![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of drug is Denosumab and what is its MOA?
|
Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody raised against the RANKL found on osteoclasts.
The mAb will bind to the RANKL and prevent the RANKL-RANK complex from forming. This would reduce osteoclast activity and therefore reduce bone resorption. * Only in Phase III trials - not available* |
|
|
What results have been observed in the beginning trial stages of Denosumab treatment for osteoporosis?
|
Within a couple hours of a 60g Denosumab injection, osteoclastogenesis stopped and bone resorption decreased.
Since injection good for 6 months. Injections were accompanied by an increase in BMD in the lumbar spine, hip and distal third of radius. |
|
|
What are the two classifications for osteoporosis drugs?
|
1) Anti-catabolic or anti-resorption
2) Anabolic |
|
|
Define osteoporosis?
|
Decrease in bone density and strength because of an increase in bone resorption or a decrease in bone formation. BONE REMODELING IMBALANCE.
|
|
|
What are some lifestyle changes that can be done to prevent osteoporosis?
|
1) Supplementation – adequate calcium (1000-2000mg/day) and vitamin D3 (400-1000 IU)
2) Exercise – 30 minutes of weight bearing exercises, 3x a week, strength and balance 3) Normal, stable weight (BMI 22-25) 4) Fall Risk Reduction in home – OT to home, good lighting, nightlights, room clutter, throw rugs, etc 5) Check hearing and eyesight 6) Reduce EtOH consumption and smoking 7) Social support 8) Hip protectors |
|
|
How would you determine if a patient needs bone density scan?
|
Has at least one major risk factor or 2 minor ones.
|
|
|
Who to you provide osteoporosis treatment to? What criteria?
|
1) High risk for fracture (i.e. elderly, women > men, low BMD)
2) Previous low trauma fracture |
|
|
What is the main goal of osteoporosis treatment and management?
|
To prevent falls and future fractures, prevent further bone loss (resorption) and improve bone strength (formation).
|
|
|
What are some drugs that cause drug-induced bone loss?
|
1) Glucocorticoids (steroids)
2) Heparin 3) Excessive Vitamin A 4) Excessive Thyroid hormone 5) Aromatase inhibitors 6) Chemotherapy drugs 7) Anti-seizure meds 8) Anti-depressants (SSRIs) |
|
|
How does glucocorticoids cause bone loss?
|
Increase bone resorption and decrease bone formation
- Inhibits osteoblast recruitment, maturation and action - Decrease collagen formation - Decrease Ca+ absorption from the gut by inhibiting vitamin D3 - Increases renal excretion of Ca+ - Increases PTH secretion - Stimulates production of osteoclasts |
|
|
How can you minimize the detrimental effects of GC (inhaled and oral)?
|
1) Use as low of dose as possible (<3mg)
2) Alternate day therapy 3) Increase supplementation 4) Anti-catabolic therapy (bisphosphonates) for those at high risk of fracture 5) Stop as soon as possible |
|
|
How much calcium and vitamin D3 should someone with osteoporosis and high risk of fracture be taking for management?
|
1500mg of calcium and 800-2000 IU of vitamin D3.
Vitamin D3 must be activated by the liver and kidney therefore make sure to check liver and kidney function. |
|
|
How should the calcium supplements be taken?
|
500mg at a time with food to increase the amount absorbed.
Important to take right before bed for overnight absorption, to help replace the bone resorption lost at night. Use calcium citrate if history of kidney stones. |
|
|
How does calcium and vitamin D3 supplementation effect bone remodeling?
|
- Vitamin D3 allows increased absorption of calcium from the gut
- Calcium slows the rate of bone loss and helps to increase bone density by being added to mineralized osteoid. |
|
|
What two hormones are used in ovarian hormone therapy (OHT)?
|
Progesterone and estrogen.
|
|
|
What is the MOA of estrogen in the treatment of osteoporosis?
|
- It decreases bone resorption by inhibiting osteoclasts indirectly via the activation of OPG secretion from the osteoblasts. This prevents RANKL-RANK complex from forming and decreases osteoclast induction.
