![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
If a patient complains of:
-change in bladder function -change in menstrual cycle -symptoms related to eating what may be a "RED FLAG" for these symptoms? |
possible GI/GU problems
|
|
|
what is the difference between a sPrain and a sTrain?
|
sPrain - ligament damage
sTrain - Tendon damage |
|
|
if a patient complains of pain:
-generally lessening @ night -being sharp/superficial ache -decreasing w/ activity -changing w/ mechanical stree is the pain systemic or musculoskeletal? |
musculoskeletal
|
|
|
If a patient complains of pain:
-distrubing sleep -deep aching/throbbing -reduced by pressure is it systemic or musculoskeletal? |
systemic pain
|
|
|
If a patient complains of:
-worst pain @ night -constant pain -unexplained weight loss what may be a "RED FLAG" for these symptoms? |
possible cancer
|
|
|
If a patient complains of:
-changes in hearing/vision -frequent/severe headaches -problems w/ balance what may be a "RED FLAG" for these symptoms? |
possible neurological disorder
|
|
|
what are 2 causes of bicipital tendinits?
|
-the long head of the bicep is impinged beneath the acromion
-the tendon is sheared in the bicipital groove, causes irritation |
|
|
If a patient complains of pain:
-constant/waves of spasm -not associated w/ mechanical stress -associated w/ other systemic changes is it systemic or musculoskeletal? |
systemic pain
|
|
|
If a patient complains of:
-frequent/severe abdominal pain -frequent heart burn/indigestion -frequent nausea/vomitting what may be a "RED FLAG" for these symptoms? |
possible GI/GU problems
|
|
|
if a patient complains of pain being sharp & superficial, is the pain most likely systemic or musculoskeletal?
|
musculoskeletal
|
|
|
If a patient complains of pain that is:
-capsular -dull -aching what structure is the pain possibly coming from? |
ligament
|
|
|
what is the difference between a shoulder dislocation and a shoulder separation?
|
-shoulder dislocation: the shoulder comes apart
-shoulder separation: clavicle comes apart |
|
|
how much is the total ScapuloThoracic ROM?
|
60 deg
|
|
|
what motions usually cause a GlenoHumeral dislocation / subluxation?
|
violent ABD & ER of the humerus
|
|
|
what is the difference between an impairment, a functional limitation, and a disability?
|
impairment - loss of...(ex. ROM, strength)
functional limitation - inability to ... (ex. put on shirt, drive) disability - cannot... (ex. play sports, go up multiple level buildlings) |
|
|
if a patient complains of pain being not associated w/ mechanical stress, is it most likely systemic or musculoskeletal?
|
systemic
|
|
|
what is a Bankart Lesion and how is it caused?
|
when the anterior labrum is disrupted due to excessive ABD & ER
|
|
|
if a patient complains of pain being constant or having waves of spasm, is it most likely systemic or musculoskeletal?
|
systemic
|
|
|
when a patient complains of pain being throbbing, where may it be coming from?
|
vascular
|
|
|
if a patient complains of pain being:
-sharp -burning -along the nerve distribution what structure is the pain most likely coming from? |
nerve
|
|
|
If a patient complains of:
-loss of appetite -unusual lumps, growths -unwarranted fatigue what may be a "RED FLAG" for these symptoms? |
possible cancer
|
|
|
If a patient complains of:
-fainting spells -sudden weakness -changes in speech -problems swallowing what may be a "RED FLAG" for these symptoms? |
possible neurological disorder
|
|
|
after performing a MMT (isometric testing), the patient states that they're PAIN-FREE, and the strength is there, what may you assume is wrong w/ the structure?
|
nothing. that is the normal response.
|
|
|
after performing a MMT (isometric testing), you notice that the contraction is WEAK and the patient is PAIN-FREE. what may you assume is wrong w/ the structure being tested?
|
there may be a rupture, avulsion, or nerve injury
|
|
|
if a pain changes w/ mechanical stress, is it most likely systemic or musculoskeletal?
|
musculoskeletal
|
|
|
if a patient complains of pain being:
-cramping -dull -aching -hard to localize what structure do you think the pain may be coming from? |
muscle
|
|
|
If a patient comes in w/ a A-C separation in where the capsule is only affected with minor deformity, what grade is that separation?
|
grade 1
|
|
|
When a patient complains of:
-fever/night sweats -recent severe emotional disturbances -swelling/redness of joint w/o trauma -pregnancy you may consider these things to be... |
RED FLAGS
|
|
|
what are some ways that you can measure loss of ROM?
|
-Goniometer:AROM/PROM
-Muscle Length Testing -Testing for Joint Play Mobility -provocation test |
|
|
what is the difference between a subluxation vs. a dislocation?
|
dislocation - when the joint comes apart & stays apart
subluxation - when the joint comes apart & goes back in |
|
|
after performing a MMT (isometric testing), the patient complains of pain & weakness. Besides the grading, what do you think may be wrong?
