![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
106 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Viewed in the electron microscope a transverse section through a skeletal muscle fiber that shows a mixture of thick and thin filaments must pass through the:
a) Z-line b) A-band c) I-band d) H-band e) M-line |
A-band
|
|
|
Intercalated disks consist in part of:
a) hemidesmosomes b) actin filaments c) tight junctions d) gap junctions |
gap junctions
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle fibers:
a) originate in embryos by fusion of myofibroblasts b) shorten by twisting c) are joined to adjacent fibers by intercalated disks d) have peripheral nuclei e) contract when they are activated by neurotransmitters diffusing through the sarcolemma |
Have peripheral nuclei
|
|
|
The perichondrium is converted to periosteum when:
a) it contacts the epiphyseal plate b) it is damaged, as in fracture c) it contacts the marrow cavity d) it is invaded by myoblasts e) the surrounding oxygen tension increases |
The surrounding oxygen tension increases
|
|
|
A lack of vitamin D would:
a) cause bones to become thicker b) cause bones to store more calcium c) decrease the weight-bearing ability of long bones d) increase the length of bones in the extremities e) have no effect on bone |
Decrease the weight-bearing ability of long bones
|
|
|
Name two multinucleated cells.
|
Osteoclast and skeletal muscle fiber
(not cardiac muscle cells) |
|
|
Is appositional growth associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Yes both
|
|
|
Is interstitial growth associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Just hyalin cartilage
|
|
|
Is vascularization associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Just intramembranous bone
|
|
|
Is lacunae associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Yes both
|
|
|
Is epiphyseal (metaphyseal) plate associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
No neither...???
|
|
|
Is canaliculi associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Just intramembranous bone
|
|
|
Is type I collagen associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Just intramembranous bone
|
|
|
Is basement membrane associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
No Neither
|
|
|
Twisted nuclei are a diagnostic feature of?
|
Contracted smooth muscle
|
|
|
During contraction of skeletal muscle fiber, all of the following occur EXCEPT:
a) the sarcomeres become narrower b) the A-bands become narrower c) the I-bands become narrower d) the H-band disappears e) bridges are formed between thick and thin filaments |
The A-bands DO NOT become narrower
|
|
|
All of the following are present in relation to cardiac muscle fiber EXCEPT:
a) central nuclei b) intercalated disks c) branching fibers d) sarcomeres e) satellite cells |
Satellite cells are NOT present in cardiac muscle fibers
|
|
|
Action potential in skeletal muscle fibers reach deeply situated myofibrils via:
a) Z-disks b) T-tubules c) intercalated disks d) sarcoplasmic reticulum e) M-lines |
T-tubules
|
|
|
Which of the following acts as an ATPase during contraction of a muscle?
a) actin b) heavy meromyosin c) light meromyosin d) tropomyosin e) calcium ions |
Heavy Meromyosin
|
|
|
Endochondral bone formation begins with the formation of:
a) a fibrous connective tissue model b) a membranous model c) a cartilaginous model d) a calcified model e) no model at all, just the presence of osteoblasts |
A cartilagenous model
|
|
|
Isogenous cells are present in:
a) intramembranous bone b) the diaphysis of mature long bones c) fibrocartilage d) the crypts of Lieberkuhn e) the thymus |
fibrocartilage
|
|
|
The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores:
a) oxygen b) glycogen c) ATP d) calcium ions e) glucose |
Calcium ions
|
|
|
Is galactosamine associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Both
|
|
|
Is reticular cells associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Intramembranous bone
|
|
|
Is gap junctions associated with hyalin cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Neither
|
|
|
Regeneration of skeletal muscle is accomplished by:
a) differentiation of satellite cells b) division of muscle fibers c) hypertrophy of myofibrils d) increase in size of the endomysium e) insertion of additional intercalated disks |
differentiation of satellite cells
|
|
|
Heavy meromyosin is located only in
a) I band b) A band c) Z disk d) intercalated disk e) H band |
b) A band
|
|
|
Twisted nuclei can be readily found in?
|
Cells of the muscularis externa...Smooth Muscle Cells
|
|
|
A transverse section through a skeletal muscle fiber that shows Only Thin Filaments must be through the
a) I band b) A band c) H band d) M line e) Z disk |
a) I band
|
|
|
A wave of depolarization, action potential, is conveyed to myofibrils in the interior of cardiac muscle fibers by means of
a) gap junctions b) elements of the sarcoplasmic reticulum c) T-tubules d) Z disks e) mitochondria |
Gap Junctions
|
|
|
Karatinocytes of the stratum spinosum are characterized by the presence of numerous
a) mitochondria b) functional melanosomes c) desmosomes d) hemidesmosomes e) stereocilia |
Desmosomes
|
|
|
In almost all cases skin is designated as thin when it?
