![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Temporal Lobe |
Auditory area. |
|
|
parietAL lobe |
Primary somatosensory cortex. |
|
|
frontal lobe |
1) Primary (somatic) motor cortex. 2) Motor speech (Broca's) area. 3) Premotor cortex. 4) Seat of intelligence, abstract reasoning |
|
|
Occipital lobe |
visual area |
|
|
Insula |
Gustatory (taste) area. |
|
|
Thalmus |
A major relay station for sensory information ascending to the cerebral cortex. Contains many specialized nuclei. |
|
|
prefrontal cortex |
This brain area associates experiences necessary for the production of abstract ideas, judgment, and conscience. |
|
|
primary (somatic) motor cortex |
The axons from this area form the major pyramidal (corticospinal) tracts. |
|
|
hypothalmus |
This area is the main visceral control center of the body. |
|

|
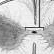
site of sensory neuron cell bodies |
|
|
gray commisure |
|

|
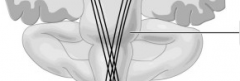
site of somatic motor neuron cell bodies |
|

|
consists entirely of interneuron cell bodies |
|
|
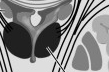
pons |
|
|
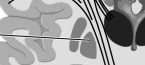
thalmus |
|
|
globus pallidus |
|

|
caudate nucleous |
|

|
corpus callosum |
|
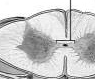
|
area that encloses the central canal |
|
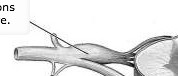
|
unipolar neurons are found here |
|

|
site of auotonomic motor neuron cell bodies |
|
|
cervial enlargement |
Where nerves serving the upper limbs arise. |
|
|
filum terminale |
Anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx. |
|
|
cauda equina |
Collection of nerve roots at the inferior end of the vertebral canal. |
|
|
conus medullaris |
Inferior point of termination of the spinal cord in an adult. |
|
|
abducens |
Turns the eyeball laterally. |
|
|
vagus |
Helps to regulate blood pressure and digestion. |
|
|
vestibulocochlear |
Serves the senses of hearing and equilibrium. |
|
|
olfactory |
Receptors located in epithelium of the nasal cavity. |
|
|
accessory |
Rootlets arise on the spinal cord, enter the skull through the foramen magnum and exit the skull through the jugular foramen. |
|
|
rufinni ending |
Bulbous corpuscle |
|
|
meissner corpuscle |
Tactile corpuscle |
|
|
pacianian corpuscle |
Lamellar corpuscle |
|
|
thalmus |
Gateway to the cerebrum. |
|
|
cerebellum |
Ensures coordination and balance. |
|
|
brainstem |
Produces automatic behaviors necessary for survival. |
|
|
cerebrum |
Executive suite. |
|
|
hypothalmus |
Visceral command center. |
|
|
plantar |
Tests both upper and lower motor pathways. The sole of the foot is stimulated with a dull instrument. |
|
|
crossed-extensor |
Consists of an ipsilateral withdrawal reflex and a contralateral extensor reflex; important in maintaining balance. |
|
|
flexor |
Produces a rapid withdrawal of the body part from a painful stimulus; ipsilateral. |
|
|
stretch |
Prevents muscle overstretching and maintains muscle tone. |
|
|
tendon |
Produces muscle relaxation and lengthening in response to tension; the contracting muscle relaxes as its antagonist is activated. |

