![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What determines the distance a muscle can shorten?
|
The number of sarcomeres in series
|
|
|
What determines the strength/power that muscle can generate?
|
The number of sarcomeres in parallel
|
|
|
What is the term for the longer delay in onset and time to peak response because it must first take up slack before shortening occurs?
|
Series Elastic Element
(rubber band example, once the tension exceends the mass, the mass moves) |
|
|
What happens to the time delay when you place a heavier load?
|
The delays are greater with a heavier load
|
|
|
What happens if the load is increased to greater than the muscle can develop tension?
|
No distance will be moved and you have an isometric contraction
|
|
|
What muscle fibers are used for antigravity, prolonged use, and slow fatigue?
|
Slow twitch
|
|
|
T/F
Fast twitch fibers have a lot of mitochondria |
False
|
|
|
T/F
Fast twitch fibers have a lot of Glycogen |
True
|
|
|
T/F
Fast twitch fibers have a lot of myoglobin |
False
White muscle has little myoglobin |
|
|
What determines the maximum velocity of the contraction of a muscle fiber?
|
Myosin cross-bridging determines velocity
|
|
|
What is the rate of myosin cross-bridging in intermediate fibers?
|
Fast
(which also means the maximum velocity is fast as well) |
|
|
What is the mitichondria content of intermediate and slow twitch fibers?
|
A lot of Mitochondria
|
|
|
How is it that Fast twitch fibers are large, while slow twitch fibers are small?
|
It has to do with surface area. Slow twitch fibers need large surface area so they are slim muscle fibers. The increased surface area to volume ratio allows oxidative phosphorylation to occur.
|
|
|
What is the glycogen content of slow twitch fibers?
|
Low glycogen content
|
|
|
What is the myoglobin content of intermediate and slow muscle fibers?
|
High - thus the red hue
|
|
|
What is the ATP source to power muscle contraction for Fast twitch fibers?
|
Glycolysis (makes ATP fast & is anaerobic)
|
|
|
What is the ATP source to power muscle contraction for intermediate twitch muscle fibers?
|
Oxidative phosphorylation
|
|
|
What is the ATP source to power muscle contraction for Slow twitch muscle fibers?
|
Oxidative Phosphorylation
|
|
|
What determines the duration of a contraction for a single twitch?
|
Duration is linked to rate of return of Ca++ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
|
|
|
What muscle has the longest duration of contraction for a single twitch?
a) occular b) gastrocnemius c) soleus |
Soleus has the longest duration
occular is for rapid eye movement gastrocnemius is for running/jumping soleus is for antigravity support |
|
|
T/F
The less discrete you need to be, the longer an individual twitch will tend to be. |
True
so, discrete motion like quick movement of the eye has a very short duration |
|
|
What stage of muscle contraction is the action potential complete?
|
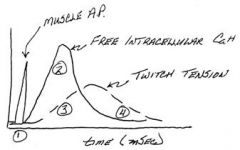
The muscle action potential is complete before tension begins to increase
|
|
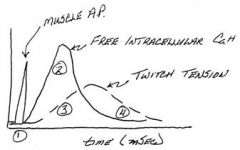
At what point does active cross-bridging occur in a muscle twitch?
|
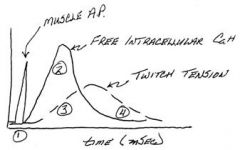
Active cross-bridging occurs while intracellular Ca++ is elevated
|
|
|
What happens to twitch tension with regard to Ca++?
|
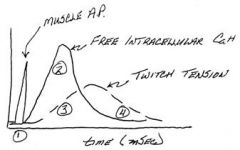
Twitch tension lags behind Ca++ elevation as the series elastic element is tightened
(so the muscle cell is still providing tension on the load even though calcium is no longer elevated) |
|
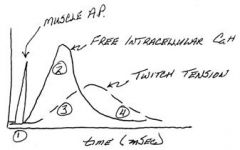
What happens to the series elastic element as the Ca++ falls?
|
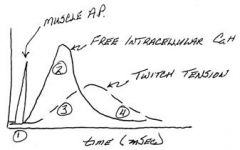
The series elastic element maintains tension even as Ca++ falls (like pulling on a rubber band to lift a weight)
|
|
|
What is the optimum length of a single sarcomere for maximal cross-bridging?
|
Lo = 2 micrometers
|
|
|
T/F
Depending on the extent a muscle is stretched prior to contraction determines how strongly it can contract. |
True
|
|
|
What state of contraction are our muscles at during rest?
|
near Lo=2microns
maximum cross-bridging |
|
|
How can we increase the strength of contraction?
|
1) Summation of contractions
2) Recruitment of motor units |
|

How does the muscle AP relate to the Ca++ levels?
|

The muscle AP is brief compared to the duration of the Ca++ and the constant pulses keep the Ca++ levels high.
|
|
|
How does the recruitment of motor units increase contractile strength?
|
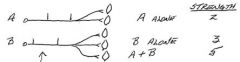
Start firing additional alpha motor neurons to activate the muscle fibers they innervate
|
|
|
What makes muscle contraction smooth during recruitment of motor units?
|
Asynchronous activation
(without this, muscle contraction would be a ratcheting motion) |
|
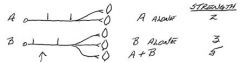
What composes a motor unit?
|
one axon and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
|
|
|
T/F
There is a single motor unit in a single muscle. |
False
There are many motor units in a single muscle |
|
|
T/F
A single axon can innervate multiple motor cells |
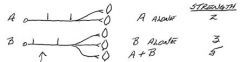
True
|
|
|
T/F
A single muscle cell is innervated by only one alpha motor neuron |
True
|
|
|
Is there summation in individual skeletal muscle fibers?
|
No because we only have one axon innervating them
|
|
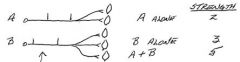
Which muscles have the largest motor units?
|
Antigravity muscles
|
|
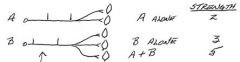
What muscles have the smallest motor units?
|
Eye muscles
|

