![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
epiphysis
|
the expanded articular end of a long bone, from 2nd ossification center
|

|
|
|
physis
|
segment of tubular bone concered with longitudinal growth
|
|
|
|
metaphysis
|
the widened part of extremity of shaft, adjacent to epiphysis
|
|
|
|
diaphysis
|
between epiphysis
(shaft) formed from 1 ossification center |
|
|
|
apophysis
|
normal developmental outgrowth of bone, from separate ossification center, fuses later in development, nb insertion for tendon or lig
|
|
|
|
dysplasia
|
abnormality of development
|
|
|
|
dystrophy
|
disorder of defective nutrition
|
|
|
|
exostosis
|
benign bony growth projecting outwards from surface of bone
|
|
|
|
osteolysis
|
destruction of bone caused by disease or infection/ inadequate blood supply. Dissolution of bone and abn dec in bone density
|
|
|
|
antalgic
|
counteracting/avoiding pain en antalgic gait lessens pain
|
|
|
|
arthralgia
|
pain in joint
|
|
|
|
causalgia
|
constant burning pain, injury to peripheral nerve, pt of complex regional pain syndrome
|
|
|
|
metatarsalgia
|
pain&tenderness in metatarsal region. in planter aspect of foot & localised over metatarsal heads
|
|
|
|
myalgia
|
pain in muscle/groups
|
|
|
|
neuralgia
|
pain along course of nerve
|
|
|
|
involucrum
|
layer of new bone growth outside existing bone seen in OM
contains sequestum of necrosed bone |
|
|
|
sequestrum
|
necrotic bone which has become walled off from its blood supply, nidus for chronic osteomyelitis
|
|
|
|
arthritis
|
disease causing painful infl and stiffness in joint
|
|
|
|
gon-arthritis
|
inflammation of KNEE joint
|
|
|
|
arthrodesis
|
surgical fixation of joint, fusion by promoting proliferation of bone cells
|
|
|
|
arthroplasty
|
surgical refashioning of joint
|
|
|
|
arthrotomy
|
surgical incision of joint, remove infected substances
|
|
|
|
osteochrondritis
|
infl of BONE and CARTILAGE
|
|
|
|
osteolysis
|
destruction of bone caused by dx or infection or inadequate blood supply, bone dissolves and density decreases
|
|
|
|
osteophyte
|
osseous outgrowth in response to micro instability of joint
|
|
|
|
osteoporosis
|
systemic, low bone mass and mirco architectural deterioration
|
|
|
|
plasmacytoma
|
localised myeloma
|
|
|
|
osteopenia
|
decr. in bone mass
insufficient compensation for N bone lysis |
|
|
|
osteomalacia
|
delayed mineralisation of osteoid in mature cortical and spongy bone
adult rickets |
|
|
|
oteoblasts
|
builds bone (type of fibroblast)
|
|
|
|
osteoclast
|
Chew bone
active when around PTH increase bone resorption and release bone salts |
|
|
|
osteotomy
|
surgical cutting of bone
allows realignment |
|
|
|
osteoarthritis
|
non infl degenerative joint dx in older people
degeneration of articular cartilage, hypertrophy of bone at margins and changes in synovial membrane |
|
|
|
osteophyte
|
osseous outgrowth in response to micro instability of joint (stabilising response)
|
|
|
|
osteosclerosis (*)
|
hardening
abnormal increase in bone density |
|
|
|
subluxation
|
incomplete or partial dislocation (loss of congruity) of a joint (between articular surfaces)
cartilage still in contact |
|
|
|
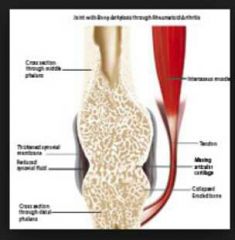
ankylosis
|
immobility and consolidation of joint
dt dx, injury or surgical procedures |
|
|
|
osteitis
|
inflammation of bone, involving haversian spaces, canals and their branches and medullary cavity
|
|
|
|
osteomyelitis
|
inflammation of bone caused by infection
usually pyogenic organism spread to involve marrow, cortex, cancellous tissue and periosteum |
|
|
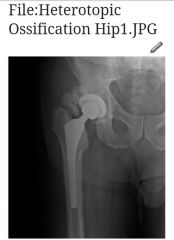
heterotropic ossification
|
process by which bone tissue forms outside skeleton
|
|
|
|
dislocation
|
total loss of congruity between articular surfaces
|
|
|
|
varus
|
inward angulation of distal segment of bone or joint
VARUS= AIRus, AIR inbetween spaces eg. bowlegged |
|
|
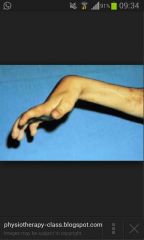
volkmann contractures
|
permanent flexion contracture of thehand at the wrist, resulting in a claw-like deformity of the hand and fingers
associated with supracondylar # |
|
|
|
neuropraxia
|
temporary paralysis of nerve caused by lack of blood flow or P with no loss of structural continuity
|
|
|
|
axonotmesis
|
neural tube intact, axons distrupted, nerves likely to recover
|
|
|
|
neurotmesis
|
neural tube severed, injuries permanent without repair
|
|
|
|
arthrogryposis
|
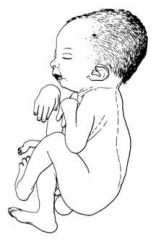
non progressive congenital dx involving multiple rigid joints (usually sym.) leading to severe limitation in motion
absence of skin creases |
|

