![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the main muscles of mastication?
|
masseter
temporalis medial and lateral pterygoid |
|
|
What are the accessory muscles of mastication?
|
digastric
mylohyoid |
|
|
What are the points of origin and insertion of masseter?
|
origin: zygomatic arch
insertion: ramus of mandible |
|
|
Masseter is supplied by which nerve?
|
masseteric nerve of mandibular division of V3
|
|
|
When is masseter most active?
|
during clinching and during forceful phase of a chewing cycle
|
|
|
What is the function of masseter?
|
elevator of mandible
|
|
|
What are the points of origin and insertion of temporalis?
|
origin: temporal fossa
insertion: coronoid process of the mandible |
|
|
Temporalis muscle is innervated by which nerve?
|
temporal branches of anterior trunk of V3
|
|
|
What motions does temporalis allow?
|
elevation of the mandible
retrusion of the mandible |
|
|
What are the points of origin and insertion for upper head of lateral pterygoid?
|
origin: infratemporal surface of the greater wing of sphenoid
insertion: articular disc and capsule of the TMJ |
|
|
What are the points of origin and insertion for lower head of lateral pterygoid?
|
origin: lateral surface of the lateral pterygoid plate
insertion: pterygoid fovea on the neck of the condyle of the mandible |
|
|
Describe the function of lateral pterygoid and state when it is most active
|
it is a protruder and depressor (partly). It is most active during the power phase of a chewing cycle.
|
|
|
When is lateral pterygoid most active?
|
during power phase of chewing cycle
|
|
|
What are the points of origin and insertion for deep head of medial pterygoid?
|
origin: medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate
insertion: medial surface of ramus and angle of the mandible |
|
|
What are the points of origin and insertion for superficial head of medial pterygoid?
|
origin: lateral surface of the pyramidal process of the palatine bone and maxillary tuberosity
insertion: medial surface of ramus and angle of the mandible |
|
|
Medial pterygoid muscle is innervated by which nerve?
|
by a branch from the mandibular nerve V3
|
|
|
What is the main function of the medial pterygoid and when is it most active?
|
Elevator and protruder. Most active during clenching of the teeth
|
|
|
List the major muscles of mastication and briefly discuss the role played by the temporalis muscle in moving the mandible during mastication (6 marks)
|
Masseter
Temporalis Medial and lateral pterygoid it is an elevator of the mandible and retrudor of the mandible Has three sections: posterior (horizontal), oblique middle and anterior (vertical). During closure the posterior activates, followed by the oblique middle and anterior. |
|
|
What are the points of insertion and origin for digastric muscle?
|
Origin: mastoid process digastric notch
Insertion: digastric fossa of the mandible |
|
|
What are the actions provided by digastric muscle?
|
elevates hyoid
depresses and retracts the mandible |
|
|
Myolohyoid can be refred to as the ___ ____
|
oral diaphragm
|
|
|
what nerve innervates myolohyoid?
|
mandibular division of V
|
|
|
what are the actions of mylohyoid?
|
raises the floor of the oral cavity
elevates the hyoid bone |
|
|
What are the groups of muscles of facial expression?
|
Muscles of lips and cheeks
muscles of the nose muscles of the eyelid muscles of the auricle of the ear muscles of the scalp platysma muscle |
|
|
Muscles of the lips and cheeks are divided into two groups. What are they?
|
deep and superficial
|
|
|
What are the muscles of superficial layer of the lips and cheeks?
|
levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
levator labii superioris levator angulari oris depressor labii inferioris depressor angulari oris zygomaticus major/minor risorius mentalis |
|
|
What are the deep layer muscles of the lips and cheeks?
|
buccinator
orbicularis oris |
|
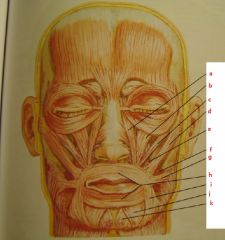
|
a. levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
b. levator labii superioris c. zygomaticus minor d. zygomaticus major e. levator anguli oris f. buccinator g. risorius h. orbicularis oris i. depressor anguli oris j. depressor labii inferioris k. mentalis |
|
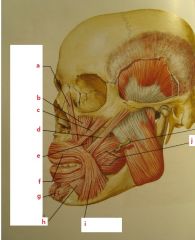
|
a. levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
b. levator labii superioris c. zygomaticus minor d. zygomaticus major e. levator anguli oris f. orbicularis oris g. mentalis h. depressor labii inferioris i. depressor anguli oris |
|
|
What is modiolus?
|
Convergence of superficial muscles to insert on a vertical musculotendinous raphe close to the corner of the mouth.
|
|
|
What are the points of attachments of buccinator muscle?
|
Origin: pterygomandibular raphe, alveolar margins of the maxilla and mandible
Insertion: obicularis oris and modiolus |
|
|
What is the name of structure which is dense fibrous connective tissue in the eyelid?
|
tarsal plate
|
|
|
Orbicularis oculi consists of two parts. These are?
|
orbital part and palpebral part
|
|
|
The orbicularis oculi muscles attaches to which points?
|
via medial and lateral palpebral ligament to adjacent bones (medial and lateral side of the orbit)
|
|
|
What are the differences in the role of orbital and palpebral fibres of orbiculris oculi?
|
orbital: allows eye to frown
papbepral: allows gentle close of the eye |
|
|
What are the layers of the scalp?
|
S: skin
C: connective tissue A: aponeurosis L: loose connective tissue P: periosteum |
|
|
To which feature does frontalis attach to?
|
procerus muscle
|
|
|
Occipitalis attach to where?
|
superior nuchal line of the occipital bone
|

