![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
257 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Do not DELEGATE what you can EAT |
EAT
E-evaluate A-asses T-teach |
|
Addison's |
Down (Na+) Down (tension), Down (blood vol), UP (Ka+) Down (GLY)
HypoNatremia, HyPOtension, decreased blood vol., HyperKAlemia, HypoGLYcemia |
|
Cushing's |
UP (Na+) UP (tension) UP (Blood Vol) Down (Ka+) UP (GLY)
HyperNatremia, Hypertension, High blood pressure, HypoKalemia, Hyperglycemia
|
|
|
No Pee, no K+ |
Check ruing output without urine output do not give Potassium (K+) |
|
|
eleVate -VEINS |
dAngle Arteries |
|
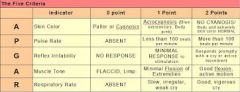
APGAR |
A- appearance (color all pink, pink and blue, blue (pale)) P-pulse (>100, <100, absent) G- Grimace (cough, grimace, no response) A- Activity (flexed, flaccid, limp) R-Respiration (strong cry, weak cry, absent) |
|
|
Transmission -Based Precautions: Airborne: MY CHICKEN HEZ TB
My- measles Chicken - Chicken Pox/Varicella (disseminated) Hez- Herpez Zoster Shingles TB |
Private Room Negative pressure with 6-12 air exchanges/ hr Mask N95 for TB |
|
|
Droplet: THINK SPIDERMAN
Private Room or cohort Mask |
S- sepsis S-scarlet fever S-Streptococcal pharyngitis P-parvovirus B19 P-pneumonia P-Pertussis I-Influenza D- Diptheria (pharyngeal) E-Epiglottitis R- Rubella M-Mumps M-meningitis M-mycoplasma or meningeal pneumonia An- Adenovirus |
|
|
Contact Precaution: VCHIPS
Gloves, gown, wash hands
|
v-Varicella Zoster C- cutaneous Diptheria H-Herpez simplex I-Impetigo P-pediculosis S-Scabies |
|
|
Contact Precautions: Mrs. wee |
M-multidrug resistant organism R-Respiratory infx S-Skin infx
W- wound infx E-enteric infx E-Eye infx
|
|
|
Pulmonary Embolism:
S&S: chest pain Difficulty breathing Tachycardia Pale/Cyanotic Sense of impending doom |
Turn patient to LEFT side and lower the HOB |
|
|
Woman in Labor w/ Un-reassuring FHR |
Late decels, decreased variability, fetal bradycardia,etc.
1)Turn on LEFT side 2) give O2 3) stop pitocin 4) increase IV fluids |
|
|
Tube Feeding with Decreased LOC |
Turn to the RIGHT side (promotes emptying of the stomach) with the HOB elevated to prevent aspiration
|
|
|
During Epidural puncture |
side lying |
|
|
After Lumbar puncture (also oil based myelogram |
pt lies in flat supine (to prevent headache and leaking of CSF) |
|
|
Pt with Heat stroke |
Lie flat with legs elevated |
|
|
During continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) |
Catheter is taped to thigh so leg should be kept straight no other positioning restrictions |
|
|
After Myringotomy |
Position on side fear after surgery (allows drainage of secretions) |
|
|
After Cataract Surgery |
pt will sleep on unaffected side with night shield for 1-4 weeks |
|
|
After Thyroidectomy |
Low or semi-fowler's support head, neck, and shoulders |
|
|
Infant with Spina Bifida |
position PRONE (on abdomen) so that sac does not rupture |
|
|
Buck's traction (skin traction) |
elevate foot of bed for counter traction |
|
|
After total hip replacement |
don't sleep on operated side dont flex hip more than 45-60 degree don't elevate HOB more than 45 degree Maintain hip abduction by separating thigh with pillows |
|
|
Prolapse Cord |
Knee to chest position or Trendelensburg |
|
|
Infant with CLEFT lip |
position on back or in infant seat to prevent trauma to suture line
while feeding hold in upright position |
|
|
to prevent dumping syndrome |
post op. ulcer/stomach surgeries -
