![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
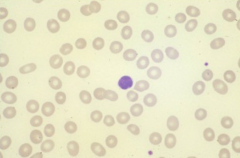
|
Normocytic MCV 80-100 |
|
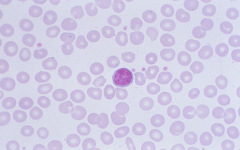
|
Microcytes MCV <80 |
|
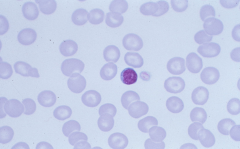
|
Macrocytes MCV > 100 |
|
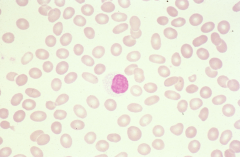
|
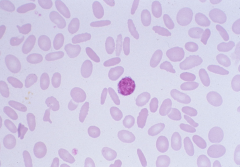
Poikilocytosis with Ovalocytes |
|
|
Elliptocyte many indicative of hereditary elliptocytosis |
|
|
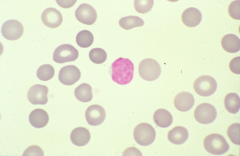
Spherocyte: no central palor -indicative of hereditary spherocytosis |
|
|
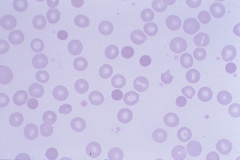
Micro-spherocyte -indicative of extravascular hemolysis |
|
|
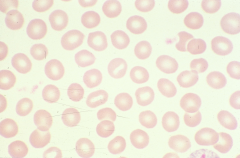
stomatocyte: central pallor is slit-like -hereditary stomatocytosis or perhaps myelodysplastic states |
|
|
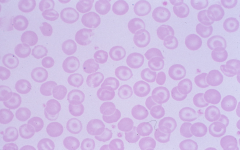
Target cell (codocyte) -caused by increased amount of cell membrane -liver disease, asplenia, hypochromic anemias, hemoglobinopathies |
|
|
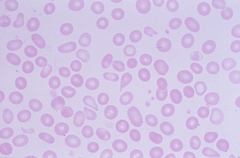
Tear Drop cells (dacrocytes) -associated with myelofibrosis |
|
|
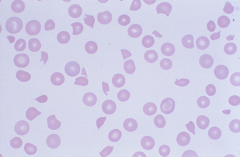
Schistocyte -indicates intravascular hemolysis; if the cell takes on particular shape can be a "helmet" cell or "bite" cell |
|
|
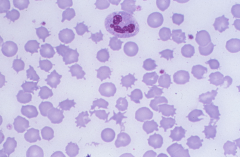
Acanthocytes (spur cells) -asymmetrical projections with bulbous ends -liver disease and a-beta-lipoproteinemia |
|
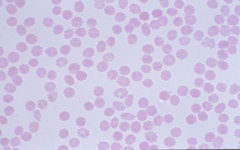
|
Burr Cell (echinocyte) -symmetrical pointy projections -renal failure |
|
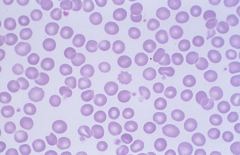
|
Crenated Cell -usually seen as drying artifact but can be associated with hyperosmolality (notice how there is only one) |
|
|
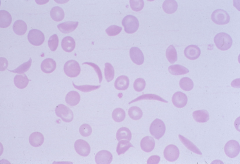
Sickle cell -most often seen in S-S disease (sickle cell anemia), can be seen in few other hemoglobinopathies |
|
|
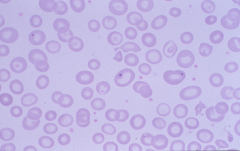
Basophilic stippling: small blue dots are remnants of RNA. Fine stippling: young RBC Coarse stippling: thalassemia, lead poisoning, myelodsyplastic states |
|
|
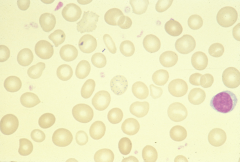
Howell-Jolly Body: single dense round inclusion of magenta color (remnant of nucleus) -asplenia, also in megaloblastic anemia, and myelodysplastic states. |
|
|
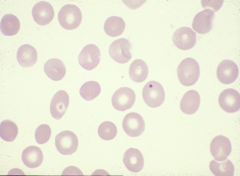
A: platelet B: Howell-Jolly body |
|
|
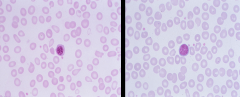
Nucleated red blood cell left: nucleated RBC? right: lymphocyte? -associated with stress such as acute hemorrhage, severe anemia, hemolysis, or a true marrow neoplasm |
|
|
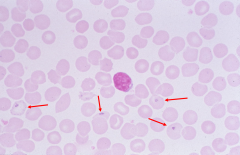