|
Includes hair follicles (*thin stratum corneum is not always a positive indicator of thin skin)
|
|
|
Epidermal cells that engage in immunological activities are
a) lymphocytes b) Langerhans cells c) merkel cells d) keratinocytes e) melanocytes |
Langerhans Cells (skin macrophages, act as APCs)
|
|
|
All of the following are present in BOTH thick and thin skin EXCEPT
a) keratin b) melanosomes c) capillaries d) stratum corneum e) desmosomes |
Melanosomes are only found in THIN SKIN (Blazing Saddles character shows palms of hands and says "I'm not black, I'm Dutch. See it's coming off)
|
|
|
Tetany is the result of
a) infection w/Clostridium tetani b) a defect in the pars nervosa c) a lack of calcitonin d) a deficiency of parathyroid hormone e) a deficiency of glucocorticoids |
Calcitonin binds Ca++ to bone so serum Ca++ is increased if there is a lack of calcitonin
|
|
|
When the arrector pili muscles contract
a) goose bumps are formed b) hairs are shed c) sweat is released from sweat glands d) shivering occurs e) the skin changes color |
A) goose bumps are formed
|
|
|
An albino person lacks
a) keratin b) carotene c) melanocytes d) tyrosinase e) MSH |
Tyrosinase
|
|
|
Keratinized stratified cuboidal epithelium is characteristically present in the
a) sebaceous glands b) ducts of eccrine sweat glands c) ducts of tracheal glands d) collecting tubules in the renal medulla e) intrapulmonary bronchi |
Sebaceous Glands
|
|
|
Thyrocalcitonin
a) counteracts the effects of thyroid hormones b) counteracts the effects of parathyroid hormone c) is formed by iodination of colloid d) affects osteoclasts e) maintains the epiphyseal plate in long bones |
Counteracts the effects of parathyroid hormone
|
|
|
Holocrine secretion occurs in
a) vagina b) bronchi c) thyroid d) thin skin e) thick skin |
Thin skin - sebaceous glands
|
|
|
What gland contains numerous lipid droplets?
|
Sebaceous glands
|
|
Where is the location of general permeability pores, but no voltage-gated sodium channels?
|
3
|
|
What shortens during contraction
|
8 (sarcomere)
|
|
What requires extracellular Ca++ to function?
|
1 (for release of synaptic vesicles)
|
|
Where do action potentials open Ca++ channels, but no transmitter release?
|
6 (received AP) & 7 (where Ca++ open)
|
|
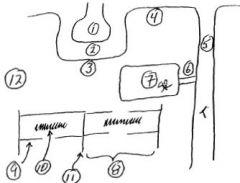
Where is the transverse tubule?
|
5 - junctional feet: AP from T-tubule -> Ca++ release from SR
|
|
|
What is the combination of a neuron and the muscle cells it innervates?
|
Motor Unit
|
|
|
What is a calcium binding protein found in the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum?
|
Calsequesterin
|
|
|
Increasing the number of sarcomeres ______ increases contractile strength
|
In Parallel
|
|
|
Tendons and other noncontractile elements are components of __________
|
Series Elastic Element (origins and intersections of skeletal muscle)
|
|
|
Smooth muscle with gap junctions is called what?
|
Single-unit smooth muscle
|
|
|
All of the following are true of ALL surface epitheia EXCEPT
a) they are avascular b) they rest on basement membranes c) they consist of multiple layers d) They consist of closely packed cells with little intercellular material e) Their cells are held together mainly by desmosomes |
?c?
|
|
|
The perichondrium is converted to periosteum when
|
The surrounding oxygen tension increases
|
|
|
A lack of vitamin D would?
|
Decrease the weight-bearing ability of long bones
|
|
|
Intercalated disks consist in part of?
|
Gap Junctions
|
|
|
T/F Osteoclasts us lysozomes to carry out bone resorption
|
Fals
|
|
|
Endochondral bone formation begins with the formation of what kind of model?
|
A cartilaginous model
|
|
|
Blood is distributed from the surface of a bone to deeper central Haversian canals by means of?
|
canaliculi
|
|
|
How would increasing the proportion of organic molecules to inorganic components in the bony matrix affect the physical characteristics of bone?
|
The bones would be more brittle
|
|
|
Where are isogenus cells present?
|
Fibrocartilage
|
|
|
Is canaliculi associated with hyaline cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Neither
|
|
|
Is galactosamine associated with hyaline cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Both
|
|
|
Is lacunae associated with hyaline cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Both
|
|
|
Is reticular cells associated with hyaline cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
intramembranous bone
|
|
|
Is epiphyseal plate associated with hyaline cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Neither
|
|
|
Is Gap junctions associated with hyaline cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
intramembranous bone? Neither
|
|
|
Is collagen that lacks axial periodicity associated with hyaline cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Hyaline Cartilage
|
|
|
Is troponin associated with hyaline cartilage or intramembranous bone?
|
Neither
|
|
|
Which of the following cels do NOT depend on bone marrow for production of that cell type?
a) osteoblasts b) osteoclasts c) erythrocytes d) lymphocytes e) platlets |
A. Osteoblasts
|
|
|
Peak body bone mass occurs around age
a) 13 b) 18 c) 25 d) 40 e) 50 |
C. 25
(18 length, 25 mass) |
|
|
The gemini study linked ________ to demineralization of bone.
