![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Define endochondral ossification |
Cartilage which is replaced by bone |
|
|
|
Define intra-membranous ossification |
Formation of bone from fibrous connective tissue |
|
|
|
What structure do the lateral palatal shelves form? |
Maxillary process |
|
|
|
At what age do palatine shelves form? |
6 weeks IU |
|
|
|
Name 5 sutures present in foetal skull |
Frontal, Sagittal, lambdoidal, coronal, squamousal |
Me |
|
|
Name 5 sutures present in foetal skull |
Frontal, Sagittal, lambdoidal, coronal, squamousal |
Me |
|
|
Describe the embryo at three weeks of IU |
Flat trilaminar discs, consisting of 3 layers |
|
|
|
Name 5 sutures present in foetal skull |
Frontal, Sagittal, lambdoidal, coronal, squamousal |
Me |
|
|
Describe the embryo at three weeks of IU |
Flat trilaminar discs, consisting of 3 layers |
|
|
|
What age does facial development begin? |
3 IU |
|
|
|
At what stage does the dental lamina grow posteriorly to form the buds for secondary molar teeth? |
Late bell |
|
|
|
At what stage does the dental lamina grow posteriorly to form the buds for secondary molar teeth? |
Late bell |
|
|
|
At what stage is dentine first layed down? |
Cap |
|
|
|
At what stage does the dental lamina grow posteriorly to form the buds for secondary molar teeth? |
Late bell |
|
|
|
At what stage is dentine first layed down? |
Cap |
|
|
|
What stage do stimulated ameloblasts lay down enamel? |
Bell |
|
|
|
What is the function of stratum inter medium? |
Protein synthesis. Transport of materials to/ from the ameloblasts |
|
|
|
What's the name for the mesenchyme surrounding the tooth germ? |
Dental follicle |
|
|
|
What are the 3 stages of tooth development? |
Initiation Morphogenesis Histogenesis |
|
|
|
the oral epithelium thickens and invaginates into mesenchyme - what does this form? |
Primary epithelial band |
|
|
|
What is present at 6 weeks IU? |
Dental laminar Tongue Meckels cartilage |
|
|
|
What is present at 6 weeks IU? |
Dental laminar Tongue Meckels cartilage |
|
|
|
What's present at 7 weeks IU? |
Dental laminar Vestibular laminar Tooth bud Ectomesenchyme Tongue Meckels cartilage Bone |
|
|
|
What are tooth germs? |
Swellings that begin to develop on the deep surface of dental lamina. They are a collection of cells who's functions are to form the dental tissues |
|
|
|
What maps out the occlusal pattern of the teeth? |
Configuration of the IEE (14th week) |
|
|
|
When does the stratum intermedium fist appear? |
Bell stage |
|
|
|
When does the stratum intermedium fist appear? |
Bell stage |
|
|
|
what does the SI consist of? |
2-3 layers of flattened cells |
|
|
|
What type of cells is the IEE made from ? |
Cuboidal > columnar Columnar at bell stage |
|
|
|
What type of cells is the IEE made from ? |
Cuboidal > columnar Columnar at bell stage |
|
|
|
What is late bell stage associated with? |
Formation of hard tissues |
|
|
|
When does the dental lamina grow backwards from the second pre primary molar to make room for permanent molar teeth ? |
18th week IU |
|
|
|
When does the dental lamina grow backwards from the second pre primary molar to make room for permanent molar teeth ? |
18th week IU |
|
|
|
What is formed at late bell? |
Dentine Triggers enamel lay down |
|
|
|
What is the inner lining of the bell compose of? |
Odontoblasts |
|
|
|
What is the inner lining of the bell compose of? |
Odontoblasts |
|
|
|
What does the out surface of the bell consist of? |
Ameloblasts |
|
|
|
What is the inner lining of the bell compose of? |
Odontoblasts |
|
|
|
What does the out surface of the bell consist of? |
Ameloblasts |
|
|
|
What happens at the late bell stage to the ameloblasts? |
They migrate outwards to create/ form the crystalline enamel of the tooth |
|
|
|
What happens to the Odontoblasts at this stage? |
The migrate inwards to form tubular dentine (like the pulp) |
|
|
|
What happens when to tooth erupts in the mouth? |
Ameloblasts de shed IEE and OEE join downwards (hurts tooth sheath) |
|
|
|
What happens when to tooth erupts in the mouth? |
Ameloblasts de shed IEE and OEE join downwards (hurts tooth sheath) |
|
|
|
When the tooth erupts in the mouth what happens to the apex? |
Tooth is still forming, apex is open. |
|
|
|
What happens when to tooth erupts in the mouth? |
Ameloblasts de shed IEE and OEE join downwards (hurts tooth sheath) |
|
|
|
When the tooth erupts in the mouth what happens to the apex? |
Tooth is still forming, apex is open. |
|
|
|
What age does the apex close? |
2 years after eruption (primary and secondary) |
|
|
|
What happens when to tooth erupts in the mouth? |
Ameloblasts de shed IEE and OEE join downwards (hurts tooth sheath) |
|
|
|
When the tooth erupts in the mouth what happens to the apex? |
Tooth is still forming, apex is open. |
|
|
|
What age does the apex close? |
2 years after eruption (primary and secondary) |
|
|
|
What happens to the Odontoblasts are eruption? |
They maintain in the tooth, lining the pulp chamber, acting as circulation for dentine |
|
|
|
Match the cells listed to the tissues they are found in: Cementocytes |
Cementum |
|
|
|
What is the brannstorms hydrodynamic theory? |
Movement of fluid within the dental tubules *most widely accepted** |
|
|
|
What does this show? |
-Enamel shows attrition and wear, -Dentine develops dead tract below the areas of wear -Pulp shrinks -Secondary dentine is laid down -Cells in pulp decrease -Vascularity of pulp decreases -Cementum becomes thicker at apex |
|
|
|
Location of Fibres Midroot to adjacent alveolar bone |
Horizontal fibres |
|
|
|
Cervical root to alveolar crest |
Alveolar crest fibres |
|
|
|
Continuous around neck of tooth |
Circumferential fibres |
|
|
|
Between the roots of the alveolar bone |
Interradicular |
|
|
|
Apical one their of the root to adjacent alveolar bone |
Oblique |
|
|
|
Cervical tooth (neck of the tooth) to tooth medial or distal to it |
Transeptal fibres |
|
|
|
Ondontoblasts |
Pulp |
|
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Bone |
|
|
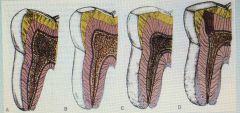
What does this show? |
-Enamel shows attrition and wear, -Dentine develops dead tract below the areas of wear -Pulp shrinks -Secondary dentine is laid down -Cells in pulp decrease -Vascularity of pulp decreases -Cementum becomes thicker at apex |
|
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Alveolar bone |
|
|
|
Fibroblasts |
Periodontal ligament |
|
|
|
How much of acellular and cellular cementum covers the root surface ? |
Acellular - 2/3 Cellular - 1/3 |
|
|
|
The apex of the root is thicker and made up of cellular cementum, true of false? |
True |
|
|
|
What is the innervation theory? |
Nerve fibres of pulp pass into dentinal tubules |
|
|
|
What is the Odontoblast receptor theory? |
Cells responsible for dentinal tubules act as receptors transmitting nerve impulses |
|