eat in a reclining position, lie down after meals for 20-30 min (also restrict fluids during meals, low CHO and fiber diet, small frequent meals) |
|
|
Above the KNEE AMPUTATION |
Elevate for first 24 hours on pillow (do not elevate), position prone daily to provide for hip extension |
|
|
Below the knee amputation |
foot of bed elevated for the first 24 hrs., position prone daily to provide for hip extension |
|
|
Detach retina |
Area of detachment should be in the dependent position |
|
|
Administration of enema |
position in left side lying (sims) with knee flexed |
|
|
After supratentorial surgery (incision behind the hairline) |
Elevate HOB 30-45 degrees
|
|
|
after infrtentorial surgery (incision at nape of neck) |
position pt flat and lateral on either side |
|
|
During internal radiation |
on bed rest while implant in place |
|
|
Autonomic dysreflexia/hyperreflexia S&S: pounding headache, nasal congestion, goose flesh, bradycardia, hypertension, profuse sweating |
place client in sitting position (elevate HOB) first before any other implementation |
|
|
SHOCK |
bed rest with extremities elevated 20 degrees knees straight, head slightly elevated (modified trendelenburg) |
|
|
Head Injury |
elevate HOB 30 degrees to decrease ICP (normal ICP 1-20 above 20 treatment) |
|
|
Peritoneal Dialysis when outflow is inadequate |
turn pt from side to side before checkin for kinks in tubing |
|
|
Lumbar Puncture |
after the procedure, the client should be placed in supine position for 4 -12 hrs. as prescribed |
|
|
Demorol for Pancreatitis |
not morphine sulfate |
|
|
Myasthenia Gravis |
worsens with exercise and improves with rest
|
|
|
Myasthenia crisis |
A positive reaction to Tensilon-will improve symptoms |
|
|
Cholinergic Crisis |
Caused by excessive medication: stop medication
GIVING tensilon test will make it worse |
|
|
Head injury medication |
mannitor (osmotic diuretic)- crystalizes at room temp so always use FILTER NEEDLE |
|
|
Prior to a liver biopsy |
It is important to be aware of the lab results for pro thrombin time (20-45) (max 112) |
|
|
From the A** (diarrhea) |
Metabolic ACIDOSIS (A**IDOSIS) |
|
|
From the Mouth (voMitus) |
Metabolic Alkalosis |
|
|
Myxedema/Hypothyroidism |
Slowed physical and mental function , sensitivity to cold, dry skin, and hair |
|
|
Grave's disease/HYPERthyroidism |
Accelerated physical and mental function, sensitivity to heat, fine soft hair |
|
|
Post thyroidectomy |
Semi-fowle's, prevent neck flexion/hyperextension, trace at bedside |
|
|
Hypo-parathyroid |
CATS: C-convulsions A-arrhythmias, T-tetany S-spams, S-stridor (decreased Ca+)
HIGH CALCIUM high (Norm: 9-11) Low phosphorous diet (3.0-4.5) |
|
|
hyper-parathyroid |
Fatigue, muscle weakness, renal calculi, back and joint pain (Increased CALCIUM)
Low Ca+ (9-11) high phosphorus diet (3.0-4.5) |
|
|
Diabetes Insipidus (decreased ADH) |
excessive urine output and thirst, dehydration, weakness, adm. Pitressin |
|
|
SIADH (increased ADH) |
Change in LOC, Decreased deep tendon reflexes, tachycardia, n/v, headache, adm. Declomycin, diuretics |
|
|
Hypovolemia |
Increased temp, rapid weak pulse, increase reap. hypotension, anxiety, urine specific gravity >1.030 not dilute |
|
|
Hypervolemia |
bounding pulse SOB Dyspnea Rares/crackles peripheral edema HTN Urine specific gravity <1.010
Semi-Fowler's |
|
|
HypoKalemia |
Muscle weakness Dysrhythmias Increase K (raisins, bananas, apricots, oranges, beans, potatoes, carrots, celery)
|
|
|
HyperKalemia (murder) |
