|
Lake effect snowfall
|
Cold dry air moves over relatively warm water, winds in winter usually from North West
|
|
|
Haboobs
|
Sandstorms, downdraft on the leading edge of a thunderstorm
|
|
|
Dust devil
|
Small spinning vortex of air formed over hot, dry land - how air rises, wind direction may change due to obstacles
|
|
|
Tropical disturbance
|
A large area of low pressure with unsettled weather
|
|
|
Tropical depression
|
An unorganized area of thunderstorms
|
|
|
Tropical storm
|
Organized area of storms with wind of 65-119km/hr
|
|
|
Hurricane
|
Area of low pressure with wind of at least 120km/hr
|
|
|
Hurricane eye
|
A region in the centre with light winds and clear to partly cloudy skies
|
|
|
Hurricane eyewall
|
A ring of intense thunderstorms that whirl directly around the eye (counterclockwise), most devastating component
|
|
|
Spiral rain bands
|
Rings of tall clouds and heavy rain that exist throughout the hurricane
|
|
|
If a hurricane is moving to the northwest, where will its highest winds be located?
|
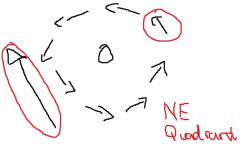
Spins counter clockwise, north east quadrant
|
|
|
Storm surge
|
Most devastating effect of hurricanes
|
|
|
Hurricanes are classified on the
|
Saffir-Simpson scale, 1 (120km/hr) - 5
|
|
|
Hurricane Juan
|
Category 2 hurricane made landfall near Halifax
|
|
|
Hurricane Hazel
|
Intense flash flood in toront, killed 81 people
|
|
|
Watch alert
|
An alert covering a wide area, conditions favour the development of hazardous weather but none has been reported
|
|
|
Warning alert
|
Usually covers smaller areas, hazardous weather is currently occurring in that area
|
|
|
Advisory alert
|
Alert the public of less hazardous weather conditions
|
|
|
During which conditions are you most likely to see clouds?
|
Low pressure
|
|
|
Passive margins vs active margins
|
Passive: sandy pebbly beaches, wide continental shelves
Active: Rocky shorelines, sea cliffs |
|
|
Swells
|
Sets of waves generated by storms far out to sea - length and velocity decrease, height increases
|
|
|
Plunging breaker wave
|
form on steep beaches and can be very erosive
|
|
|
Spilling breaker wave
|
Develop on wide, gently sloping beaches, less erosive
|
|
|
Tidal bore
|
Waves that form when inflowing tidal water is slowed by outflowing river water
|
|
|
Sea cliff/bluff
|
Erosional landform that marks the landward boundary of a beach
Cliff: ocean |
|
|
Berm
|
An onshore portion of the beach that is generally flat and formed by deposition of sediment
|
|
|
Beach face
|
Onshore portion of the beach that slopes seaward - lies within the swash zone
|
|
|
Surf zone
|
Area where waves move toward the shore after they break
|
|
|
Breaker zone
|
Area where incoming waves peak and break
|
|
|
Longshore bar
|
Low ridge on the seafloor in the breaker zone - circular motion causes a depression along the shoreline
|
|
|
Longshore trough
|
Depression on the seafloor formed by wave action inward of the landward of the longshore bar
|
|
|
Littoral transport
|
Sand movement parallel to the shore, consits of beach drift or longshore drift
|
|
|
Beach drift
|
San moving in a zigzag pattern in the swash zone
|
|
|
Longshore drift
|
Transport of sediment by currents that flow parallel to the shoreline
|
|
|
Both beach and longshore drift occur where waves strike the coast an an angle...
