![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Frontal belly (Frontalis) of the Epicranius
|
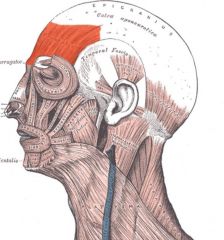
Origin: Galea aponeurotica (cranial aponeurosis)
Insertion: Skin of eyebrows and root of nose |
With aponeurosis fixed, frontal belly raises eyebrows
|
|
|
Occiptal belly (Occipitalis) of the Epicranius
|
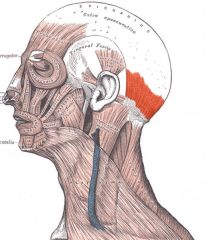
Origin: Occipital and temporal bones
Insertion: Galea aponeurotica |
Fixes aponeurosis and pulls scalp posteriorly
|
|
|
Orbicularis Oculi
|
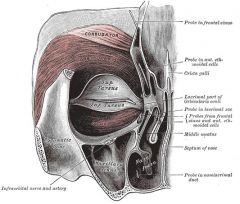
Origin: Frontal and maxillary bones and ligaments around orbit
Insertion: Encircles orbit and inserts in tissue of eyelid |
Various parts can be activated individually; closes eyes, produces blinking, squinting, draws eyebrows inferiorly
|
|
|
Zygomaticus major and minor
|
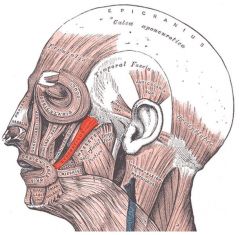
Origin: Zygomatic bone
Insertion: Skin and muscle at corner of mouth |
Raises lateral corners of mouth upward (smiling muscle)
|
|
|
Orbicularis Oris
|
Origin: Arises indirectly from maxilla and mandible; fibers blended with fibers of other muscles associated with lips
Insertion: Encircles mouth; inserts into a muscle and skin at angles of mouth |
Closes mouth; purses and protrudes lips (kissing and whistling muscle)
|
|
|
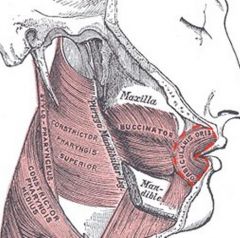
Buccinator
|
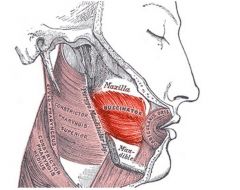
Origin: Molar region of maxilla and mandible
Insertion: Orbicularis oris |
Draws corner of mouth laterally; compresses cheek (as in whistling); holds food between teeth during chewing
|
|
|
Masseter
|
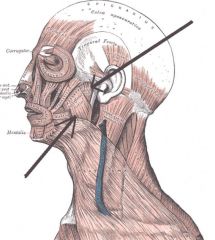
Origin: Zygomatic arch and maxilla
Insertion: Angle and ramus of mandible |
Closes jaw and elevates mandible
|
|
|
Temporalis
|
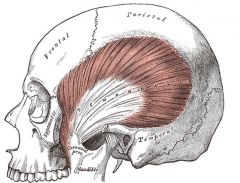
Origin: Temporal fossa
Insertion: Coronoid process of mandible |
Closes jaw; elevates and retracts mandible
|
|
|
Platysma
|
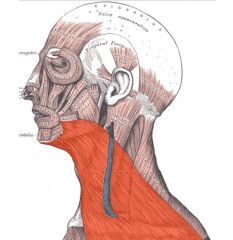
Origin: Fascia of chest (over pectoral muscles) and deltoid
Insertion: Lower margin of mandible, skin, and muscle at corner of mouth |
Depresses mandible; pulls lower lip back and down (ie. Produces downward sag of the mouth
|
|
|
Sternocleidomastoid
|
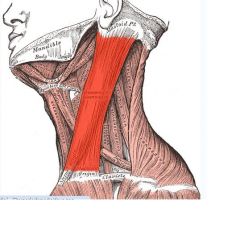
Origin: Manubrium of sternum and medial portion of clavicle
Insertion: Mastoid process of temporal bone and superiar nuchal line of occipital bone |
Simultaneous contraction of both muscles of pair causes flexion of neck forward, generally against resistance (as when lying on the back); acting independently, rotate head toward shoulder on opposite side
|
|
|
Different Pectoralis Major Portions
|
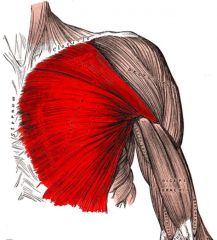
Origin: Clavicle, sternum, cartilage of ribs 1-6 and aponeurosis of external oblique muscle