Pappenheimer Bodies: small blue inclusions usually eccentrically located (accumulations of iron) -associated with iron overload in marrow and asplenia |
|
|
cell with Pappenheimer bodies |
siderocyte |
|
|
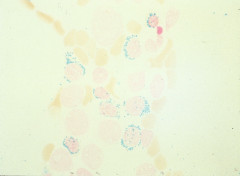
sideroblast:nucleated RBC with Pappenheimer bodies |
|
|
nucleated RBC with iron around nucleus |
ringed sideroblast |
|
|
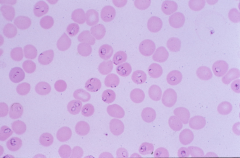
Malaria - Plasmodium falciparum |
|
|
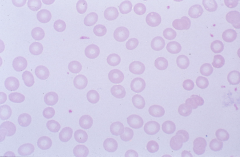
-ringed-shaped structure that stains red-blue and thought to be remnant of microtubules -associated with disordered erythropoiesis |
Cabot Ring |
|
|
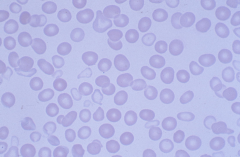
Hypochromic RBC |
|
|
Dimorphic RBC -normocytic, normochromic cells and microcytic, hypochromic cells -seen in patients with transfusions |
|
|
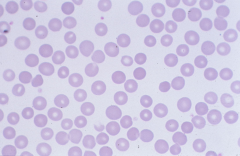
Spherocytes - hyperchromic: absent central palor -only seen in hereditary spherocytosis |
|
|
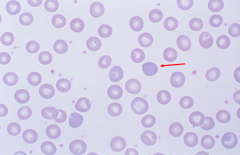
Polychromasia: diffuse blue color of RBC, indicative of young RBC (reticulocyte) |
|
|
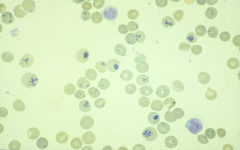
Reticulocytes: young RBC that is slightly larger than mature RBC -may be seen as polychromasia, but best detection is by reticulocyte count |
|
|
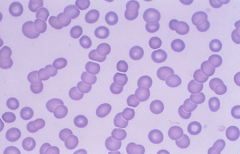
Rouleaux: sticking together of RBCs due to loss of zeta potential caused by increase of fibrinogen or gamma globulins |
|
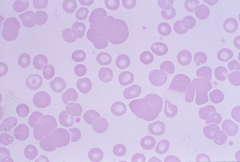
|
Cold Agglutinin: agglutinated clumps of RBCs due to auto antibodies of IgM type |
|
|
formula for RI |
RC x (Hct/45) x (1/f) = RI greater than 35: f =1 greater than 25: f = 1.5 greater than 15: f = 2 less than 15: f = 2.5 |
|
|
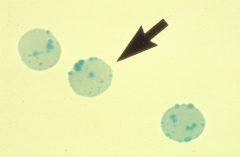
Heinz bodies: only seen in supra-vital staining -precipitated hemoglobin -indicative of unstable hemoglobin -associated with G-6-PD deficiency |
|
|
target cell differential |
-iron deficiency anemia -beta thalassemia -sickle cell anemia |
|
|
ringed sideroblasts differential |
-sideroblastic anemia
-hemochromatosis -myelodysplastic disorder (dyserythropoiesis) -RARS |
|
|
Howell Jolly Body differential |
-HS patient who has undergone splenectomy -sickle cell anemia - autosplenectomy |
|
|
Heinz Body differential |
G6PD deficiency |
|
|
bite cell differential |
G6PD deficiency |
|
|
helmet cell differential |
microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (TTP, DIC, HUS) |
|
|
tear drop cells differential |
primary myelofibrosis |
|
|
Pseudo-Pelger-Huet cells and donut cells |
Dysmyelopoiesis PPH cells: hypolobated, hypogranular neutrophils |
|
|
smudge cells, soccer ball cells, |
CLL |

