![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a circumscribed lesion of < 5mm diameter characterized by FLATNESS & usually distinguished from surrounding skin by its COLORATION?
|

Macule
|
|
|
What is a circumscribed lesion of > 5mm diameter characterized by FLATNESS & usually distinguished from surrounding skin by its COLORATION?
|
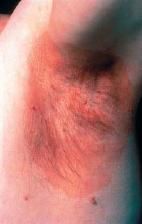
Patch
|
|
|
What is an elevated dome-shaped or flat-topped lesion < 5mm in diameter?
|
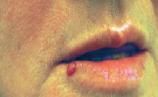
Papule
|
|
|
What is an elevated lesion with spherical contour > 5mm in diameter?
|
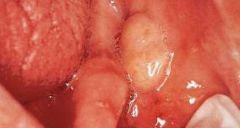
Nodule
|
|
|
What is an elevated flat-topped lesion, usually > 5mm in diameter
|
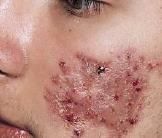
Plaque
|
|
|
What is a Fluid-filled raised lesion < 5mm in diameter?
|
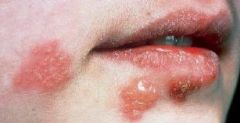
Vesicle
|
|
|
What is a Fluid-filled raised lesion > 5mm in diameter?
|
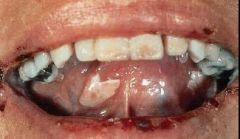
Bulla
|
|
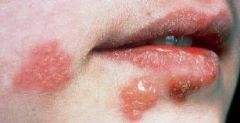
What is a common term used for either a vesicle or bulla?
|
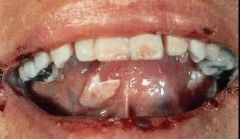
Blister
|
|
|
What is a discrete, puss-filled, raised lesion?
|
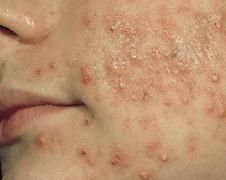
Pustule
|
|
|
What is an itchy, transient, elevated lesion with variable blanching and erythema formed as the result of dermal edema
|
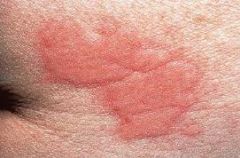
Wheal
|
|
|
What is a drym horny, platelike excresence, usually the result of imperfect cornification?
|
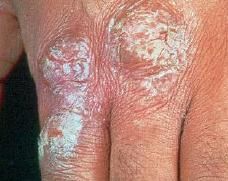
Scale
|
|
|
What is a thickened and rough skin characteried by prominent skin markings; can be the result of repeated rubbing?
|
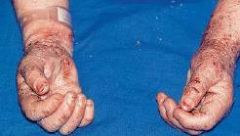
Lichenification
|
|
|
What is a traumatic lesion characterized by breakage of the epidermis causing a raw linear area; often self-induced?
|
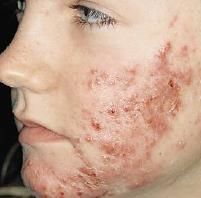
Excoriation
|
|
|
What is a separation of the nail plate from the nail bed?
|
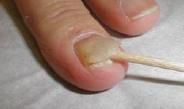
Onycholysis
|
|
|
What is the theckening of the stratum corneum, often associated with a qualitative abnormality of the keratin?
|
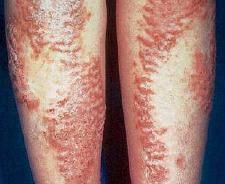
Hyperkeratosis
|
|
|
What is a diffuse epidermal hyperplasia?
|
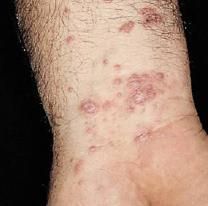
Acanthosis
|
|
|
What is a surface elecation caused by hyperplasia and enlargemnet of contiguous dermal papillae?
|
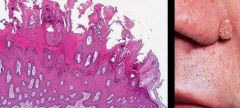
Papillomatosis
|
|
|
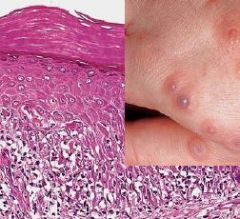
What is an abnormal keratinization occurring prematurely within individual cells or groups of cells below the stratum granulosum?
