![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Muscle Tissue |
Three types: Smooth or non-striated muscle Cardiac striated muscle Skeletal striated muscle producing body movements stabilizing body positions (joints and standing) storing and moving substances within the body (propel food and matter through body systems) generating heat |
|
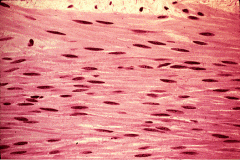
Smooth or non-striated muscle |
Long spindle shaped cells
Nucleus centrally located Thin sheets Arrector Pili muscles (muscles that move hair follicles) Tubuler Organs - Blood vessel walls, in the tube walls of the digestive, urinary, respiratory and reproductive systems) Involuntary (cant regulate consciously) Contracts to move things through tubes |
|
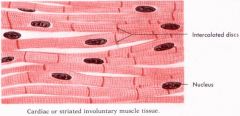
Cardiac striated muscle |
Striated - stripe like appearance Long tubular cells which some branch Dark bands, membrane between two abutting cells. Muscle fibers made up of many cells connected Forms heart wall Involuntary (can't regulate consciously) Pump blood in the heart and through blood vessels |
|
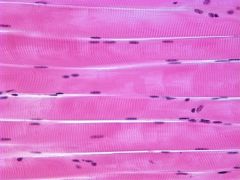
Skeletal striated muscle |
Long bands, very striped, each one is a cell but multiple nucleus on each band which get pushed to the surface. Most common muscle tissue makes up 45% of body Voluntary (consciously controlled) Moves the skeleton Stabilize it (standing, maintain position) Source of body heat (energy lost as thermal energy) |
|
|
Skeletal Muscle Fibers |
Slow-oxidative (SO) type 1 Large amount of capillaries, Red color fibers, Slow speed of contraction, many mitochondria (energy), high resistance to fatigue Fast-Oxidative-Glycolytic (FOG) type IIa Large amount of capillaries, red color fibers, fast speed of contraction, many mitochondria, intermediate resistance to fatigue.
Small amount of capillaries, white color fibers, fast speed of contraction, few mitochondria, low resistance to fatigue |
|
|
Significance |
Difference because of function Back muscles can be slow-oxidative because need to last longer and doesn't need to twitch fast. Eye muscles need to be fast-glycolytic, twitch and move fast. Some muscles are a mixture of fibers. |
|
|
Muscle organ |
Muscle belly - muscular part of the muscle, cells are not red but blood gives the red color. Lots of blood vessels in tissue Tendon - dense regular CT At the end of muscles, connects to bone When tear a tendon, will tear at point of attachment on bone |

