![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
in a sprain, what kind of tissue is affected?
|
Ligamentous
|
|
|
in a strain, what kind of tissue is affected?
|
muscle
|
|
|
strain or sprain:
Result of sudden trauma that tears ligament and joint capsule |
Sprain
|
|
|
strain or sprain:
Occurs as a result of a sudden stretch on a muscle that is actively contracting. |
strain
|
|
|
maybe want to look at mech of injury slide... don't think it will be that important but who knows
16 |
yaya
|
|
|
When the foot plantar flexes, it loses its snug mortise, talucrural fit. It becomes susceptible to inversion, collapse...what kind of sprain is this?
|
inversion
|
|
|
most common ligament sprained?
**** |
anterior talo-fibular ligamet
|
|
|
foot plantar flexes, and damges the ATFL what is the next likely ankle ligament to be injured?
*** |
calcaneofibular ligament
|
|
|
“I heard a pop”- a snap commonly occurs at time of acute event
Difficulty with weight bearing or applying stress to involved area Pain Edema Ecchymosis may often occur 24-48 hours after injury this describes what? |
sprain
|
|
|
Snap or tearing sensation may also occur
Pain or swelling may not be noted on the day of injury with mild injury what would you see this in? |
strain
|
|
|
with a sprain or strain, what should you do in your palpation first? what would this show?
|
Palpate area for site of maximal tenderness
palpate the bone first (followed by soft tissue) tenderness of bone can show fracture |
|
|
Strain vs rupture
|
rupture is a complete separation of the muscle and its insertion
|
|
|
Plastic deformation of the tissue without tearing
what degree strain? **** |
0
|
|
|
Partial tear but no instability or opening of joint on stress maneuvers
what degree strain? **** |
I
|
|
|
Partial tear with some instability indicated by partial opening of joint on stress maneuvers
what degree strain? **** |
II
|
|
|
Complete tear with complete opening joint on stress
what degree strain? **** |
III
|
|
|
when is the anterior drawer test positive for the ankle?
|
positive in 2nd and 3rd degree sprain
|
|
|
you perform a talar tilt test and it is positive, what does this mean?
|

3rd degree tear in the ankle
|
|
|
according to the Ottawa Criteria, when do you need to take an ankle series of x-ray?
|
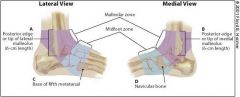
pain in the malleolar zone and any of these findings:
bone tenderness at A bone tenderness at B inability to bear weight immediately and in the emergency department (or physician's office). |
|
|
according to the Ottawa criteria, when do you get a foot series of x-rays?
*** |
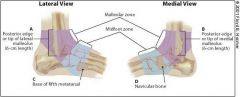
if a patient has pain in the midfoot zone and any of these findings:
bone tenderness at C bone tenderness at D inability to bear weight immediately and in the emergency department (or physician's office). |
|
|
what is a high ankle sprain?
|
disruption of syndesmosis; should be 5mm or less
|
|
|
patient continues to have swelling and pain in the area of the ankle after weeks of it occurring. What is a possible cause?
|
Osteochondritis Dessicans- chip fracture of talus, may be undiagnosed, but prevents normal healing of ankle.
|
|
|
patient has a complete rupture of a muscle. What should you do?
|
send to an orthopedic surgeon
|
|
|
patient has a grade III sprain what should you do?
|
send to orthopedic surgeon
|
|
|
should severe grade II sprains see an orthopedic surgeon?
|
probably
|
|
|
Treatment of inversion ankle sprain?
|
PRICEM
Protect with crutches/splinting as necessary Relative rest- active range of motion exercises as soon as pain permits Ice helps reduce inflammation. Compression- ACE wrap or U-shaped Compression pad Elevation- of extremity above heart. Manipulation/Manipulation |
|
|
you have a patient with a grade I sprain, do you brace? grade II?
|
Grade I: you can, but don't have to
Grade II: you absolutely have to |
|
|
if a patient has a grade II or I sprain, what is the most appropriate OMT treatment?
|
indirect myofacial release
|
|
|
what is stage 1 for acute rehab for inversion ankle sprains?
|
RICE
|
|
|
what is stage 2 for acute rehab for inversion ankle sprains?
|
Subacute (Pain-free range of motion)
Initiate non-weight bearing exercises Proprioceptive training (Biomechanical Ankle Platform system Board, Wobble-Board-seated) |
|
|
what is stage 3 for acute rehab for inversion ankle sprains?
|
Restorative
Single-leg balance Heel raises/toe raises Pronation and supination exercises |
|
|
what is stage 4 for acute rehab for inversion ankle sprains?
|
Activity and function
Initiate agility drills Frontal plane reactive drill Heel and toe walking Return to sport training |