Insertion: Fibers converge to insert by short tendon into intertubercular sulcus of humerus |
Prime mover of arm flexion; adducts, medially rotates arm; with arm fixed, pulls chest upward (thus also acts in forced inspiration)
|
|
|
Serratus Anterior
|
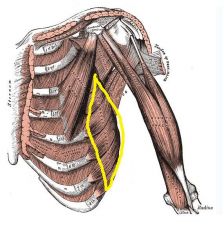
Origin: Lateral aspect of ribs 1-8 (or 9)
Insertion: Vertebral border of anterior surface of scapula |
Moves scapula forward toward chest wall; rotates scapula, causing inferior angle to move laterally and upward; abduction and raising of arm
|
|
|
Deltoid
|
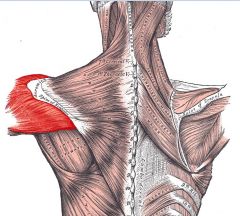
Origin: Lateral 1/3 of clavicle; acromion and spine of scapula
Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus |
Acting as a whole, prime mover of arm abduction; when only specific fibers are active, can aid in flexion, extension, and rotation of humerus
|
|
|
Pectoralis Minor
|
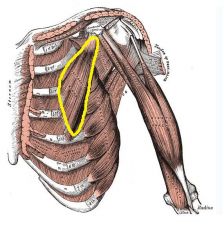
Origin: Anterior surface of ribs 3-5, near their costal cartilage
Insertion: Coracoid process of scapula |
With ribs fixed, draws scapula forward and inferiorly; with scapula fixed, draws rib cage superiorly
|
|
|
External Intercostals
|
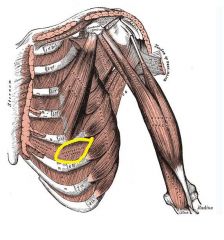
Origin: Inferior border of rib above
Insertion: Superior border of rib below |
Pulls ribs toward one another to elevate rib cage; aids in inspiration
|
|
|
Internal Intercostals
|
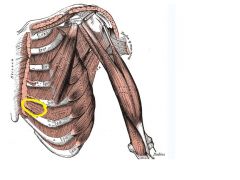
Origin: Superior border of rib below
Insertion: Inferior border of rib above |
Dwars ribs together to depress ib cage; aids in forced expiration; antagonistic to external intercostals
|
|
|
Diaphragm
|
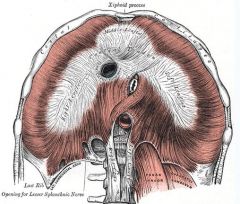
Origin: Inferior border of rib and sternum, costal cartilages of last six ribs and lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: Central tendon |
Prime mover of inspiration flattens on contraction, increasing vertical dimensions of thorax; increases intra-abdominal pressure
|
|
|
Rectus Abdominis
|
Origin: Pubic crest and symphisis
Insertion: Xiphoid process and costal cartilages of ribs 5-7 |
Flexes and rotates vertebral column; increases abdominal pressure; fixes and depresses ribs; stabilizes pelvis during walking; used in sit-ups and curls
|
|
|
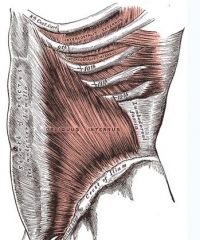
External Obliques
|
Origin: Anterior surface of last eight ribs
Insertion: Linea alba, pubic crest and tubercles, and iliac crest |
Functions of rectus abdominis and also aids muscles of back in trunk rotation and lateral flexion; used in oblique curls
|
|
|
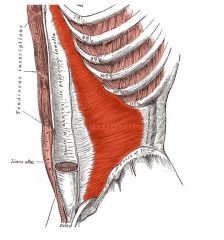
Internal Obliques
|
Origin: Lumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inguinal ligament
Insertion: Linea alba, pubic crest, and costal cartilages of last three ribs |
Functions of rectus abdominis and also aids muscles of back in trunk rotation and lateral flexion; used in oblique curls
