![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
99 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Captopril |
Ace-inhibitor that has shortest half-life, must be given 3-4 times a day |
|
|
Captopril |
Has been shown to minimize or prevent left ventricular dilatation and dysfunction. (Ventricular remodeling) that can arise after an MI |
|
|
Alpha1 blockers |
Have ability to dilate arteries and veins which reduces peripheral vascular resistance and decreases blood pressure |
|
|
Labetalol and carvedilol |
These two medications have dual alpha and beta antihypertensive effects, they reduce heart rate (beta) and cause vasodilation (alpha) |
|
|
Clonidine |
Alpha2-adrenergic receptor stimulator (agonist) |
|
|
Clonidine |
Primarily used for ability to decrease BP, useful in opioid withdrawal management, but has side effects such as orthostatic hypotension, fatigue, dizziness so it is not commonly used. |
|
|
Doxazosin, prazosin, tamsulosin, terazosin |
Alpha1 blockers |
|
|
Doxazosin (cardua, cardura XL) |
Commonly used alpha1 blocker, reduces PVR and BP by dilating blood vessels, matrix capsule expelled in stool-causes confusion for pts who then take more |
|
|
Carvedilol (coreg) |
Treats hypertension, indicated also for mild to moderate heart failure in conjunction with digoxin, diuretics and ACE inhibitors, contraindicated for those with severe bradycardia, bronchospastic asthma, or heart problems related to conducting system |
|
|
Nebivolol |
Newest beta blocker, bet1 selective beta blocker treating hypertension, also used for heart failure, produces vasodilatation which decreases SVR, causes less sexual dysfunction. |
|
|
ACE-inhibitor |
First line of defense for heart failure and hypertension |
|
|
Captopril |
This ACE-inhibitor requires multiple doses, may not be a good choice for pt with compliance issues |
|
|
Captopril and lisinopril |
Good for pts with liver failure because they are not inactive prodrugs that need to be metabolized in liver, they work automatically |
|
|
Enalapril |
Only ace-inhibitor that is available in parental preparation. |
|
|
ACE-inhibitor |
Class c drug in first semester, class D in second and third, do not use unless no other options available |
|
|
ACE-inhibitor |
Beneficial for heart failure pts because they prevent water resorption by inhibiting aldosterone secretion. |
|
|
Cardioprotective effect |
ACE-inhibitors decrease SVR and preload, thus stopping progression of left ventricular hypertrophy which is seen in MI. This is called a- |
|
|
ACE-inhibitors |
Protect kidneys because they also reduce glomerular filtration pressure - are cardiovascular drug of choice for diabetic pts because inhibits diabetic nephropathy |
|
|
ACE-inhibitor |
This anti-hypertensive is contraindicated if pt's potassium level is 5 or greater because it increases risk of hyperkalemia |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
Promote k absorption, and sodium secretion |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
May cause angioedema |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
May cause dry cough |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
May cause loss of taste |
|
|
NSAIDs |
Should not be used with an ACE inhibitor concurrently because it can cause renal failure and reduce effects of the ACE inhibitor |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |

May cause kidney failure for pt who relies on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system |
|
|
Angiotensin II receptor blocker |
Affect primarily smooth muscle and adrenal gland |
|
|
Enalaprilat (vasotec) |
Parental form of this ACE inhibitor offers hemodynamic benefit of inhibiting ACE activity in acutely ill patients, does not require cardiac monitoring |
|
|
-an |
ARBs |
|
|
ARBs |
Work to decrease SVR without cough |
|
|
Cough and hyperkalemia |
These symptoms are less likely when pt takes an ARB versus an ACE inhibitor |
|
|
Oral enalapril (vasotec) |
Must have functioning liver to be converted from a produg to active drug |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker |
Primary use to treat angina, hypertension |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker |
Treats hypertension by causing smooth muscle relaxation by preventing contraction |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker |
A first line of defense because safe and effective |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker |
Effective antidysrhythmics |
|
|
Nimodipine (CCB) |
Specificly prevents cerebral artery spasms after subarachnoid hemorrhage |
|
|
Diuretics |
Antihypertensive drug that decreases plasma and extracellular fluid |
|
|
Vasodilators |
Act by directly causing vasodilation and venous smooth muscle, do not affect adrenergic receptors |
|
|
Diuretic |
Hydrochlorothiazide |
|
|
Vasodilator |
Hydralazine (Apresoline) |
|
|
Vasodilator |
Minoxidil |
|
|
Vasodilator |
Diazoxide (hyperstat) |
|
|
Vasodilator |
Nitroprusside (nitropress) |
|
|
Vasodilator |
Directly cause peripheral vasodilation |
|
|
Diazoxide, hydralazine, minoxidil |
Cause arteriolar vasodilation |
|
|
Nitroprusside |
Causes both arteriolar and venous effect |
|
|
Sodium nitropusside and IV diazoxide |
Reserved for management of hypetensive emergencies-BP severely elevated |
|
|
Non-selective beta blocker |
Has both cardiovascular and respiratory effects which is bronchoconstriction must monitor pts respiratory system |
|
|
Beta1-blocking |
Only cardiac system is effected so monitor BP and HR |
|
|
Beta1-blocker |
If pt needs a bet a-blocker but has respiratory issues she or he will need this type of beta-blocker |
|
|
Centrally acting alpha blocker |
Assess WBC, serum k, sodium levels, protein in urine levels |
|
|
Alpha-adrenergic agonist |
Close assessment of BP, HR, weight before and during treatment because of strong vasodilating properties, and subsequent hypotensive adverse effects |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
Assess BP, HR and respiratory because of adverse effect of hacking cough |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
-il, -ec, -en, -ik |
|
|
Angioedema |
Potenti ally fatal effect of ACE inhibitor, inflammation of submucosal tissue |
|
|
Captopril |
Can cause granulocytosis, neutropenia |
|
|
Vasodilator |
Assess for baseline neurological function, attention to LOC and cognitive ability |
|
|
Vasodilator |
Extreme caution for older patients, may experience more sensitivity and experience hypotension, dizziness and syncope |
|
|
Hydralazine |
Adverse effects include dizziness, anxiety, tachycardia, headache, nausea, edema, hepatitis, systemic lupus erythematosus |
|
|
Sodium nitroprusside |
Used in ICU for severe hypertensive emergencies, titrated by IV infusion, contraindicated if there is known inadequate cerebral perfusion |
|
|
Sodium nitropusside |
Onset 2 min peak 2-5 elimination 2 min, 1-10 min |
|
|
Epleronone (inspra) |
Selective aldosterone blocker |
|
|
Epleronone (inspra) |
Monitor K level, contraindicated if it is greater than 5.5, or there is renal impairment |
|
|
Thiazide-type diuretics and calcium channel blocker |
First-line therapy |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker |
Asian population benefit from |
|
|
ACEIs and ARBs |
Recommended for hispanic american because of increased cardiac morbidity |
|
|
Adrenergic drug |
Adverse effects include bradycardia with reflec tachycardia, postural and postexercise hypotension, dry mouth, dizzy, edema, constipation and sexual dysfunction |
|
|
Adrenergic antihypertensive |
Monitor cbc, k, sodium and creatinine |
|
|
Carvedilol |
Contraindicated if pt has asthma because it is not cardioselective beta blocker |
|
|
Clonidine, methyldopa |
Not first line defense because of rough side effects such as orthostatic hypotension, fatigue and dizziness |
|
|
Alpha2 Adrenergic receptor stimulator |
Reduces production of norepinephrine to reduce hypertension |
|
|
Alpha-adrenergic agonist |
Pt must be taught to take BP and HR at home to ensure they're within perimeters to reduce risk of orthostatic hypotension |
|
|
Alpha-adrenergic antagonist |
Associated with first dose syncope, keep pt in supine position |
|
|
Sodium nitroprusside |
Always dilute, very potent, can cause severe drops in BP, leading to irreversible ischemic injury |
|
|
Calcium channel blockers |
Are negative inotropic drugs (decrease contractility of heart) |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
Can cause renal impairment, you can identify by a serum creatinine |
|
|
Captopril |

|
|
|
ACE inhibitors |

|
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
|
|
|
Alpha1 blockers |
|
|
|
Beta 2 non-selective blocker |
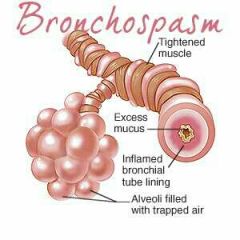
|
|
|
Calcium channel blocker |
Can cause bradycardia |
|
|
Calcium Channel Blocker |
Reduces contractility of heart |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker |
Reduces heart rate |
|
|
ACE inhibitors |
A Pril |
|
|
Beta Blockers |
LOL!!!! |
|
|
Calcium channel blockers |
V ery N ice D rugs |
|
|
Captopril |
Can cause neutropenia |
|
|
Captopril |

Remodel left ventricle, wear a hard CAP |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |

#1 choice for diabetes |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |

promotes healthy kidneys, GFR |
|
|
Sodium nitroprusside |
reduces both total peripheral resistance and venous return, thus decreasing both preload and afterload. So, it can be used in severe congestive heart failure where this combination of effects can act to increase cardiac output |
|
|
Adrenergic drug |
May increase heart rate |
|
|
ARBs and ACEs |
NSAIDs is contraindicated |
|
|
ACE inhibitor |
Teach erectile dysfunction |
|
|
-artan |
ARBs |
|
|
Beta blocker |
Monitor weight gain (CHF) |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker |
Can cause Photosensitivity |
|
|
Calcium channel blocker |
Goto er if you experience chest pain, arrythmia |