|
other than 90 degrees
|
|
|
Spits
|
Ridges that extend parallel to the shore from a point of land on a coast
|
|
|
Barrier islands
|
Long, narrow islands separated from the mainland by a bay or lagoon
|
|
|
Eustacy
|
Global changes in sea level from melting ice sheets
|
|
|
Iostasy
|
Forces that elevate or depress Earth's crust
Large ice sheet melts off a continent, reduction in weight causes the crust to rise |
|
|
Rip currents
|
Horizontal currents that move away from a shoreline, sometimes called undertow - about 100 people drown in rip currents every year
|
|
|
Hard stabilization
|
Structures designed to protect the shoreline (like levees)
|
|
|
Soft stabilization
|
Addition of sand to depleted beaches
|
|
|
Land-use
|
Avoidance of building in hazardous areas
|
|
|
Seawalls
|
Hard stabilization, vertical design reflects waves, redirects energy
Erodes faster at the base |
|
|
Groins
|
Built perpendicular to the shoreline in groups, trap sand carried by longshore drift - erosion still occurs in the downdrift area
|
|
|
Breakwaters
|
Built parallel to shores and designed to protect boats in a harbour or marina
|
|
|
Jetties
|
Extend perpendicular to shores at the mouth of a river
Prevent sediment from accumulating at the mouth of the river, shelter the river channel from large waves |
|
|
E-line
|
Expected position of the shoreline after a specific number of years
|
|
|
E-zone
|
Area between present shoreline and respective E-line
|
|
|
Extreme hazards
|
Widespread and long term (nuclear accidents)
|
|
|
Rare catastrophes
|
Airplane crashes, mine collapses, shipwrecks
|
|
|
Common environmental hazards
|
Car accidents, poisons
|
|
|
Cumulative effects
|
Conditions worsen slowly over time - toxic chemicals, acid precipitation, groundwater contamination, ozone depletion
|
|
|
Calculating risk - large-scale structures
|
probability of failure during the lifetime of that structure
|
|
|
Calculating risk - transportation
|
Probability of death or injury per km travelled
|
|
|
Calculating risk - industry
|
probability of death or injury per person per number hours exposed
|
|
|
Radon
|
Natural decay of uranium in rock/soil, 2nd leading cause of lung cancer in N. america. Lodges in the lungs as polonium
|
|
|
Nuclear meltdown
|
Accident that results in damage from overheating - fuel rods turn to liquid and the walls of the reactor core melt from extreme heat
|
|
|
Three Mile Island Nuclear Accident
|
Worst nuclear disaster in US history, failure of a valve that controlled cool water entering the reactor core
|
|
|
Worst nuclear disaster in world history
|
Chernobyl, result of a flawed design, operator error and disregard of safety regulations
|
|
|
Exxon Valdez Oil Spill
|
Oil tanker striking a rocky reed of the south coast of Alaska, 75 million of litres of oil spilled
|
|
|
Deepwater Horizon
|
Oil rig explosion in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010 - 8.5 million litres of oil every day for 5 months
|
|
|
Tacoma narrows bridge collapse
|
design of bridge did not provide any open trusses for wind to pass through
|
|
|
Challenger shuttle
|
Faulty O-ring due to cold weather, failed to seal a joint leading to the release of hot gas
|
|
|
Columbia shuttle
|
Piece of insulation broke off from the external tank and damaged the system that protects left wing from intense eat from re-entry
|
|
|
Spilling breakers are common on which type of shoreline?
|
Gently sloping sandy beach
|
|
|
Nitrogen in the atmosphere
|
Added by decaying plant matter, removed by bacteria in soil
|
|
|
Carbon dioxide
|
Gas most responsible for climate change
|
|
|
Methane
|
Natural from bacterial decay/intestinal tracts of cows, gas of the atmosphere
|
|
|
Halocarbons
|
CFCs, refridgerants and industrial processes
|
|
|
Aerosols
|
tiny particles that are small enough to remain suspended in the atmosphere for an extended period of time
contribute to smog |
|
|
Gravitational settling
|
Large particles fall more quickly due to gravity
|
|
|
Climate is a function of the interaction of many spheres
|
Atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, cryosphere, biosphere
|
|
|
The Holocene Epoch
|
Time of warming - Medieval Warm Period
The Little Iceage - widespread cooling |
|
|
Causes of climate change
|
Variations in solar radiation
Changes in composition of the atmosphere Changes in the earth surface (plate tectonics, ocean size) Variations in Earth's orbit |
|
|
Sunspot activity
|
Every 11 years, emits more energy, surrounded by faculae
|
|
|
Maunder Minimum
|
time period with no sunspots, corresponds to the Little Ice Age
|
|
|
Addition of greenhouse gases
|
CO2 has a 100 year residence time, absorb infrared radiation, rapidly increasing in China and India
|
|
|
Ice cores
|
Provide climate data for up to 600,000 years in the past
|
|
|
Dendrochronology
|
Study of tree rings, provide climate data for up to 1000 years
|
|
|
Milankovitch theory
|
Three separate phenomena relating to Earth's orbit lead to climate change
Eccentricity, precession, obliquity |
|
|
Eccentricity
|
Changes in the earth's orbit from circular to elliptical - accounts for ice ages
|
|
|
Precession
|
Wobble of the earth's axis
|
|
|
Obliquity
|
Changes in the tilt of the earth's axis
|
|
|
Ozone in the stratosphere
|