|
|
|
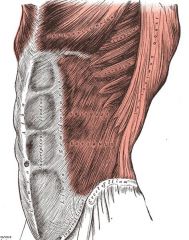
Transverse Abdominis
|
Origin: Inguinal ligament, iliac crest, cartilages of last five or six ribs, and lumbar fascia
Insertion: Linea alba and pubic crest |
Compresses abdominal contents
|
|
|
Trapezius
|
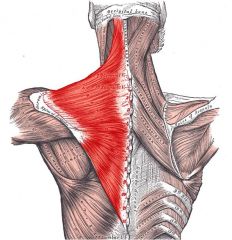
Origin: Occcipital bone; ligamentum nuchae; spines of C7 and all thoracic vertebrae
Insertion: Acromion and spinous process of scapula; lateral third of clavicle |
Extends head; raises, rotates, and retracts (adducts) scapula and stabilizes it; superior fibers elevate scapula (as in shrugging the shoulders); inferior fibers depress it
|
|
|
Latissimus Dorsi
|
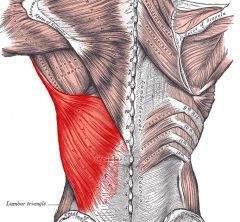
Origin: Indirect attachment to spinous processes of lower six thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, last three to four ribs, and iliac crest
Insertion: Floor of intertubercular sulcus of humerus |
Prime mover of arm extension; adducts and medially rotates arm; depresses scapula; brings arm down in power stroke, as in striking a blow
|
|
|
Infraspinatus
|
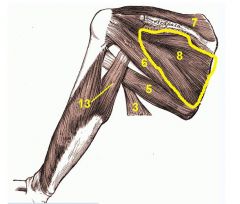
Origin: Infraspinous fossa of scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle of humerus |
Lateral rotation of humerus; helps hold head of humerus in glenoid cavity; stabilizes shoulder
|
|
|
Teres Minor
|
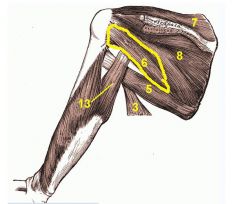
Origin: Lateral margin of scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle of humerus |
Lateral rotation of humerus; helps hold head of humerus in glenoid cavity; stabilizes shoulder
|
|
|
Supraspinatus
|
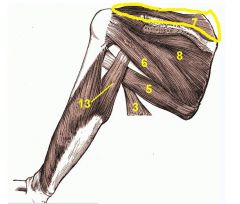
Origin:Supraspinous fossa of scapula
Insertion: Greater tubercle of humerus |
Assists abduction of humerus; stabilizes shoulder joint
|
|
|
Teres Major
|
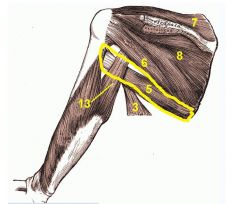
Origin: Posterior surface at inferior angle of scapula
Insertion: Intertubercular sulcus of humerus |
Extends, medially rotates, and adducts humerus; synergist of latissimus dorsi
|
|
|
Rhomboids Major
|
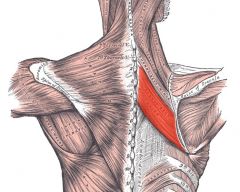
Origin: Spinous processes T1-T5*
Insertion: Medial border of scapula |
Pulls scapula medially (retraction); stabilizes scapula; rotates glenoid cavity downward
|
|
|
Rhomboids Minor
|
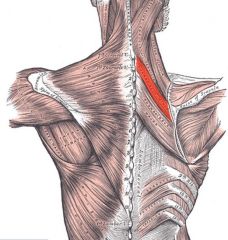
Origin: Spinous processes C7
Insertion: Medial border of scapula |
Pulls scapula medially (retraction); stabilizes scapula; rotates glenoid cavity downward
|
|
|
Triceps Brachii
|
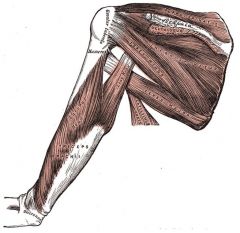
Origin:Long head—inferior margin of glenoid cavity; lateral head—posterior humerus; medial head—distal radial groove on posterior humerus
Insertion: Olecranon process of ulna |
Powerful forearm extensor; antagonist of forearm flexors (brachialis and biceps brachii)
|
|
|
Brachioradialis
|

