![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Occiptofrontalis
|
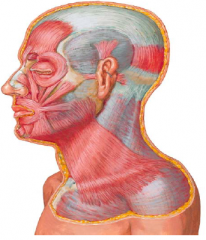
• The occipitofrontalis is a flat digastric
muscle, with occipital and frontal bellies that share a common tendon, the epicranial aponeurosis • The occipital belly attaches to the superior nuchal line • The frontal belly inserts into the skin and subcutaneous tissue of eyebrows and forehaad • Action: Independent contraction of the occipital belly retracts the scalp and contraction of the frontal belly protracts it • Innervation: – Occipital belly: Posterior auricular branch of facial nerve – Frontal belly: Temporal branches of facial nerve |
|
|
Orbicularis Oris
|
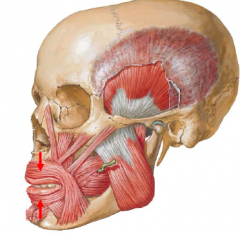
• The orbicularis oris, encircles the mouth within the lips, controlling entry and exit through the oral fissure
• The orbicularis oris is also important during articulation (speech) • Attachments: – Medial maxilla and mandible, and angle of mouth – Inserts within the mucous membrane of the lips • Action: – Tonic: closes mouth – Phasic: compresses and protrudes lips • Innervation: – Buccal and marginal mandibular branches of facial nerve |
|
|
Buccinator
|
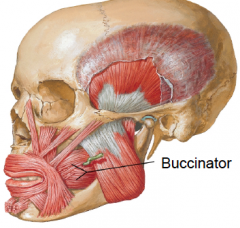
• The buccinator is a thin, flat, rectangular muscle that attaches laterally to the alveolar processes of the maxillae and mandible, opposite the molar teeth, and to the pterygomandibular raphe, a tendinous thickening of the buccopharyngeal fascia. Anteriorly, its fibers blend with the orbicularis oris muscle fibers.
• It occupies a deeper, more medially placed plane than the other facial muscles, passing deep to the mandible so that it is more closely related to the buccal mucosa than the skin of the face. •Innervation: buccal branch of facial nerve • The buccinator, active in smiling, also keeps the cheek taut, thereby preventing it from folding and being injured during chewing. |
|
|
Platysma
|
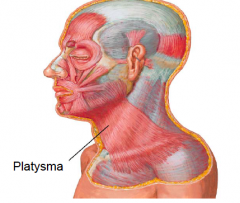
• Attachments:
– Subcutaneous tissue of supra and infraclavicular regions – Base of mandible, skin of cheek, angle of mouth and orbicularis oris • Action – From superior attachment, tenses the skin, producing vertical skin ridges – From inferior attachment, helps depress the mandible and draw the corners of the mouth inferiorly, as in a grimace. • Innervation: – Cervical branch of facial nerve |
|
|
Levator anguli oris
|
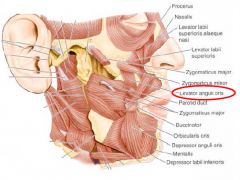
• The levator anguli oris muscle originates from the
canine fossa of the maxilla immediately inferior to the infraorbital foramen. • It inserts into the angle of the mouth, blending with fibers of the orbicularis oris muscle. • Action: Lifts the angles of the mouth. • Innervation: Buccal br. of facial nerve |
|
|
Depressor anguli oris
|
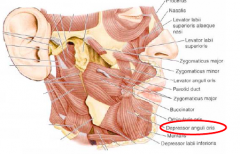
• The depressor anguli oris is a triangular muscle
• It originates from the external oblique line of the mandible. • The ascending fibers converge at the apex to insert into the angle of the mouth from below and blend with the fibers of the orbicularis oris muscle. • Action: Pulls the angles of the mouth downward • Innervation: Marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve |
|
|
Zygomaticus major
|
• The zygomaticus major muscle arises from the lateral aspect of the zygomatic bone.
