![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2. Discuss the concepts of homologous chromosome, diploidy,haploidy. What characteristics are share between two chromosomes consider to be homologous?
|
homologous chrmsme shre properties: overall lenght,position cetromere(metacentric,submetacentric, acrocentric, telocentric)
homologous not identical but similiar diploidy 2n-both memberss of homologous pair of chromosomes are present humans 46 haploid n-contains one chromosome of each homologous pair of chromosomes human 23 |
|
|
What characteristics are share between two chromosomes consider to be homologous?
|
the change from a diploid(2n) to haploid(n) occurs during reduction division whn tetrads become dyads during meiosis I.
refering to # human chrmsme, prmary spermatocyte(2n=46)becomes two secondary spermatocytes each with n=23 |
|
|
interphase
|
interphase-intial stage of cell cycle replication of DNA of each chromosome (S-Phase) synth DNA)
-no DNA synthesis occurs before and after interphase GI & GII(G2) interphase-absent visible chromosomes |
|
|
what genetic material is partitioned into daughter cell during nuclear division___________.complex and precise.
|
karyokinesis
|
|
|
what do we call cytoplasmic division?less complex than karyokinesis*
|
cytokenesis
|
|
|
cytoplasmic organelles either replicate themselves, arise from existing membrane structure or are synthesized_______(anew) in each cell.
|
de novo
|
|
|
What is going during G1,G2 and interphase S-phase?
|
intesive metabolic activity, cell growth, and cell differentiation
|
|
|
What happens by the end of G2 cell size?
|
the volume of the cell has roughly doudble, DNA is replicated, and Mitosis is intaited
|
|
|
What is G1 an interesting in study of cell proliferation and its controll?
|
cell either withdraws from the cycle or becomes quiescent and enter the G0 STAGE(don't proliferate)
or become committed to initiating DNA synthesis and completing the cycle |
|
|
4) Describe the events that characterize each stage of mitosis?
|
interphase_chrmsme extended,uncoiled form chromatin
there are five stages of mitosis* prophase-chrms coil up,shrten,centrioles divide&move apart prometaphase:chrm clrly dble strctre, centrle reach oppste poles,spindle fibers form metaphase:centromere aling on metaphase plate anaphase: centromeres split and daughter chromosomes migrate to opposite poles.motor proteins,daught telophase:daughter chromosomes arrive at the poles, cytokenesis commences plan however form cell plate midle lamell |
|
|
What is mitosis?*
|
cell division resulting in the rpoduction of two cells, each with same chromosome and genetic complement as the parent cell
|
|
|
during anaphase migration is made possible by the binding of spindle fibers to structure associated with centromere of each chromosome called_________. what?
|
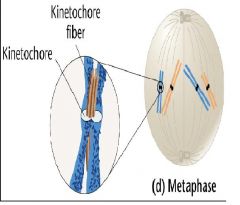
Kinetochore
|
|
|
What does spindle fiber consist of ?
|
microtubules which further consist of subunits of protien tubilin. grow out of the opposite poles of cell two region containing centriole
|
|
|
what is refered to each sister chromatids when each sister chrmd dijoin move opposite of the pole(anaphase)?
|
daughter chromosomes
motor protien atp propel chromosome daughter to opposite end of cell |
|
|
5# if an organism has diploid # of 16, how many chromatids are visible at the end of mitotic prophase? how many chromosomes are moving to each pole during anaphase of mitosis?
|
prophase double the chromoses2n=16-- 32
prophase 32 chromotids are visible anaphase 16 and 16 different poles daughter chromosomes |