Origin: Lateral ridge at distal end of humerus
Insertion: Base of styloid process of radius |
Synergist in forearm flexion
|
|
|
Brachialis
|
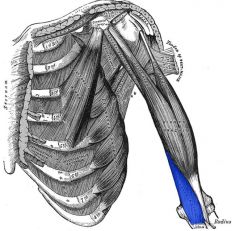
Origin: Distal portion of anterior humerus
Insertion: Coronoid process of ulna |
A major flexor of forearm
|
|
|
Pronator Teres
|

Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus and coronoid process of ulna
Insertion: Midshaft of radius |
Acts synergistically with pronator quadrates to pronate forearm; weak elbow flexor
|
|
|
Flexor Carpi Radialis
|

Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: Base of metacarpals 2 and 3 |
Powerful flexor of wrist; abducts hand
|
|
|
Palmaris Longus
|

Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: Palmar aponeurosis; skin and fascia of palm |
Flexes wrist (weak); tenses skin and fascia of palm
|
|
|
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
|
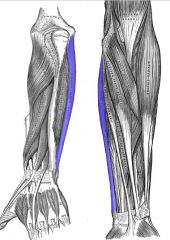
Origin: Medial epicondyle of humerus and olecranon process and posterior surface of ulna
Insertion: Base of metacarpal 5; pisiform and hamate bones |
Powerful flexor of wrist; adducts hand
|
|
|
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
|
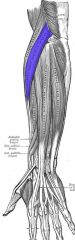
Origin: Lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus
Insertion: Base of metacarpal 2 |
Extends and abducts wrist
|
|
|
Supinator
|
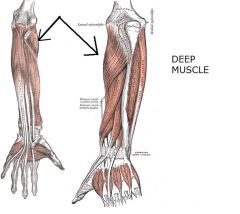
Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus; proximal ulna
Insertion: Proximal end of radius |
Acts with biceps brachii to supinate forearm; antagonist of pronator muscles
|
|
|
Extensor Digitorum
|
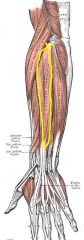
Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: By four tendons into distal phalanges of fingers 2-5 |
Prime mover of finger extension; extends wrist; can flare (abduct) fingers
|
|
|
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
|
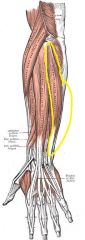
Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus; posterior border of ulna
Insertion: Base of metacarpal 5 |
Extends and adducts wrist
|
|
|
Iliopsoas (Iliacus)
|
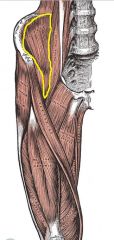
Origin:Iliacus—iliac fossa and crest, lateral sacrum; psoas major—transverse processes, bodies and discs of T12 and lumber vertebrae
Insertion: On and just below lesser trochanter of femus |
Flex trunk on thigh; flex thigh; lateral flexion of vertebral column (psoas)
|
|
|
Sartorius
|
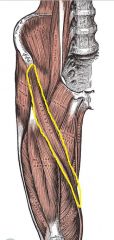
Origin: Anterior superior iliac spine
Insertion: By an aponeurosis into medial aspect of proximal tibia |
Flexes, abducts, and
Laterally rotates thigh; Flexes knee; known as “tailor’s muscle” because it Helps cross-legged Position in which tailors Are often depicted |
|
|
Adductor Magnus
|
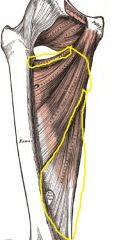
Origin: ischial and pubic rami and ischial tuberosity
Insertion: linea aspera and adductor tubercle of femus |
Adduct and medially rotate and flex thigh; posterior part of magnus is also a synergist in thigh extension
|
|
|
Adductor Longus
|
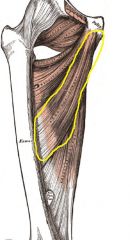
Origin: pubis near pubic symphysis; brevis—body and inferior ramus of pubis
Insertion: linea aspera |
Adduct and medially rotate and flex thigh
|
|
|
Gracilis
|
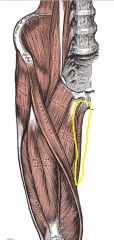
Origin: Inferior ramus and body of pubis
Insertion: Medial surface of tibia just inferior to medial condyle |
Adducts thigh; flexes and medially rotates leg, especially during walking
|
|
|
Rectus Femoris
|
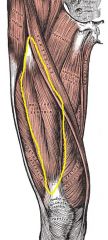
Origin: Anterior inferior iliac spine and superior margin of acetabulum
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity and patella |
Extends knee and flexes thigh at hip
|
|
|
Vastus Lateralis
|
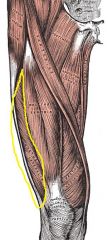
Origin: Greater trochanter, intertrochanteric line, and linea aspera
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity and patella |
Extends and stabilizes knee
|
|
|
Vastus Medialis
|
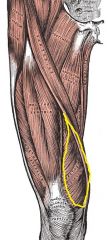
Origin: Linea aspera and intertrochanteric line
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity and patella |
Extends knee; stabilizes patella
|
|
|
Vastus Intermedius
|
Origin: Anterior and lateral surface of femus
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity and patella |
Extends knee
|
|
|
Tensor Fasciae Latae
|
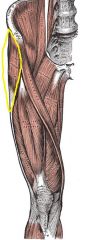
Origin: Anterior aspect of iliac crest and anterior superior iliac spine
Insertion: Iliotibial tract (lateral portion of fascia lata) |
Flexes, abducts, and medially rotates thigh; steadies trunk
|
|
|
Biceps Femoris
|
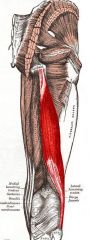
Origin: Ischial tuberosity (long head); linea aspera and distal femur (short head)
Insertion: Tendon passes laterally to insert into head of fibula and lateral condyle of tibia |
Extends thigh; laterally rotates leg; flexes knee
|
|
|
Semitendinosus
|
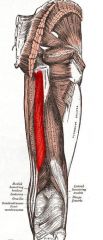
Origin:Ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Medial aspect of upper tibial shaft |
Extends thigh; flexes knee; medially rotates leg
|
|
|
Semimembranosus
|
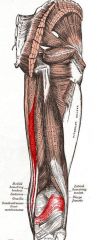
Origin: Ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Medial condyle of tibia; lateral condyle of femur |
Extends thigh; flexes knee; medially rotates leg
|
|
|
Gluteus Maximus
|

