![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
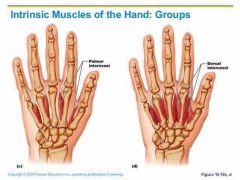
Intrinsic muscles |
Contained within a region and have both origin and insertion there |
|
Extrinsic muscles |
Act upon a designated region but origin elsewhere |
|
|
Intrinsic and extrinsic describes muscles of |
Hand, foot, tongue, larynx, back |
|
|
Cranial nerve |
Arise from the brain Exit the skull foramina Numbered from 1 to 12 Innervate head and neck muscles |
|
|
Spinal nerves |
Arises from the spinal cord Exit through the intervertebral foramina Named with letters and numbers (represents vertebrae) |
|
|
International system of Latin names |
Nomina Anatomica (1895) Terminologica Anatomica (1998) |
|
|
Size |
Gluteus maximus |
|
|
Shape |
Deltoid |
|
|
Location |
External intercostals |
|
|
Number of heads |
Triceps brachii |
|
|
Orientation |
External oblique |
|
|
Action |
Extensor digitorum |
|
|
Muscles of facual expression |
Small muscles that insert the dermis Found in scalp, forehead, eye, nose, mouth and neck |
|
|
Zygomaticus |
Curls the corner of the mouth when smiling |
|
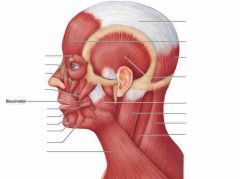
Buccinator |
Keeps food on top of the mouth, and is used for blowing and sucking |
|
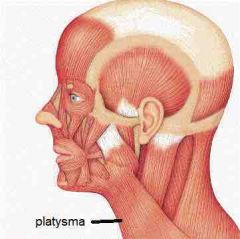
Platysma |
Open and widen mouth, and for pouting |
|
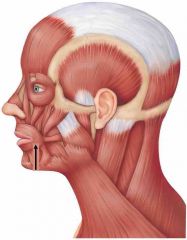
Orbicularis oris |
Encircles mouth and closes it |
|
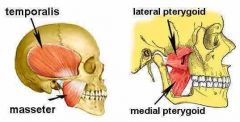
Muscles of Mastication |
Temporalis Masseter Lateral and medial pterygoid |
|
|
Temporalis & Masseter |
Elevate mandible |
|
|
Medial & Lateral pterygoid |
Help elevate the mandible, but produce lateral swinging of jaw (used to grind molars) |
|
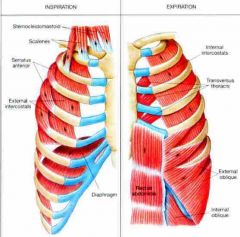
Muscles of respiration |
Diaphragm External and internal intercostal muscles |
|
|
Contraction (Diaphragm & External intercostals) |
Produces inspiration |
|
|
Contraction (internal intercostals) |
Produces forced expiration |
|
|
Normal expiration |
Little muscle activity Elastic recoil of tissues and gravity to collapse the chest |
|
|
Diaphragm |
Muscular dome (cover) between the thoracic and abdominal cavities |
|
|
Muscle fascicles extend to |
Fibrous central tendon |
|
|
Contraction (diaphragm) |
Flattens the diaphragm Increases the vertical dimension of thorax drawing air into the lungs Raises the abdominal pressure to help expel urine, feces, and facilitating childbirth |
|
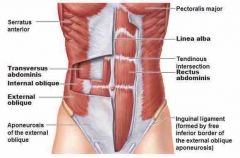
Muscles of the abdomen |
External & Internal oblique Transverse & Rectus abdominis |
|
|
Functions
|
Support the viscera Stabilize the vertebral column Help in respiration, urination, defecation, and childbirth |
|
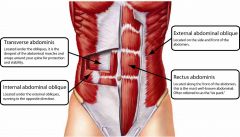
Transverse Abdominis
|
Horizontal fascicle orientation deepest layer
|
|
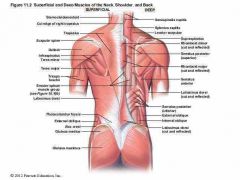
Superficial Muscles of the Back
|
Trapezius Latissimus Dorsi Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Gluteus Medius Gluteus Maximus |
|
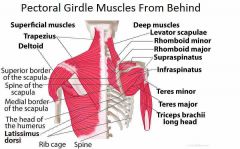
Muscles Acting on Pectoral Girdle
|
Originate on axial skeleton and insert onto clavicle or scapula |
|
|
Anterior Muscle Group
|
2 muscles
|
|
|
Posterior Muscle Group
|
4 muscles
|
|
|
Scapular movements include
|
-medial and lateral rotation -elevation and depression -protraction and retraction |
|
|
Clavicle
|
braces the shoulder and releases movement
|
|
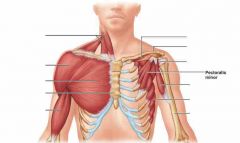
Pectoralis Minor
|
ribs 3-5 to coracoid process of scapula protracts and depresses scapulaa lifts ribs during forceful inspiration
|
|
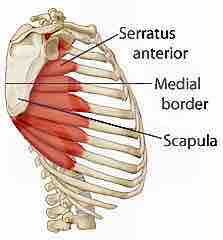
