![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Function of Na/K channel during AP
*4 steps* |
1. Na channel opens depolarizing mmb potential away from resting potential towards E_na
2. FAST: depolarization opens more Na+ channels ( + feedback) 3. SLOW: Delay; K+ channels open causing hyperpolarization of mmb potential to E_k 4. Delay; Na+ channels inactivate helping K+ channels hyerpolarize mmb potential |
|
|
Important properties of voltage-gated ion channels
1. Pore |
pore controls ion permeation
-selectivity: which ions go through the channels -channel conductance: how rapidly ions pass -channel blockers: bind w/i the pore |
|
|
Important properties of voltage-gated ion channels
1. Pore 2. Gates |
gates control the gating of the channel
-acitivation --> channel opening -inactivation/deactivation --> channel closing |
|
|
Molecular identification of voltage gated K+ channels involved a
|
mutant fly (shaker) w/ defective muscle K+ channel
|
|
|
1. Fly with shaker mutation are ..
2. Treat WT flies with drug that blocks K+ channel causes... Suggests that..... 3. Gene identified using... |
1. hyperexcitable Ishake their legs uner anesthesia)
2. causes similar phenotype Suggests that --> K+ channel is defective 3. positional cloning |
|
|
Expression of gene for functional analysis
Step 1 |
1. synthesize mRNA corresponding to the gene of interest
|
|
|
Expression of gene for functional analysis
Step 2 |
express the mRNA by injecting into into Xenopus (frog) oocyte
|
|
|
Expression of gene for functional analysis
Step 3 |
measure the channels function by voltage clamp
|
|
|
Expression of gene for functional analysis
*picture of process |
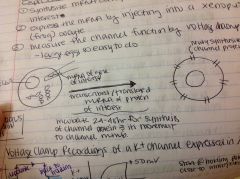
|
|
|
Voltage clamp recordings of K+ channel expressed in Xenus oocytes
*Conclusions from experiment* |

1. expressed protein conducts K+ ions
2. opens among mmb depolarization and closes on repolarization 3. particular K+ channel investigated does not inactivate (others do) --> as long as you depolarize it stays open |
|
|
From learning the sequence of the proteins, the scientists were able to do 3 things.
|
1. functional expression of mRNA
2. predict the structure of the channel (look for long stretches of hydrophobic a.a. for transmmb domains) 3. identify homologous proteins |
|
|
Predicting mmb topology (structure) of voltage gated K+ channel
|

1) Voltage gated K+ channel subunits contain: 6 alpha helical segments termed S1-S6
2) a re-entrant loop between S5-S6 3) large N terminal segment 4) Functional channels are tetramers a) 4 subunites are designated I-IV |
|
|
From genome, found a large number of voltage gated- channel genes which are called...
-Sequence homology among which channels? - Why so many? |
Protein Superfamily
-Na+, Ca+, K+ channels (Cl- unrelated) -different neurons respond differently to certain excitation (release more or less ions, time open) |
|
|
Different K+ channel genes encode channels w/ functional differences.
-two different ones |
Normal channels open for depol. and inactivate when depol. remains
-Inward rectifier & 2-pore |
|
|
K+ channel: Inward Rectifier
-----> Function & structure |
Function: K+ channel that opens in response to hyperpolarization (negative current, -120 mV)
Structure: only has re-entrant loop (S5-S6) and lacks the N terminal 4 transmmb domains -has 4 subunits |
|
|
K+ channel: 2-pore
-----> Function & structure |
Function: K+ channel modulated by pH --> responds to basic pH conditions
-not gated by voltage Structure: only 2 subunits (min. req to be a fxn-al channel) -two S5-S6 subunits on either side |
|
|
Inward Rectifier and 2-pore similarities
-I.R. looks like it is gated by voltage but it is actually... |
Both lack the 4th N terminal transmmb domain so both are not gated by voltage
-has something in its structure that is sensitive to changes in mmb potential |
|
|
Diverse channel types underlie...
-voltage clamp recording involves -Look at AP fired what can be seen? |
different firing properties
-intracellular recordings: inject current --> initial depol. --> reach threshold --> neuron fires AP -some fire fast and inactivate quickly & vice versa because *** expression of different types of voltage gated potassium channels causes differences in the electrical properties of the channel *** |
|
|
-Structure of Voltage Gated Na+ and Ca+ channels (2)
-Each domain has? -They are... |
1) 4 main domains, each domain subunit contains 6 transmmb domains
2) each domain is homologous to a K+ channel subunit -they are monomers 1) 6 alpha helical segments termed S1-S6 2) a non-helical re-entrant loop (P-Loop) between S5-S6 -monomers |
|
|
-Many K+, Na+, and Ca+ channels also have a ___ subunit
-What does this subunit do? -Subunits that form the actual channel are? |
Beta subunit
-not req. to make the channel work, they MODULATE (regulate) the FUNCTION of the ion channel ----> Regulate by: making the channel more or less sensitive, incr/decr conduction, incr/decr closure time -the ALPHA subunits form the channel |