Origin: Dorsal ilium, sacrum, and coccyx
Insertion: Gluteal tuberosity of femur and iliotibial tract |
Complex, powerful thigh extensor (most effective when thigh is flexed, as in climbing stairs—but not as in walking); antagonist of iliopsoas; laterally rotates and abducts thigh
|
|
|
Gluteus Medius
|
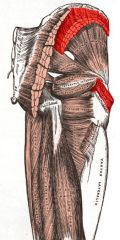
Origin: Upper lateral surface of ilium
Insertion: Greater trochanter of femur |
Abducts and medially rotates thigh; steadies pelvis during walking
|
|
|
Tibialis Anterior
|
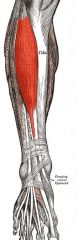
Origin: Lateral condyle and upper 2/3 of tibia; interosseous membrane
Insertion: By tendon into inferior surface of first cuneiform and metatarsal 1 |
Prime mover of dorsiflexion; inverts foot; supports longitudinal arch of foot
|
|
|
Extensor Digitorum Longus
|

Origin: Lateral condyle of tibia; proximal ¾ of fibula; interosseous membrane
Insertion: Tendon divides into four parts; inserts into middle and distal phalanges of toes 2-5 |
Prime mover of toe extension; dorsiflexes foot
|
|
|
Gastrocnemius
|
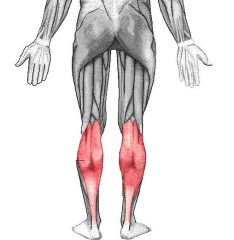
Origin: By two heads from medial and lateral condyles of femur
Insertion: Calcaneus via calcaneal tendon |
Plantar flexes foot when kenee is extended; crosses knee joint; thus can flex knee (when foot is dorsiflexed)
|
|
|
Soleus
|
Origin: Proximal portion of tibia and fibula; interosseous membrane
Insertion: Calcaneus via calcaneal tendon |
Plantar flexion; is an important muscle for locomotion
|
|
|
Popliteus
|

Origin: Lateral condyle of femur and lateral meniscus
Insertion: Proximal tibia |
Flexes and rotates leg medially to “unlock” extended knee when knee flexion begins
|
|
|
Tibialis Posterior
|

Origin: Superior portion of tibia and fibula and interosseous membrane
Insertion: Tendon passes obliquely behind medial malleolus and under arch of foot; inserts into several tarsals and metatarsals 2-4 |
Prime mover of foot inversion; plantar flexes foot; stabilizes longitudinal arch of foot
|
|
|
Flexor Digitorum Longus
|

Origin: Posterior surface of tibia
Insertion: Distal phalanges of toes 2-5 |
Flexes toes; plantar flexes and inverts foot
|
|
|
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
|
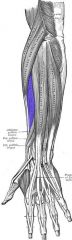
Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Insertion: Base of metacarpal 3 |
Extends and abducts wrist; steadies wrist during finger flexion
|
|
|
Supinator
|
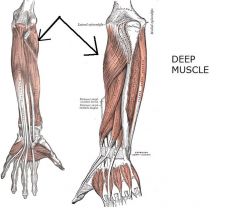
Origin: Lateral epicondyle of humerus; proximal ulna
Insertion: Proximal end of radius |
Acts with biceps brachii to supinate forearm; antagonist of pronator muscles
|

