![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
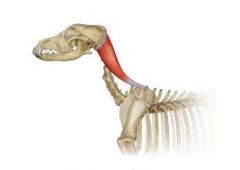
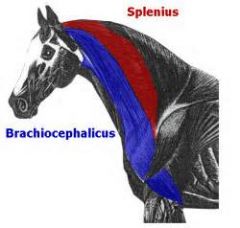
Splenius Extend (raise) the neck. Origin - T1/T2. Insertion – Occiput. |
|
|
|
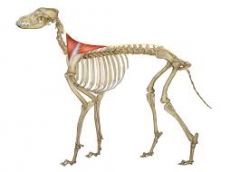
Trapezius Extend (raise) the neck. Origin - band from C3 to T9. Insertion – spine of scapula |
|
|
|
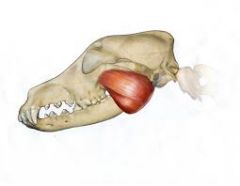
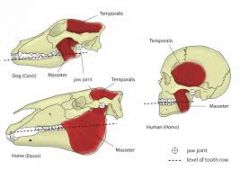
Masseter Closes the jaw, used when chewing. Origin - zygomatic arch on maxilla Insertion - ramus on mandible. |
|
|
|
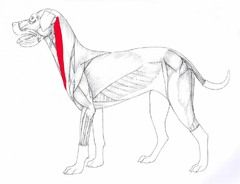
Sternocephalicus Flexes (lowers) the neck. Origin – Manubrium Insertion – mastoid part of occipital bone. |
|
|
|
Brachiocephalicus Pulls forelimb forward. Origin – distal humerus, cranial aspect. Insertion – dorsal surface of neck. Deeper than sternocephalicus. |
|
|
|
Temporalis Closes mandible. Origin - parietal, temporal, occipital bones. Insertion - Medial condyle of mandible |
|
|
|
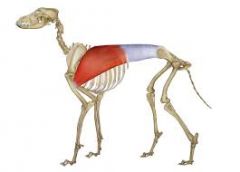
Latissimus dorsi Broad, triangular muscle that flexes shoulder. Origin – lumbar spine. Insertion – greater tubercule of humerus |
|
|
|
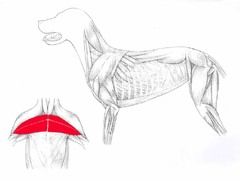
Pectoral Stops forelimbs abducting away, assists to draw forelimb forward or backward. Origin – cranial end of sternum. Insertion – greater tubercule of humerus. |
|
|
|
Deltoid Flexion and abduction of shoulder joint. Origin – scapular spine. Insertion – deltoid tuberosity of humerus |
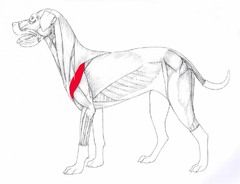
|
|
|
Biceps brachii Flexes the elbow joint. Origin – Proximal part of the caudal surface of the humerus. Insertion – proximal radius. |
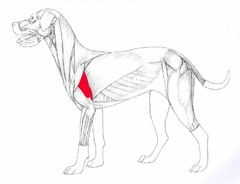
|
|
|
Triceps brachii Extends the elbow joint. Origin – distal scapula and proximal humerus. Insertion – olecranon process of ulna. |
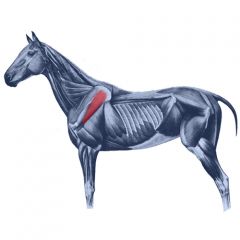
|
|
|
External abdominal oblique Internal abdominal oblique Rectus abdominus Transverse abdominus |
Order of muscles of the abdomen, from superficial to deep |
|
|
External Abdominal Oblique Origin – T4 to T12. Insertion – pubic symphsis to xyphoid process. Abdominal obliques – run in aslanting direction (internal andexternal obliques run in opposite direction) |
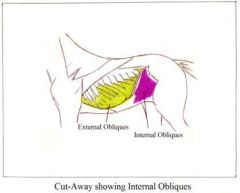
|
|
|
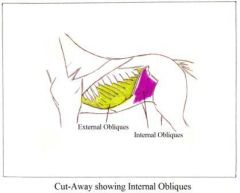
Internal Abdominal Oblique Origin – tuber coxae Insertion – T12 – T13 Abdominal obliques – run in a slanting direction (internal and external obliques run inopposite direction)
|
|
|
|
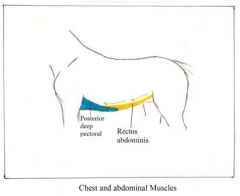
Rectus abdominus Compression of abdominal organs. Involved inurination, defecation, parturition. Lateral movement. Flexion of vertebral column Origin – sternum to costal cartilage. Insertion – pectinous tendon and pre-pubic tendon |
|
|
|
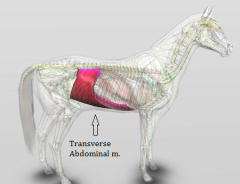
Transverse abdominus Origin – T8 cartilage, L7 transverse process, and tuber coxae. Insertion – inner rectus abdominus. |
|