- Increases calcium absorption from the gut - Increases IGF-1 and other growth hormones while decreasing cytokine production. |
|
|
What are the pros and cons of using estrogen OHT therapy for osteoporosis treatment?
|
PROS
– decreased osteoporotic fractures and hip fractures therefore effective for preventing further fractures - slows down bone loss - decreased colorectal cancers CONS - increased thrombotic events - increased strokes - increased breast cancers - increased MI |
|
|
What is the MOA of progesterone and how does it affect osteoporosis?
|
- Increased osteoblast activity
- Stimulated osteoblast osteoid production Progesterone stimulates bone formation and therefore slows down further bone density loss. It also reduces menopausal symptoms (hot flashes and night sweats). Further research is needed on fracture prevention. |
|
|
Who would you provide OHT therapy and why?
|
1) A women in early menopause (<40yo)
2) Women with severe night sweats/menopausal symptoms 3) When other therapies aren’t working *Note – cyclical therapy of progesterone has prevented bone loss in premenopausal women with abnormal cycles. Make sure that the pros of OHT outweigh the risks therefore assess for cardiac, cerebrovascular and cancer risks before starting on OHT. |
|
|
What is the golden standard drug treatment(s) for osteoporosis?
|
1) Bisphosphonates
2) OHT (or HRT) 3) SERMs |
|
|
What is the MOA of bisphosphonates in treatment of osteoporosis?
|
ANTI-CATABOLIC, pyrophosphate analogue
- Bisphosphonates bind irreversibly to the hydroxyapatite crystals on the surface on the bone and are internalized by osteoclasts which disrupts their function. - Bisphosphonates resist metabolic degradation via two mechanisms acting on the osteoclasts: i) reduce their ability to resorb bone ii) accelerate osteoclast apoptosis. - Bisphosphonates decrease the solubility of the bone matrix therefore making it more resistant to bone resorption. |
|
|
What are the four oral bisphosphonates drugs available in Canada?
|
1) Etidronate
2) Alendronate 3) Risedronate 4) Clodronate |
|
|
What are some of the IV bisphosphonates drugs available?
|
1) Zoledronic acid
2) Pamidronate 3) Clodronate |
|
|
How should bisphosphonates be taken?
|
Poorly absorbed therefore should be taken on an empty stomach with no food or drink for 60 minutes prior to taking the pill.
Bisphosphonates bind to Ca+2 and iron therefore wait 2 hours before taking these supplements |
|
|
What are some side effects of bisphosphonates?
|
Usually well tolerated
Esophagitis with the nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate therefore take while standing and remain upright for 30 minutes afterwards – don’t take right before bed. Take with water. Osteonecrosis of the jaw (rare) – occurs more often with IV therapy, check dental hygiene before giving. Hypocalcemia – 2000U of Ca+2 and 800-1400 IU of vitamin D3 supplementation. |
|
|
What are the two non-nitrogen containing bisphosphonates and what benefit do they pose?
|
Etidronate and Clodronate – don’t cause esophagitis
|
|
|
What is special about the dosing schedule of etidronate?
|
Inhibits osteoclasts and decreases mineralization therefore given cyclically; 400mg x14 consecutive days, every 3 months.
Can take lying down. S/E of diarrhea |
|
|
What are the prevention and treatment doses for alendronate (Fosamax)?
|
Prevention = 35mg once weekly
Treatment = 70mg once weekly |
|
|
How effective has alendronate been in preventing fractures and increasing BMD?
|
- Shown to increase spinal bone density by almost 10% after 3 years
- Shown to reduce the frequency of fracture of vertebral, hip and wrist fractures by about 50% |
|
|
What is the MOA of calcitonin?
|
ANTI-CATABOLIC nasal spray
- Directly inhibits osteoclasts by binding to a receptor on its surface; reducing bone resorption. Analgesic effect – stronger narcotic then morphine without the addiction; used to manage pain from vertebral fractures. |
|
|
What effects has calcitonin had on preventing new fractures and BMD?
|
- Proven to prevent new spinal fractures (33%) with very modest effect on spinal BMD. No evidence of preventing non-vertebral fractures was observed. Further research is needed.
- Used to treat postmenopausal osteoporosis but not approved for GC-induced osteoporosis |
|
|
What are the side effects of calcitonin?
|
- Injection = tachypylaxis (rapidly decreasing response to a drug following administration on the initial dose)
- Nasal spray (200 IU/day) – usually well tolerated. |
|
|
What type of drug is Raloxifene?
|
Selective estrogen receptor modulator – AKA SERM
ANTI-CATABOLIC |
|
|
What is the MOA of Raloxifene?
|
Binds to estrogen receptors and produces different expression of estrogen-regulating genes in different tissues, activating some and inhibiting others.
