![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
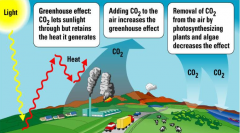
Greenhouse Effect
|
|
|
|
Karyotype
|
A picture of chromosomes taken during mitosis and cut out and arranged into homologous pairs
|
|
|
Diploid Cell
|
Two sets of homologous chromosomes. Human diploid cell has 46 chromosomes
arranged in 23 pairs The 46 chromosomes contain 6 billion nucleotide pairs. |
|
|
Pedigree Chart
|
shows the relationship within a family and can be useful to help with genetic inheritance problems within families. It is another way to predict the outcome of a particular cross and the genotype of the family members.
|
|
|
Male Sex Chromosome
|
XY
|
|
|
Female Sex Chromosomes
|
XX
|
|
|
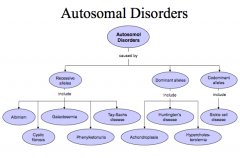
Autosomal Disorders
|
|
|
|
Sickle Cell Anemia
|
The patient’s blood cells were found to be irregularly shaped, like a sickle, and this is how the disease got its name. In normal red blood cells the hemoglobin molecule carries oxygen and distributes it around the body. In sickle cell disease, the red blood cells are sickle–shaped,
causing the blood hemoglobin to no longer carry oxygen as well and disrupts the normal functioning of the bodies cells, tissues and organs. This person is deprived of oxygen and the result is physical weakness, and damage to the brain, heart, spleen. The cause: A single base in the DNA that codes for Hemoglobin polypeptides is changed. This substitutes Valine for glutamic acid. This change makes the hemoglobin less soluble in blood. This will cause the hemoglobin to come out of the blood and crystallize. This crystallization causes the sickle shape of the blood cells and the medical consequences. The genetics: The allele for sickle cell (HS) is codominant with the allele for normal. sort of mutation |
|
|
Colorblindness
|
recessive disorder in which people can’t distinguish between certain colors.
Red-green colorblindness is most common. XC and Xc are for normal and colorblind vision. |
|
|
Hemophilia
|
Recessive Sex Linked Disorder in which one is unable to clot their blood.
Also known as “bleeders disease”. -caused by a defect in a gene and the protein for normal blood clotting is missing. |
|
|
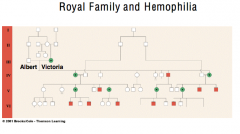
Royal Family and Hemophilia
|
|
|
|
Muscular Dystrophy
|
sex-linked recessive disease.
Here the affected individual inherits a degenerative muscle disorder. The gene that codes for a muscle protein is defective. They rarely live past early adulthood. Treatments are being explored that replace the defective gene. |
|
|
Down Syndrome
|
example of nondisjunction of an autosome,
specifically chromosome 21. In Down’s syndrome there is an extra copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21). Doing a karyotype(display of all the chromosomes in a cell nucleus) and looking at the chromosomes under a microscope detect the extra chromosome. Characteristics of Down’s syndrome include mental retardation, physically challenged, facial. |