Muscle weakness Urine (oliguria/aniuria) Respiratory depression Decreased cardiac contractility ECG changes Reflexes |
|
|
HypoNatremia |
Nausea, muscle cramps, increased ICP, muscular twitching, convulsions,
osmotic diuretics and FLUIDS |
|
|
HYPERnatremia |
Increased temp Weakness Lack of coordination abd pain confusion absent tendon reflexes sedative effect on CNS |
|
|
HypoCalcemia:CATS |
Convulsions Arrythmias Tetany Spasms and stridor |
|
|
HyperCalcemia |
muscle weakness lack of coordination abdominal pain confusion Absent tendon reflexes sedative effect on CNS |
|
|
Hypomagnesium |
tremors tetany seizures Dysrhythmias depression confusion dysphagia dig toxicity
|
|
|
HyperMG |
depresses the CNS Hypotension facial flushing muscle weakness absent deep tendon reflexes shallow respiration EMERGENCY |
|
|
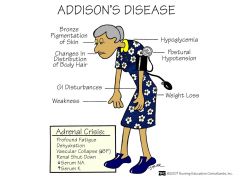
Addison's |
Hypo NA hyperK HypoGLY dark pigmentation decreased resistance to stress fractures alopecia wgt loss GI distress
|
|
|
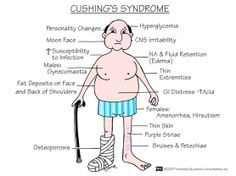
Cushing's |
HyperNa HypoK hYperGLY prone to infection muscle wasting weakness edema HTN hirsutism moonface buffalo hump |
|
|
Addisonian Crisis |
N/V Confusion abd. pain extreme weakness hypoglycemia dehydration decreased BP
|
|
|
Pheochromocytoma |
Hypersecretion of EPI/norepi, persistent HTN, increased HR hyperglycemia diaphoresis tremor pounding headache avoid stress frequent bathing and res breaks avoid cold stimulating food surgery to remove tumor |
|
|
Neuroleptic malignant syndrom (NMS) |
NMS is like S&M: -you get hot (hyperpyrexia) -Stiff (increased muscle tone) -sweaty (diaphoresis) -BP, Pulse, and respirations go up and -you start to drool |
|
|
never get pregnant with a German |
dangerous when you get pregnant with german measles |
|
|
when drawing up regular insulin and NPH together remember: RN |
Regular comes before the NPH |
|
|
Tetralogy of Fallot: HOPS |
Drop (child drops to the floor or squats) defect, septal right ventricular hypertrophy overriding aorta Pulmonary stenosis |
|
|
MAOI's that are used as antidepressants |
weird way to remember: pirate say ARRR so think;
Parrrnate Narrrdil Marrplan
PANAMA - metallic bitter taste |
|
|
Digoxin |
check pulse, less than 60 hold check dig levels (0.5-2) & potassium (3.5-5.0) |
|
|
Amphojel: |
tx of GERD and kidney stones
watch out for constipation |
|
|
Vistaril |
Tx of anxiety and also itching
Watch for dry mouth, given preoperatively commonly |
|
|
Versed |
Given for conscious sedation watch for respiration depression and hypotension |
|
|
PTU and Tapazole |
prevention of thyroid storm |
|
|
Sinemet |
tx. of parkinsons sweat saliva urine may turn reddish brown occasionally causes: drowsiness |
|
|
Artane |
Tx of parkinson Sedative effect also |
|
|
congentin |
tx of parkinson and extrapyramidal effects of other drugs |
|
|
Tigan |
tx. of post op N/V and for nausea associated with gastroenteritis |
|
|
Timolol (timoptoc |
tx. of glaucoma |
|
|
Bactrim |
Antibiotic Don't take if allergic to sulfa drugs common SE: diarrhea Drink plenty of fluids |
|
|
Gout meds |
Probenecid (Benemid) Colchicine Allopurinol (Zyloprim) |
|
|
Apresoline (hydralazine) |
tx of HTN or CHF
Report flu like symptoms Rise slowly from sitting Lying position Take with meals |
|
|
Bentyl |
tx of irritable bowel
Assess for anticholinergic side effects
|
|
|
Calan (verapamil) |
Calcium Channel Blocker
Tx of HTN, angina
Assess for constipation |
|
|
Carafate |