|
Dyskeratosis
|
|
|
What is a loss of intercellular connections resulting in loss of cohesion between keratiocytes?
|
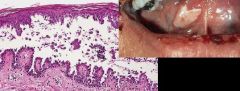
Acantholysis
|
|
|
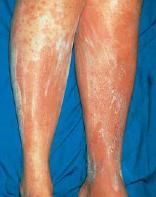
What is intercellular edema of the epidermis?
|
Spongiosis
|
|
|
What is infiltration of the epidermis by inflammatory or circulating blood cells?
|
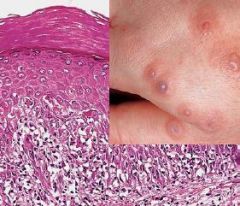
Exocytosis
|
|
|
What is discontinuity of the skin exhibiting INcomplete loss of the epidermis?
|
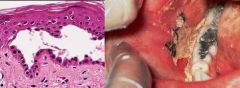
Erosion
|
|
|
What is discontinuity of the skin exhibiting Complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and even subcutaneous fat?
|
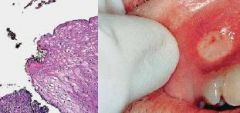
Ulceration
|
|
|
What is a linear pattern of melanocyte proliferation within the epidermal basal cell layer?
|

Lentiginous
|
|
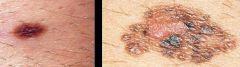
What are the ABC's that differentiate Nevocellular nevus from melanomas in pigmented lesions?
|
Assymetry
Border Irregularity Color Variability Diameter > 6mm Enlargement- increase in size |
|
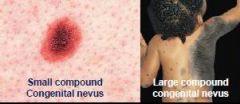
T/F
Congenital nevi carry decreased risk for development into melanoma. |
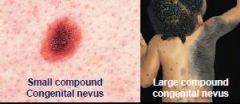
False
Increased Risk |
|
|
What condition presents clinically as:
Waxy, tan to dark brown plaque Arise spontaneously and may be solitary or multiple May be difficult to distinguish from melanoma clinically May occur explosively in large numbers, as part of paraneoplastic syndome (LESER-TRELAT sugn) |
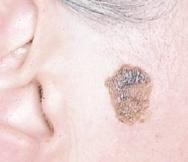
Seborrheic Keratosis
(benign epithelial tumor) |
|
|
What condition presents clinically as:
Flesh colored, dome shaped nodule with a central erosion Predilation for dacial skin, including the cheeks nose and ears and the dosa of the hands RAPID GROWTH RATE and spontaneous remission differentiate keratocanthoma from squamous cell carcinoma |
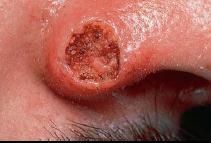
Keratocanthoma
|
|
What are two types of malignant epithelial tumors?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma & Basal cell carcinoma
|
|
|
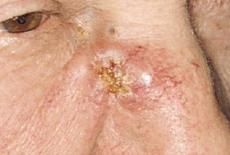
What presents clinically as:
A malignant neoplasm of keratinocytes 2nd most common skin cancer Rarely metastisize Nodule or plaque +/- ulceration Risk factors: sun exposure, skin type, immunosuppression, HPV infection, chronic inflammation, industrial carcinogens |
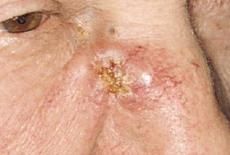
Squamous cell carcinoma
|
|
|
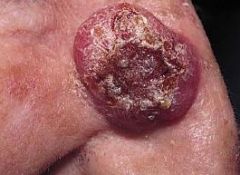
What condition presents clinically as:
A malignant neoplasm of basal keratinocytes Most common type of skin cancer Pearly papule or nodulecontaining prominant dilated subepidermal blood vessels +/- ulceration Risk factors: sun exposure, skin type, immunosuppression Locally invasive, slow-growing tumors that rarely metasticize |
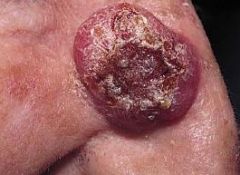
Basal cell carcinoma
|
|
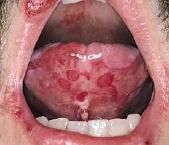
What condition is characterized by urticaria & erythema multiforme?
