![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Contractability |
Ability of muscle to contract |
|
|
|
Excitablility |
Ability of muscle to react to electrical stimuli |
|
|
|
Extensibility |
Muscle can be stretched beyond normal length and can still contract |
|
|
|
Elasticity |
Muscle can spring back to original length after it has been stretched. |
|
|
|
Perimesyum |
Connective tissue that surrounds the fascicles. |
|
|
|
Epimysium |
Surrounds entire muscle. |
|
|
|
Motor neurons |
Cells responsible for stimulating skeletal muscle contraction |
|
|
|
Myoblasts |
Muscle fibers develop from less mature cells called ___________. |
|
|
|
Sarcoplasmic Recticulum |
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum of muscles |
|
|
|
Sarcoplasmic Recticulum |
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum of muscles |
|
|
|
Sarcolemma |
Action potentials occur here, plasma membrane of muscle fiber. |
|
|
|
Z disk |
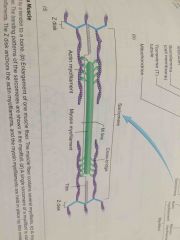
Forms stationary anchor for attachment of actin myofilaments |
|
|
|
I bands |
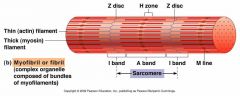
Light staining bands, includes a Z disk, extends to the ends of the myosin myofilaments |
AKA isotropic bands |
|
|
M line |
Helps hold myosin myofilaments in place |
|
|
|
Actin myofilaments |
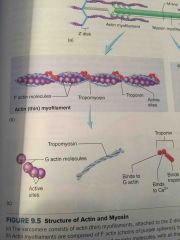
Composed of 2 strands of F actin, tropomyosin, & troponin. Each G actin monomer has an active site, where myosin binds. |
|
|
|
What happens when a sacromere contracts? |
A bands, myosin and actin stay the same. H zone, I band & sacromere shorten.
|
|
|
|
What happens when a muscle relaxes? |
Actin & myosin overlap, and the H zone is visible. Sacromere is at it's normal resting length. |
|
|
|
What are the functions of the muscular system? |
Body movement, posture, respiration, communication, contraction of heart, production of body heat, construction of organs &a blood vessels. |
|
|
|
What is the sliding filament model? |
When a muscle contracts, actin & myosin myofilaments slide past each other, but remain the same length. |
|
|
|
What is resting membrane potential? |
Concentration of K+ inside the plasma membrane is higher than outside. The concentration of Na+ is higher outside than inside. & the plasma membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+ |
|
|
|
Isometric contractions |
Muscle length does not change |
|
|
|
Isometric contractions |
Muscle length does not change |
|
|
|
Isotonic contractions |
Force is generated, muscle lengthens |
|
|
|
Concentric isotonic contractions |
Muscle shortens |
|
|
|
Eccentric isotonic contractions |
Muscle lengthens |
|
|
|
What is a motor unit? How does it affect muscle control? |
A motor unit is a single motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates. Having many small motor units allows for a great deal of control. |
|