Serratus Anterior
|
ribs 1-9 to medial border of scapula abducts and rotates or depresses scapula the "throwing" muscles
|
|
|
Four muscles
|
Contains superficial and deep muscles
|
|
|
Superficial muscle
|
Trapezius
|
|
|
Deep muscles
|
rhomboideus major and minor and levator scapulae
|
|
|
Trapezius |
Rotate scapula upward Retract scapula With levator scapulae and rhomboideus elevates scapula With serratus anterior depresses scapula |
|
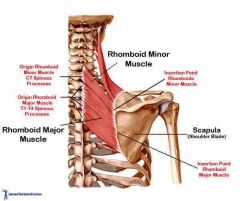
Rhomboideus |
Medical border of scapula to C7-T1(minor) and T2-T5 (major) |
|
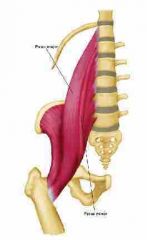
Levator scapulae |
From superior angle of scapula to C1-C4 |
|
Muscles acting on the Humerus
|
9 muscles cross the shoulder joint to the humerus |
|
|
2 axial muscles arise from the axial skeleton
|
pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi: prime movers of humerus in flexion and extension arise from sternum and clavicle for T7-L5 and ilium
|
|
|
7 scapular muscles arise from scapula
|
Deltoid (prime mover) Flexion, extension and abduction of humerus |
|
|
Coracobrachialis
|
assists in flexion
|
|
|
Teres major
|
assist in extension
|
|
|
Remaining 4 muscles
|
form rotator cuff in order to reinforce shoulder joint caapsule
|
|
|
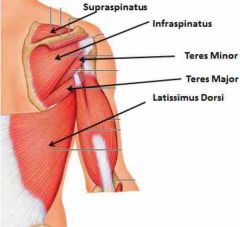
Rotator Cuff Muscles
|
Supraspinatusm-> Infraspinatus-> Posterior Teres Major-> Subscapularis -> Anterior |
|
|
Muscles of Posterior Forearm |
Extension of wrist/fingers = adduct/abduct wrist Extension and abduction of thumb (pollicis) |
|
|
Anterior Muscles of Hip
|
Iliopsoas muscle
|
|
|
Illiopsoas muscle
|
Crosses anterior surface of hip joint and inserts on femur Psoas portion (Psoas major) arises from lumbar vertebrae Major hip flexor |
|
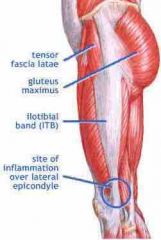
Ilioptibial band
|
band of fascia attached to the tibia
|
|
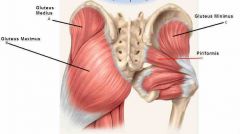
Deep Gluteal muscles |
Lateral rotation of the femur except the gluteus minimus which rotates femur medially Important in walking to shift body weight when foot is lifted |
|
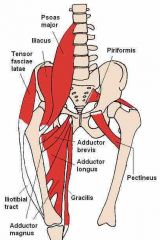
Gracilis |
Flexor of the knee |
|
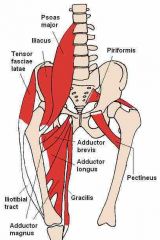
Adductor Magnus |
Extensor of hip joint |
|
|
Gracilis |
Flexor of the knee |
|
|
Pectineus, adductor brevis, and adductor longus |
Adduct the femur |
|
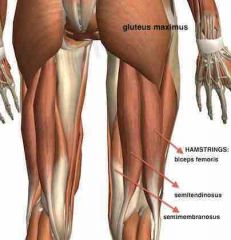
Hamstrings |
Group of muscles posterior to the femur Flexes the knee and extend the hip - Biceps Femoris - Semitendinosus - Semimenbranosus
|
|
|
Quadratus Femoris |
Adductor of hip |
|
|
Sartorius |
Crosses over the quadriceps and is the longest muscle in the body Flexes the hip and knee in laterally rotates the thigh |
|
|
Hamstrings |
Group of muscles posterior to the femur Flexes the knee and extend the hip - Biceps Femoris - Semitendinosus - Semimenbranosus
|
|
|
Muscles of the lower leg |
Contains three compartment: interior compartment m, posterior compartment, lateral compartment |
|
|
Anterior compartment of the leg |
Extensor digitorum longus Tibialis anterior |
|
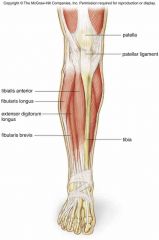
Extensor digitorum longus |
Extension of toes and ankle |
|
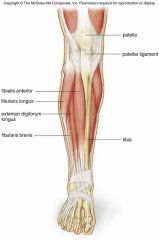
Tibialis Anterior |
Dorsiflexes and inverts foot |
|
|
Posterior compartment of the leg (Deep Group) |
Tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum, flexor hallucis longus and plantar flexors |
|
|
Posterior compartment of the the leg |
(Superficial Group) Gastrocnemius Soleus |
|
|
Lateral compartment of the leg |
Fibularis longus and brevis Both plantar flex in evert the foot Provide lift and forward thrust |

