![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skeletal Muscle
|
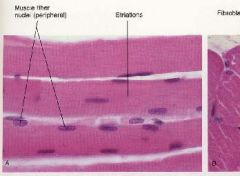
Striated, strong, quick, voluntary, can fatigue, MULTINUCLEATED, and large cells
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|
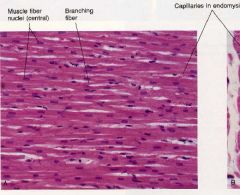
Striated, strong, quick, involuntary, must not fatigue, uninucleated central cells, branched cells, intercalated discs
|
|
|
Smooth Muscle
|
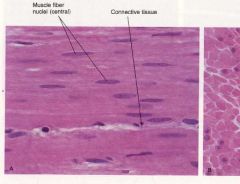
Nonstriated, weaker, slow/rhythmic at times, involuntary, uninucleated with cigar shaped nuclei, different arrangement of contractile elements
|
|
|
Epimysium, Endomysium, Perimysium, Fascicle, Sarcolemma, sarcoplasm, myofibril
|
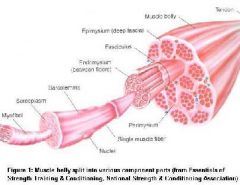
Check Image
|
|
|
Sarcomere
|
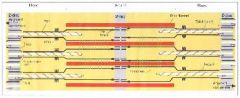
Basic contractile unit of a striated muscle - This is in between two Z disks
|
|
|
A band and I band
|

A band stains dark because of all of the Myosin
I band stains light because of thin filaments |
|
|
H band
|

In the middle of the dark A band, an area where actin fibers do not reach. Wider in a noncontracted state and narrow when the muscle is contracted
|
|
|
M Line
|
In the middle of the H band. I believe Myosin are anchored here but I am not 100% sure.
|
|
|
Z Disk
|
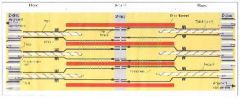
area in the middle of an I band which the actin is anchored to
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types: Type one and Type Two
|
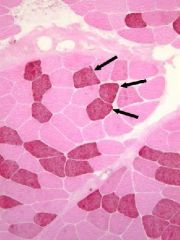
Type I-stability and endurance, slow twitch, mitochondria rich "one slow red ox"
Type 1 Fibers stain darker than type 2 Type II-burst of speed, fast twitch, loaded with glycogen All human muscles are mixed. |
|
|
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
|
Modified smooth ER that runs from the surface to the tips of the myosin filament and spreads out laterally from there. It carries the calcium ion signal to contract muscle
|
|
|
Terminal Cisternae
|
Enlarged areas of the SR which are sitting right next to a t tubule to wait for an AP. These will release calcium quickly when stimulated by an ACTION POTENTIAL
|
|
|
Triad
|
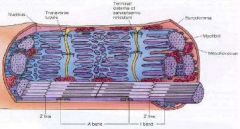
2 terminal cisternae which sandwich a t tubule at an A and I band junction
|
|
|
Mitochondria of Muscles
|
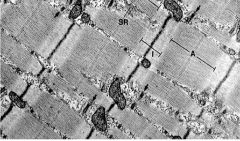
Cardiac Muscle has more than skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Motor Nerve Ending vs Sensory Nerve Ending
|
Motor never ending at NMJ
Sensory nerve endings at Muscle Spindle and Golgi Tendon Organ |
|
|
Motor Unit
|
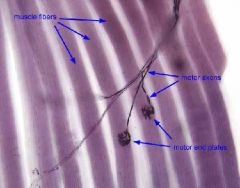
A single axon and all of the muscle fibers that it innervates
|
|
|
Muscle Spindles
|
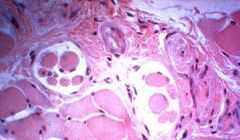
Utilize Intrafusal fibers innervated by gamma motoneurons: fibers anchored to the perimysium and endomysium of extrafusal(muscle) fibers
The function of this is to detect changes in extrafusal fiber length and the rate of change of length (STRETCH RECEPTOR) Smaller muscles have more muscle spindles than larger muscles |
|
|
Golgi Tendon Organ
|
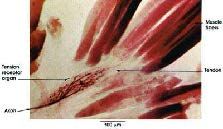
Located at musculotendonous areas made up of encapsulated collagen fibers with nerve endings in them
When a muscle contracts/or contracts too strenuously, the nerve endings in the capsule get compacted due to the pressure and this causes an action potential to let the body know. |
|
|
Muscle Response to Injury: Skeletal Muscle
|
Mature fibers CANNOT undergo mitosis
Satellite cells in the basal lamina, which are normally quiescent cells, mononucleate, and capable of mitosis, differentiate into myoblasts and fuse to form new skeletal muscle fibers. CD56 stains satellite cell perinuclear regions but not differentiated myocytes |