Increases calcium absorption from the gut. |
|
|
What effect does SERMs (Raloxifene) have on preventing new fractures and increasing BMD?
|
Mild increase in bone density
30% decrease in new vertebral fractures No effect was observed on nonvertebral fractures * Less effective at spinal fracture prevention than estrogen or bisphosphonates* |
|
|
What are some side effects of SERMs (Raloxifene)?
|
Increased risk of thromboembolism (similar to estrogen)
Increased hot flashes and leg cramps Neutral for CV disease and associated with reduced incidence of breast cancer and no increased in endometrial cancer |
|
|
When is Raloxifene use not recommended?
|
In a women with breast cancer history
Past tamoxifen use. |
|
|
What type of drug is Teriparatide?
|
- Recombinant 1-34 aa parathyroid horomone
- ANABOLIC |
|
|
How does PTH Teriparatide increase bone formation – MOA?
|
- At intermittent levels PTH will stimulate bone formation
- Binds directly to the osteoblast and stimulate maturation and inhibits osteoblast apoptosis - It also stimulates osteoclasts therefore paradoxically increasing resorption. |
|
|
What effect was PTH (Teriparatide) treatment shown to have on BMD and fracture prevention?
|
- Spine BMD was shown to increase 2-3x more then that shown with anti-catabolic drugs, although decrease in BMD in the shaft of the radius in the first year (resorption of cortical bone?).
- Vertebral and non-vertebral fractures where reduced by 55-65% over 18-20 months in the Fracture prevention trial. |
|
|
What are the side effects/disadvantages of PTH (teriparatide) therapy?
|
- Subcutaneous injection (20ug)
- Expensive ($20/day) - Headache, dizziness, esophageal reflux, nausea - Hypercalcemia - Osteosarcoma |
|
|
Who can receive Teriparatide (PTH) therapy for osteoporosis?
|
- Reserved for high risk patients due to the cost and the lack of both safety and efficacy data.
- Use limited to 2 years. |
|
|
What are the only two osteoporotic drugs that are anabolic (bone formation)?
|
- PTH (Teriparatide)
- Progesterone |
|
|
Which drug, only available in Europe, both increases bone formation and decreases bone resorption?
|
Strontium ranelate – ANABOLIC and ANTI-CATABOLIC
Reduced vertebral fractures by 6% (absolute) Oral with no food avoidance Side effects include diarrhea |
|
|
What osteoporotic drugs are anti-catabolic/anti-resorption
|
1) Estrogen
2) Bisphosphonates 3) SERMs 4) Calcitonin |
|
|
Which combination therapies are effective for osteoporosis treatment?
|
1) Estrogen + Progesterone
2) Estrogen + Progesterone + bisphosphonates 3) Estrogen + PTH 4) Calcium + vitamin D + all the above |
|
|
What combination therapies are NOT effective treatment options for osteoporosis?
|
Bisphosphonates + PTH – but you can start with PTH, increase bone formation and stop it and start bisphosphonates to prevent the new bone formation from being lost.
|
|
|
What % lifetime risk does a 60 year old man have of having an osteoporotic fracture?
|
25% lifetime risk.
|
|
|
What are some risk factors for osteoporosis in men (and women)?
|
1) Smoking
2) Excess alcohol (>2 drinks/day) 3) Physical inactivity and decreased strength 4) Poor nutrition – calcium and vit D intake 5) Low androgen levels (hypogonadism or prostate cancer rx) 6) Low estrogen levels (thin) 7) Drug-induced (GC) |
|
|
How would you manage a man with osteoporosis?
|
1) Vit D and calcium supplementation
2) Exercise program 3) Decrease drinking and smoking 4) Improve nutrition 5) Androgen therapy (testosterone) only if hypogonadism 6) Bisphosphonates 6) PTH in rare cases |
|
|
How would you treat a young woman with high risk factor for osteoporosis due to abnormal ovulation?
|
1) First figure out why she is oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea (i.e. weight loss, excessive exercise, hormonal, stress) – provide emotional and social support
2) Increase calcium and vitamin D supplementation 3) Nutrition – balance energy, return weight to normal 4) Cyclic progesterone therapy 5) Avoid oral contraceptives – associated with lower BMD and bone loss. |
|
|
For a young women with an abnormal ovulation cycle, when would you prescribe progesterone (medroxyprogesterone or micronized progesterone)?
|
During the days when she would physiologically normally have progesterone; Days 14-27 of her cycle.
300mg if progesterone, 10mg if medroxyprogesterone. |
|
|
Which bisphosphonates is covered by medicare?
|
Etidronate
|
|
|
In the 1994 study by J. Prior investigating the effects of cyclic progesterone on bone density, what did she find?
|
Females on cyclic progesterone + calcium supplementation (1000mg) had increased bone mineral density compared to those on only progesterone, calcium or none.
Adding MPA increased BMD 2-3% in young females. |
|
|
What effect does oral contraceptives have on bone density?
|
Shown to decrease BMD (statistically significant) in the spine and trochanter.
|
|
|
Compare and contrast the absolute fracture risk reduction of alendronate, risedronate, OHT, Raloxifene (SERM) and Teriparatide (PTH)?
|
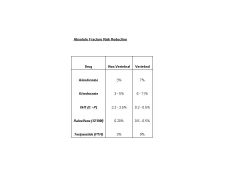
|