|
Low activity (exercise)
|
|
|
Bone remodeling
a) occurs throughout life b) is the balance between bone synthesis and resorption c) is greatest in cancellous bone d) is greater in children than in adults e) all of the above |
e) all of the above
|
|
|
A plasma concentration of 4 mM would likely result in?
|
Calcium Phosphate Precipitation
|
|
|
Most dietary Ca++ ends up in?
|
Poop
|
|
|
Most of the phosphate in our body is found in?
|
Bone
|
|
|
Collagen is present in bone to provide?
|
Tensile Strength
|
|
|
Which of the following hormones promotes bone growth by inhibiting resorption?
a) growth hormone b) thyroid hormone c) cortisol d) estrogen e) insulin |
D. Estrogen inhibits resorption
b) thyroid hormone (increased resorption) c) cortisol (increased resorption) |
|
|
What is a local signal in producing bone loss with periodontal disease?
|
Prostaglandin E
|
|
|
The covalent crosslinks between collagen fibrils are formed by the enzyme?
|
Lysyl Oxidase
|
|
|
Which of the following would NOT cause spastic paralysis?
a) Carbachol b) Curare c) Physostigmine d) Nerve gas e) Methacholine |
b) curare because is binds to ACh receptors but doesn't stimulate paralysis
|
|
|
What would increasing the load prior to an isotonic twitch do to delay, distance moved and velocity of shortening?
|
Increases Delay
Decreases Distance Moved Decreases Velocity of Shortening |
|
|
Which of the following would you NOT expect to be characteristic in antigravity muscles?
a) many mitochondria b) myoglobin c) high glycogen d) slow myosin ATPase e) all of the above would be expected |
c) High glycogen is found in Fast Twitch
|
|
|
Muscle fatigue and rigor mortis share what characteristic?
|
Low ATP levels
|
|
|
Summation of muscle twitch tension is possible even though muscle action potentials cannot summate because?
|
Calcium remains elevated longer than the duration of the muscle action potential
|
|
|
Which is NOT a difference between skeletal and smooth muscle?
a) Breadth of length-tension relationship b) Maximal tension that can be developed c) Presence of troponin d) Inhibition of contraction by norepinephrine e) presence of slow waves |
b) maximal tension that can be developed
|
|
|
Activation of myosin light chain kinase is Inhibited by what?
|
Inhibited by calcium unbinding from calmodulin
(or does it activate when troponin binds to calcium) |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a component of thin filaments?
a) G-actin b) Tropomyosin c) Troponin C d) ADP e) All of the above are found in filaments |
e. all of the above
|
|
|
Transmission at the neuromuscular junction is primarily terminated by?
|
Catabolism, by ACh-Esterase
|
|
|
Crossbridging occurs within the
a) Z disk b) I band c) H zone d) A band e) M line |
d) A band
|
|
|
In skeletal muscle, calcium binds to
a) tropomyosin b) myosin phosphorylase c) calmodulin d) troponin C e) troponin I |
d) Troponin C
|
|
|
In comparison to adults, Ca++ turnover in children's bones is more/less?
|
More
|
|
|
Increased activity during childhood would tend to
a) increase bone length b) increase bone thickness c) increase bone calcium d) all of the above e) A and B but not C |
All of the above
|
|
|
Osteoblasts decrease the chance of exceeding solubility product inside the cell by
a) forming phosphate esters b) pumping Ca++ into the osteoid c) activating alkaline phosphatase d) all of the above e) A&B but Not C |
A&B but NOT C
|
|
|
What is an important protein found in both osteoblasts and osteoclasts?
|
Carbonic Anhydrase
|
|
|
Which of the following would not be found in thin filaments?
a) F-Actin b) Tropomyosin c) Troponin C d) Light chain myosin e) ADP |
Light chain myosin is found in THICK filaments
|
|
|
ATP is used to
a) Break existing crossbridges b) Cock the myosin head c) Act as a binding site on thin filaments d) all of the above e) A&B but NOT C |
A&B but NOT C
|
|
|
What is the most likely result if calsequestrin is destroyed in a muscle cell?
|
Increased Muscle Tone
|
|
|
Twitch tension exists after active contraction because of the presence of?
|
The Series Elastic Element
|
|
|
Smooth muscle contraction is regulated by?
|
Phosphorylation of myosin by myosin light chain kinase
|
|
|
What can stimulate smooth muscle contraction?
|
ACh
NE Stretch Depolarization of Slow Wave Potentials |
|
|
Which muscle type is maintained below the peak of the length tension curve?
|
Cardiac
|
|
|
What causes Slow Wave Polarization in the GI tract?
|
Norepinephrine
|
|
|
What can trigger peristalsis?
|
Local distension
Vagal innervation Local irritation Activation of myenteric reflex |
|
|
What bone disease is caused by defective Osteoid formation NOT defective mineralization?
|
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
|
|
|
What bone disease exhibits signs of premature sexual development and hyperpigmentation of the skin?
|
Polystotic Fibrous Dysplasia
|
|
|
What bone disease is charactarized by short arms and legs, normal torso size and depressed nasal bones?
|
Achondroplasia
|