tx of duodenal ulcers Coats the ulcer so take before meals
|
|
|
Theophylline |
Tx of asthma or COPD Therapeutic drug level 10-20 |
|
|
Mucomyst |
Is the Antedote to tylenol and administered orally |
|
|
Diamox |
tx of glaucoma, high altitude sickness
don't take if allergic to sulfa drugs |
|
|
Indocin (NSAID) |
tx of arthritis (osteo, rheumatoid, gouty) bursitis and tendonitis |
|
|
synthroid |
tx of hypothyroidism May take several weeks to take effect Notify doctor of chest pain Take in the AM on empty stomach Could cause hyperthyroidism |
|
|
Librium |
Tx of alcohol w/d don't take alcohol with this
very bad N/V |
|
|
Oncovin (vincristine) |
tx of leukemia give IV only |
|
|
Kwell |
Tx of scabies and lice (scabies) apply lotion once and leave on for 8-12 hrs. (lice) use the shampoo and leave on for 4 min. with hair uncovered then rinse with warm water and comb with a fine tooth comb |
|
|
Premarin |
tx after menopause estrogen replacement |
|
|
Dilantin |
Tx of seizures therapeutic drug level 10-20 |
|
|
Navane |
tx. schizophrenia Assess for EPS |
|
|
Ritalin |
tx of ADHD
Assess for heart related side effects report immediately child may need drug holiday b/c it stunts growth |
|
|
Dopamine (Inotropine) |
Tx of Hypotension Shock Low cardiac output poor perfusion to vital organs monitor EKG for arrhythmias monitor BP |
|
|
FHR patterns in OB |
V C E H A O L P
V-variable decels C-cord compression cause E-early decals H- head compression caused A-accels O-Okay, not a problem L-late decels P-placental insufficiency can't fill
|
|
|
For cord compression, place the mother in the trendelenberg position because this removes pressure of the presenting part off the cord. If her head is down, the baby is no longer being pulled out of the body by gravity
If the cord is prolapsed, cover it with sterol saline gauze to prevent drying of the cord and to minimize infection |
For late decels., turn the mother to her left side, to allow more blood flow to the placenta
For any kind of bad fetal heart rate pattern, you give O2, often by mask
when doing an epidural anesthesia hydration before hand is a priority
Hypotension and bradypnea/bradycardia are major risks and emergencies |
|
|
Never check the monitor or a machine as a first action always assess the patient first. For example listen to the FETAL heart tones with a stethoscope in nclex land. Sometimes its hard to tell who to check on first, the mother or the baby |
It's usually easy to tell the right answer if the mother or baby involves a machine. If you are not sure who to check first, and one of the choices involves the machine that;s a wrong answer |
|
|
IF a baby is posterior presentation sounds are heard at the sides |
if baby is anterior the sounds are heard closer to midline between the umbilicus and where you would listen to a posterior presentation |
|
|
If the baby is breech |
the sounds are high up in the funds near the umbilicus and where you would listen to a posterior presentation |
|
|
Ventilator alarms;
HOLD
|
H-high alarms = O- obstruction due to increase secretions, kinks, pt coughs, gag or bites
L-low alarm = D-disconnection or leak in ventilator or in pt airway cuff, pt stops spontaneous breathing |
|
|
Blood sugarS |
HOT AND DRY sugar high (hyperglycemia)
Cold and clammy need some candy (hypoglycemia) |
|
|
ICP vs. SHOCK have opposite V/S
|
ICP- Increased BP, Decreased PULSE, decreased RR
Shock- decreased BP, Increased PULSe, increased RR |
|
|
Cor pulmonae |