|
possible severe lesion in the muscle or tendon
|
|
|
if a patient complains of pain being:
-deep -boring -localized where may the pain be coming from? |
bone
|
|
|
If a patient complains of:
-shortness of breath -unexplained swelling -dizziness what may be a "RED FLAG" for these symptoms? |
possible cardiovascular problems
|
|
|
if a pain is disturbing during sleep, is it most likely systemic or musculoskeletal?
|
systemic
|
|
|
what are one of the possible interventions for A-C arthritis?
|
distal clavicular resection
|
|
|
If a patient comes in w/ a A-C separation in where A-C & C-C ligaments are disrupted and there is significant deformity, what grade is that separation?
|
grade 3
|
|
|
if a patient states that the pain generally lessens @ night, is it most likely systemic or musculoskeletal?
|
musculoskeletal
|
|
|
if a pain is, deep aching/throbbing, is it most likely musculoskeletal or systemic?
|
systemic
|
|
|
what is a possible cause of rotator cuff impingement?
|
the bursa of the supraspinatus flaring up due to irritation from the acromion
|
|
|
what is the function of the middle GlenoHumeral ligament?
|
limits ER in neutral
|
|
|
what is the function of the superior GlenoHumeral ligament?
|
prevents inferior subluxation of the humerus
|
|
|
what are 2 possible causes of scapular winging?
|
1. poor posture
2. long thoracic nerve palsy |
|
|
Describe the medical model that PT's normally follow.
|
-physical examination
-diagnostic testing -developing a diagnosis -creating a plan of care -implementing a plan of care -assessing outcomes |
|
|
what is the closed-pack position of the GlenoHumeral joint?
|
90 deg ER along with 90 deg of ABD
|
|
|
if a pain reduced by pressure, is it most likely musculoskeletal or systemic?
|
systemic
|
|
|
If a patient complains of:
-chest pain/ heaviness -constant severe leg/arm pain -pulsating pain -discolored, painful feet what may be a "RED FLAG" for these symptoms? |
possible cardiovascular problems
|
|
|
If a patient comes in w/ a A-C separation & the capsule is affected, the C-C ligament is stretched, and there is moderate deformity, what grade is that separation?
|
grade 2
|
|
|
after performing a MMT (isometric testing), the patient complains that there is pain, but the strength is strong, what may you assume is wrong w/ the structure?
|
that there is a local lesion in the muscle or tendon
|
|
|
what directions do the most GH dislocations occur at?
|
anterior & inferior
|
|
|
what structures may cause a loss of ROM?
|
-joint capsule restriction
-tight muscles -muscle spasm -muscle weakness -pain |
|
|
what is a Hills Sach Lesion?
|
when the humeral head is indented due to repeated banging of the humerus on the posterior labrum.
|
|
|
what are the functions of the inferior glenohumeral ligament?
|
-limits ER in 90/90 position
-prevents anterior dislocation |
|
|
what is a SLAP lesion?
|
disruption of the Superior Labrum Anterior & Posterior caused by a tear in the long head of the biceps attachment
|
|
|
name & describe the first stage of a frozen shoulder?
|
freezing stage - starts w/ inflammatory process & may appear as impingement syndrome; shoulder becomes painful and then stiff; the subscap trigger point limits ER & ABD
|
|
|
what is the final stage of a frozen shoulder and when does it occur?
|
thawing stage - spontaneously return ROM & pain goes away. ocrrus w/in 5-12 months
|
|
|
name & describe the second stage of a frozen shoulder?
|
frozen shoulder - adhesive capsulitis. PT intervention does nothing.
|
|
|
in an acute phase of an injury, what physical therapy intervention would you give a patient?
|
-Anti-inflammatory modalities
-Graded Passive ROM -Mobilization |
|
|
in a sub-acute phase of an injury, what physical therapy intervention would you give a patient?
|
-progressive AROM
-graded PRE's -functional activities |
|
|
Name some local modalities that you would use on shoulder pain.
|
-ice
-heat -ultrasound -phonophoresis -electrical stimulation |
|
|
Name some manual therapy techniques that you would use on shoulder pain.
|
-oscillatory techniques
-graded mobilization |
|
|
Name some AROM techniques that you would use on shoulder pain.
|
-pendulum exercises
-light teraband exercises |
|
|
In the mobilization grades, what is the purpose of grade 1 & 2?
|
to reduce pain
|
|
|
In the mobilization grades, what is the purpose of grade 3-5?
|
to increase mobility w/in the joint range
|
|
|
In the mobilization grades, what is done in grade 5?
|
manipulation of the joint
|
|
|
Name some accessory motions of the shoulder.