|
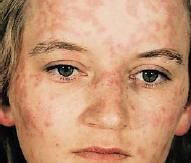
Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses
|
|
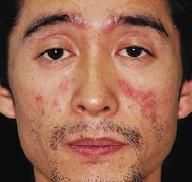
What condition is characterized by psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, lichen planus?
|
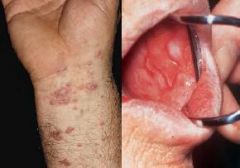
Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses
|
|
|
What has lesions that last from days to weeks.
Inflammation & edema +/- epidermal, vascular or subcutaneous injury. Diagnosis requires combination of clinical and pathologic findings? |
Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses
|
|
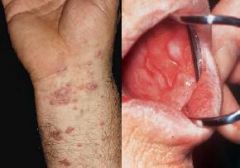
What condition persists for months to years
In addition to inflammation these lesions often show significant components of altered epidermal growth (atrophy or hyperplasia) +/- dermal fibrosis Diagnosis requires combination of clinical and pathologic findings? |
Chronic inflammatory dermatoses
|
|
|
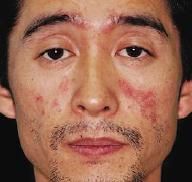
What consists of transient, slightly erythematous pruritic papules and edematous plaques (wheals)
|
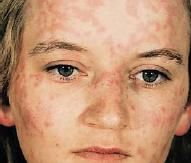
Urticaria
|
|
|
What is a blistering disorder of adults characterized by superficial vesicles and bullae that are easily ruptured. Autoimmune, detected by direct immunofluorescence. Antibodies form against a component of desmosomes (desmoglein 3)?
|
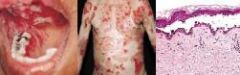
Pemphigus vulgaris
|
|
|
What is a distinct vesicobullous disease affecting elderly individuals characterized by formation of tense bullae?
|
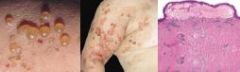
Bullous Pemphigoid
|
|
|
What is a chronic inflammatory dermatosis that has macules and papules on an erythematous, often greasy base +/- scaling and crusting?
|
Chronic dermatoses
(dandruff) |
|
|
What is a common, chronic, T-cell mediated inflammatory deramatosis?
|
Chronic Dermatoses
|
|
|
What condition is a self-limiting, chronic inflammatory dermatosis of unknown etiology?
|
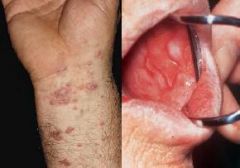
Lichen Planus
|
|
|
What presents as white dots or lines associated with chronic dermatoses?
|
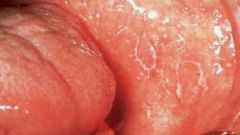
Wickham Striae
|
|
|
What is an uncommon self-limited disorder that appears to be a hypersensitivity reaction to certain infections and drugs?
|
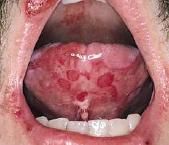
Erythema multiforme
|
|
|
***What is the most common fatal malignancy among young adults?
|
Melanoma: a malignant neoplasm of melanocytes that, in the skin, begins as a macule and may become a patch or a papule.
|
|
|
***What disease may occur explosively in large numbers, as part of a paraneoplastic syndrome (Leser-Trélat sign)?
|
Seborrheic Keratoses - this could indicate a neoplasm in the GI tract
|
|
|
***What differentiates Keratocanthoma from Squamous cell carcinoma?
|
Rapid Growth Rate
|
|
|
***What is the 2nd most common skin cancer and is primarily attributed to the sun?
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
***What is the Most common type of skin cancer and is primarily attributed to the sun?
|
Basal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
***What are the 4Ps of Lichen Planus?
|
Pruritic (itchy)
Purple Polygonal Papules |