Protects from UV rays which can cause damage to unprotected skin
Destroyed by chlorine released by CFCs (high residence time) |
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Precipitation that combines with pollutants (sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides) that turn the precipitation acidic
|
|
|
Positive feedback system of acid rain
|
Energy into melting snow instead of warming land, ice sheet melting = warmer water = more melting
|
|
|
Albedo
|
Amount of reflection
|
|
|
Kyoto Protocol
|
A global agreement aiming to slow climate change
|
|
|
The most serious impact of climate change to humans is
|
the spread of malaria
|
|
|
Adaptations to wildfires
|
Oak and redwood trees have bark that can resist fire, some pine trees have seeds that only open after a fire
|
|
|
3 elements required by wild fire
|
Fuel, oxygen, heat
|
|
|
Pre-ignition phase
|
Vegetation reaches a temperature at which it can ignite, pyrolysis (degradation of large hydrocarbon molecules)
|
|
|
Combustion phase
|
Not all ignitions will result in a wildfire, but phase begins with ignition
|
|
|
Flaming combustion
|
Rapid, high temperature conversion of fuel into heat - flames and large amounts of unburned material
|
|
|
Smoldering combustion
|
Areas with burned material and ash that covers new fuel
|
|
|
Conduction heat transfer
|
Molecule to molecule contact
|
|
|
Radiation heat transfer
|
Form of invisible waves
|
|
|
Convection heat transfer
|
Movement of a liquid or a gas
|
|
|
Transfer of heat in wildfires
|
Mainly radiation and convection
|
|
|
Extinction phase
|
Combustion has ceased, no longer sufficient heat or fuel to sustain the fire
|
|
|
Topography & fuel
|
South-facing slopes are relatively warm and dry, slopes exposed to prevailing winds are often drier
Wildfires burning on steep slopes preheat fuel upslope from the flames, results in the spreading of a fire upslope |
|
|
Surface fire
|
Travel close to the ground and burn shrubs, leaves, twigs, grass - move relatively slowly
|
|
|
Crown fires
|
Move rapidly through the forest canopy, can be fed by surface fires or spread independently - driven by strong winds
|
|
|
Regions at risk in Canada
|
British Columbia and in the boreal forests of the Canadian shield
Changes annually to those experiencing drought |
|
|
Hydrophobic layer wildfire effect
|
Caused by the accumulation of chemicals from burning vegetation, may increase surface runoff and erosion
|
|
|
Climate change + wildfire
|
Temperature + precipitation, grasslands replace forests, insect infestation can make a forest more vulnerable
|
|
|
Mountain Pine Beetle
|
80% of mature mountain pines are impacted, consequences felt for decades in british columbia - able to survive through the winter in B.C
|
|
|
Natural service functions of fires
|
Reduces competition for sunlight/moisture
Release of seeds/flowering Clear meadows for grazing Remove surface litter to allow moisture into soil |
|
|
Pioneer vegetation
|
First plant species to grow after a fire
|
|
|
Yellowstone National Park Wildfire
|
Series of lightning strikes caused 50 fires in the park, became uncontrollable because of many years of fire-suppression policies that allowed fuel to build up
|
|
|
Fire regime
|
Potential for wildfire in an area
|
|
|
Fire break
|
An area with no fuel, such as a river, lake, road
|
|
|
Prescribed burns
|
Controlled fires that are purposely ignited to reduce the amount of fuel in an area
|
|
|
Bolides
|
Extraterrestrial bodies that originate in outer space
|
|
|
Asteroid
|
Rocky metallic material in space 10m to 1000km in diameter originating in the asteroid belt
|
|
|
Meteroid
|
Smaller objects in space up to 10m in diameter
|
|
|
Meteor
|
A meteoroid that has entered Earth's atmosphere
|
|
|
Meteorite
|
A meteor that strikes Earth's surface
|
|
|
Comet
|
Distinguishable by a glowing tail of gas and dust
|
|
|
Haley's Comet
|
Passes close to Earth every 75 years
|
|
|
Tunguska Airburst
|
Explosion destroyed over 2000 square km of forest, no crater
|
|
|
Chelyabinsk Airburst
|
Largest bolide to enter Earth's atmosphere since the Tunguska airburst
|
|
|
ejecta blanket
|
Layer of debris that were blown out of the crater on impact
|
|
|
Breccia
|
fragmented rock falling back into the crater shortly after impact, making the craters not as deep as the original impact crater
|
|
|
Barringer Crater
|
Arizona, 50,000 years old
|
|
|
Simple crater
|
less than a few km in diameter, do not have an uplifted center
|
|
|
Complex crater
|
consists of a rim that collapses under extreme faulting and a centre floor that rises following impact - greater than 6km
|
|
|
Manicouagan crater
|
Complex impact crater is 100km in diameter, located in central Quebec, 214 million years ago
|
|
|
Why are craters much more common on the moon than Earth?
|
Most impacts over oceans
Impacts with land have been eroded or burried Smaller bolides often burn up and disintegrate in the atmosphere |
|
|
K-T Boundary mass extinction
|
65 million years ago, abrupt cooling caused by an asteroid impact. Mass extinction of the dinosaurs
Chicxulub Crater in Mexico |
|
|
Managing the bolide impact hazard
|
Blowing up an approaching bolide not advisable - instead, nuclear explosions to shift orbit
|
|
|
Old craters are hard to identify because
|
they have been extensively eroded
|