|
-lateral distraction
-anterior glide -posterior glide -inferrior glide -A/p & inf/sup glide of the A-C joint -A/p & inf/sup glide of the S-C joint -passive motion of the scapula |
|
|
How would you set up for lateral distraction of the shoulder?
|
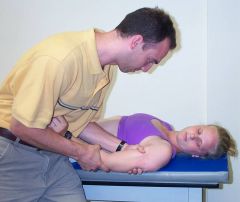
|
|
|
what is an important step in performing an anterior glide of the GH?
|
take up the slack before applying gentle glide
|
|
|
How would you set up for an anterior shoulder glide?
|
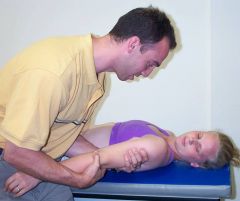
|
|
|
how would you set up for an inferior shoulder glide?
|
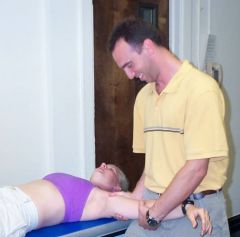
|
|
|
what is an important step in GH posterior glide?
|
IR humerus before applying downward pressure
|
|
|
how would you set up for a posterior GH glide?
|
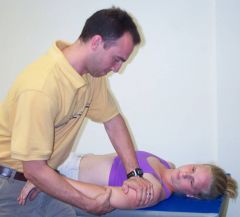
|
|
|
what are some treatments of tendinitis?
|
-transverse friction massage
-local modalities (heat, ice, US, estim) -stretching -strengthening -scapula stabilization -posture correction |
|
|
what muscles may require a transverse friction massage?
|
-supraspinatus
-infraspinatus -long head of biceps -periscapular trigger points (pec minor, subscap, levator scap) |
|
|
how do you set up to palpate the supraspinatus?
|
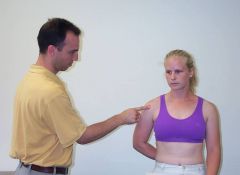
|
|
|
how do you set up to palpate the infraspinatus tendon?
|
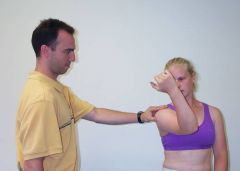
|
|
|
how do you set up to palpate the bicep long head tendon?
|

|
|
|
how do you set up to palpate the subscapularis tendon?
|

|
|
|
how do you strengthen type I muscles?
|
-low resistance, high reps/volume
-isolate joint motions |
|
|
what are some kinds of type I muscles?
|
rotator cuff muscles
|
|
|
how do you strengthen type II muscles?
|
-high resistance, low reps/volume
-single or multiple joint movements |
|
|
name some kinds of type II muscles.
|
-deltoids
-pec major |
|
|
what does TUBS stand for?
|
-Traumatic
-Unilateral -Bankart Lesion -Surgery |
|
|
with a Bankart lesion (TUBS), what motion needs to be avoided in the initial stage?
|
ABD & ER
|
|
|
when would a shoulder patient be in the maximum protection phase?
|
post-op
|
|
|
what are restrictions in the maximum protection phase?
|
-limit both AROM & PROM
-no resistive exercise -pain relieving modalities |
|
|
what thereapy can be done in the moderate protection phase?
|
-increase PROM
-begin selective AROM -limited resistive exercise -little or no "passive" modalities |
|
|
what therapy can be done in the minimum protection phase?
|
-full AROM & PROM
-vigorous strengthening exercises -functional activities |
|
|
how do you treat scalene thoracic outlet syndrome?
|
-gently stretch scalenes
-soft tissue mobilization to the scalenes -mobilizae 1st rib as needed -correct postureal fault -instruct in diaphragmatic breathing |
|
|
how do you treat pec minor thoracic outlet syndrome?
|
-stretch pec minor
-soft tissue mobilization -MFR pec minor -correct forward shoulder posture -strengthen scapula stabilizers |
|
|
set up for a supraspinatus tendinitis provocation test?
|
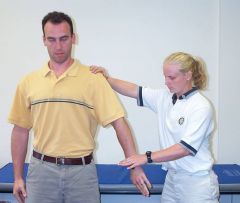
|
|
|
set up for a infrapspinatus tendinitis provocation test.
|
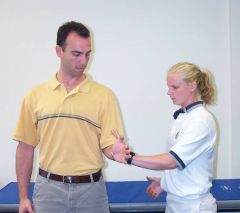
|
|
|
set up for long head of biceps tendinitis provocation test.
|
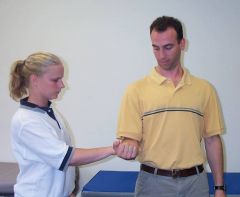
|
|
|
in graded mobilization, what is the purpose of grades 1 & 2?
|
to control pain
|
|
|
in graded mobilization, what is the purpose of grades 3 & 4?
|
to increase motion
|

