![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the term that encompasses bone infections?
|
Osteomyelitis
|
|
|
What are the categories of Osteomyelitis?
|
- Hematogenous
- Direct Implantation - Contiguous - Infection of Prosthetic Device |
|
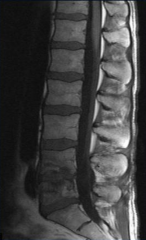
What is the cause of Hematogenous Osteomyelitis?
|
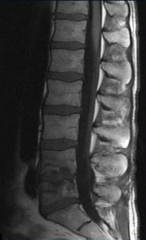
Seeding of bone related to a previous bacteremia (e.g., vertebral bodies and disc are irregular and loose; bacteria got into disc and then spread into vertebral bodies)
|
|
|
What is the cause of Direct Implantation Osteomyelitis?
|

Penetrating injury
|
|
|
What is the cause of Contiguous Osteomyelitis?
|
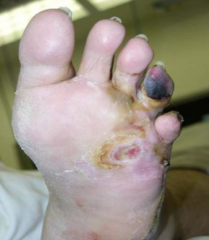
Direct spread of bacteria from an overlying wound or pressure ulcer (common in diabetes)
|
|
|
What is the cause of Osteomyelitis from Prosthetic Devices?
|
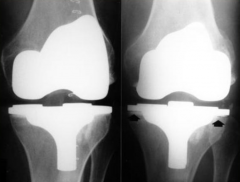
When there is an infection on the prosthetic material that is implanted in the bone, it spreads to the adjacent bone
(picture: before & 3 months later) |
|
|
What kind of Osteomyelitis is most common in children?
|
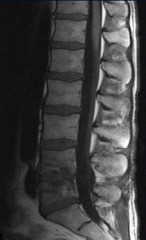
Hematogenous (results from seeding of bone related to a previous bacteremia)
|
|
|
What kind of Osteomyelitis is most common in adults?
|
- Contiguous (from direct spread of bacteria from overlying wound or pressure ulcer)
- Infection of Prosthetic Device |
|
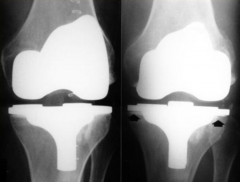
What can happen when someone has an infection caused by their prosthetic joint?
|
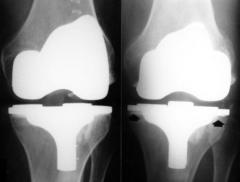
Can cause joint loosening and leading to joint needing to be removed
|
|
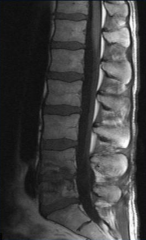
What are the most common bacteria that cause Hematogenous Osteomyelitis?
|
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus species - Gram-negatives * Mycobacterium tuberculosis * Salmonella species (in sickle cell) (* = unique to this type) |
|

What are the most common bacteria that cause Osteomyelitis by Direct Implantation?
|

* Pseudomonas aeruginosa - water dwelling bacteria (e.g., it gets into wet sneakers and they if they step on nail it gets directly into bone)
|
|
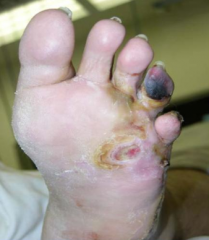
What are the most common bacteria that cause Contiguous Osteomyelitis?
|
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Gram-negatives - Streptococcus species * Anaerobes * Candida species (* = unique to this type) |
|
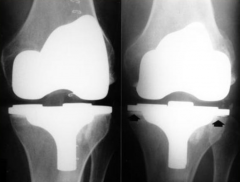
What are the most common bacteria that cause Prosthetic Joint Osteomyelitis?
|
* Coagulase negative Staphylococci
- Staphylococcus aureus - Gram-negatives - Streptococcus species (* = unique to this type) |
|
|
What bacteria all can commonly cause Hematogenous, Contiguous and Prosthetic Joint Osteomyelitis?
|
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus species - Gram-negatives |
|
|
What are the general characteristics of Osteomyelitis?
|
- Chronic infections
- Difficult to eradicate - Damages periosteum - may result in pieces of dead bone (sequestrum) or new external bone formation (involucrum) - May involve localized abscesses (Brodie's abscesses) |
|
|
How can you diagnose Osteomyelitis?
|
- X-rays not very sensitive
- Bone/WBC scans or MRI more effective - Bone biopsies or blood cultures (sometimes) to determine bacteria |
|
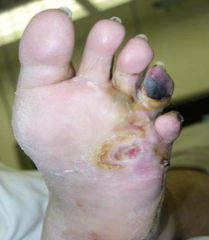
In contiguous osteomyelitis, how do the bacteria in the ulcer compare to the bacteria in the bone?
|
Cultures of open ulcers overlying contiguous osteomyelitis are notoriously unreliable; bacteria in bone underneath may be entirely different
|
|
|
What happens if a bone biopsy can't be done or culture results are negative in osteomyelitis?
|
Need to try empiric treatment of antibiotics
|
|
|
What can make Osteomyelitis particularly difficult to treat?
|
Biofilms may develop on infected bone (or especially on prostheses)
|
|
|
What are biofilms?
|
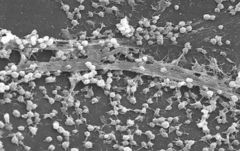
- Aggregations of microorganisms adherent to a surface, particularly to a hard surface like bone or teeth or prosthetic materials
- Microorganisms frequently are embedded in matrix they produce called slime or extracellular polymeric substance or glycocalyx |
|
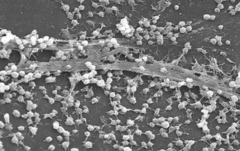
What is "slime" / "extracellular polymeric substance" / "glycocalyx"?
|
A matrix produced by microorganisms in biofilms that the microorganisms adhere to
|
|
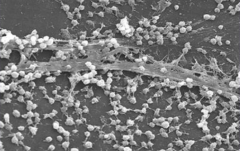
How do bacteria in biofilms compare to those that are planktonic (suspended)?
|
Biochemistry and physiology are often very different; biofilm bacteria are more resistant to antibiotics
|
|
|
How do you treat Osteomyelitis?
|
- Long courses of antibiotics
- 6 weeks of IV antibiotics - Sometimes months of oral antibiotics may be needed too (especially for prosthetic infections) - Sometimes surgery to remove sequestra or prostheses (when antibiotics fail) |
|
|
What antibiotic is particularly good for treating biofilm organisms?
|
Rifampin
|
|
|
What is necessary for antibiotic treatment to be effective?
|
If bone is covered by tissue (otherwise new organisms can continuously invade bone)
|