• Its fibers angle downward and medially to insert into the angle of the mouth and blend with the orbicularis oris muscle. • Action: draws the angle of the mouth upward and backward. • Innervation: Buccal branch of facial nerve (+ some fibers from zygomatic branch) |
|
|
Zygomaticus minor
|
• The zygomaticus major muscle arises from the
anterior aspect of the zygomatic bone. • Its fibers angle downward and medially to insert into the skin of the upper lip • Action: Assists in elevation of the the upper lip • Innervation: Buccal branch of facial nerve |
|
|
Risorius
|
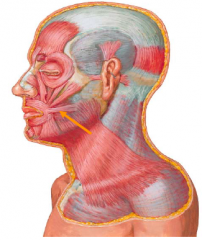
• The risorius muscle is a thin muscle that arises from parotid and masseteric fascia, and buccal skin
• The risorius muscle inserts transversely into the angle of the mouth • Action: Retracts the angle of the mouth posteriorly • Innervation: Mandibular and/or Buccal br. of facial nerve (highly variable) |
|
|
Levator labii superioris
|
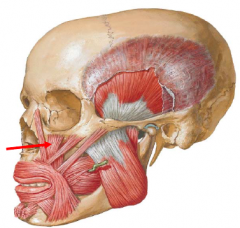
The levator labii superioris muscle arises originates from the inferior orbital margin.
• It inserts into the upper lip • Action: Raise the upper lip. • Innervation: Buccal br. of facial nerve |
|
|
Depressor labii inferioris
|
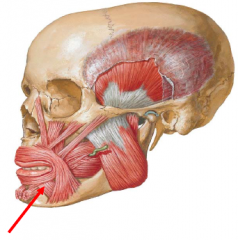
• The depressor labii inferioris muscle arises from the lowest portion of the oblique line of the mandible
• It inserts into the skin of the lower lip • Action: Depresses the lower lip • Innervation: marginal mandibular br. of facial nerve |
|
|
Orbicularis oculi (Eye)
|
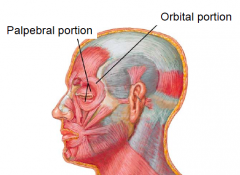
• Originates from medial orbital margin and lacrimal bone
• Inserts into skin around orbit • Two parts with different actions: – Palpebral (blinking) – Orbital (forceful closing) Palpebral portion Orbital portion • Innervation: temporal and zygomatic branches of facial nerve |
|
|
Corrugator Supercilli (Forehead)
|
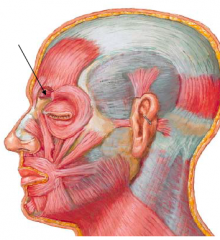
• Attachments
– Medial end of supercilliary arch (ridge superior to the supraorbital margin) – Skin overlying the supercilliary arch and supraorbital margin • Action: Draws eyebrows medially and inferiorly • Innervation: Temporal br. of facial nerve |
|
|
Mentalis (Chin)
|
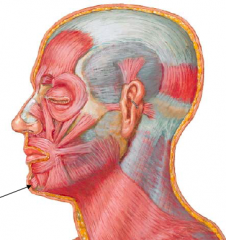
• Attachments:
– Body of mandible anterior to the roots of inferior incisors – Skin of chin • Action: – Elevates and protrudes lower lip • Innervation: – Marginal mandibular br. of facial nerve |
|
|
Nasal muscles: Levvator labi superioris alaeque nasii and alar part of nasalis
|
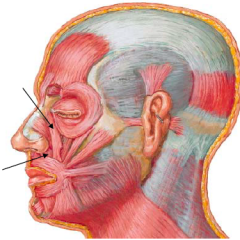
– Attachments:
• Frontal process of maxilla • Alar cartilage – Action • Depresses ala laterally (dilates nasal aperture) – Innervation: Buccal br. of facial nerve |
|
|
Nasal Muslces: Procerus and transverse part
of nasalis |
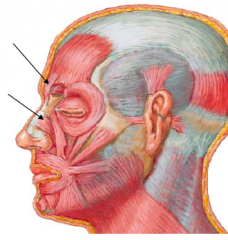
– Attachments:
• Fascia on dorsum of nose and lateral nasal cartilage • Skin of inferior forehead between brows – Action • Depresses medial end of brow, wrinkles skin on dormsum of nose – Innervation: Buccal br. of facial nerve |