Right heart failure caused by left ventricular failure (pick edema, JVD, if it is a choice) |
|
|
Heroin withdrawal |
neonate irritable, and poor sucking |
|
|
Jews do not eat |
meat and milk together |
|
|
brachial pulse |
pulse area CPR on an infant |
|
|
Test child for lead poisoning around |
12 months of age |
|
|
bananas, potatoes, citrus fruits |
source of potassium (3.5-5.0) |
|
|
Cultures are obtained before starting |
any IV antibiotics |
|
|
a pt with leukemia may have epistaxis (nose bleeds) b/c of |
low platelets (150,000-450,000) |
|
|
Best way to warm a newborn |
skin to skin contact covered with a blanket on mom |
|
|
when a pt comes in and she is in active labor |
the nurse first action is to listen to the FHR |
|
|
Phobic disorders |
Use systemic desensitization |
|
|
Hyperthyroidism Think: |
Michael Jackson Thriller: Skinny Nervous Bulging EYES Up all night Heart beating fast |
|
|
Atropine |
Used to decrease secretions |
|
|
Phenergan |
An antiemetic used to reduce nausea |
|
|
Diazepam |
Is commonly used tranquilize given to reduce anxiety before O.R. |
|
|
demerol |
is used for pain control
Do not give demerol to pt with sickle cell crisis |
|
|
Iron injections should be given Z-track |
So they do not leak into SQ tissues |
|
|
A-aortic P-pulmonic E-Erb's point To-Tricuspid Man- Mitral |
APE to Man |
|
|
Oh (olfactory I) Oh (Optic II) Oh (Oculomotor (III) To ( trochlear IV) Touch (Trigeminal V) And (Abducens VI) Feel (Facial VII) A (Auditory VIII) Girls (Glossopharyngeal IX) Vagina (vagus X) And (Accessory XI) Hymen (hypoglossal XII)
|
Some Say S-Sensory, M-Motor, B-Both Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Bras Matter More |
|
|
Hyper NA tremia (135-145)
|
Skin flushed Agitation Low grade fever Thirst |
|
|
Development |
2-3 mo. -turns head side to side 4-5 mo.-grasps, switch and roll 6-7 mo.- sit at 6 and waves bye bye 8-9 mo.- stands straight at eight 10-11 mo. belly to butt 12-13 mo. twelve and up, drink from a cup |
|
|
hepatitis |
Hepatitis-ends in a VOWEL, comes from the BOWEL (HEP. A)
Hep B- Blood and bodily fluids Hep C- is just like B |
|
|
Apgar measures HR, RR, Muscle tone, Reflexes, skin color |
each 0-2 points 8-10 you're ok 0-3 resuscitate
|
|
|
Glasgow coma scale: EYES, verbal , Motor |
It is similar to measuring dating skills, max 15 points one can do it if below 8 you are in coma |
|
|
4.So to start dating you gotta open your eyes first, if you are able to do spontaneously and use them correctly to see whom you are dating you earn a 4. 3. If she has to scream on you to make you open them then you get a 3 1. you don't car to open even if she tries to hurt you
|
eyes |
|
|
Talk to him/her if you can: 4. You are oriented in situation and catches up to what you are saying you get a 4 3. if you like her to try not to be confused or get inappropriate words 3 2. if you just make incomprehensible sounds 2 1. no verbal response 1 |
verbal |
|
|
6. if you move well and appropriate 6
|
motor response |
|
|
the person who hyperventilates |
experiences respiratory alkalosis |
|
|
avoid salt substitutes when taking |
DIG (0.5-2) and K (3.5-5.0) supplements because many are potassium based |
|
|
signs of hypoxia |
restless anxious cyanotic tachycardia increased resp. (monitor ABG's) |
|
|
Addison's disease |
needs to "ADD" hormone |
|
|
Cushing's syndrome |
Have extra "cushion" of hormones |
|
|
Dumping syndrome |
Increase fat and protein, small frequent meals, lie down after meal to decrease peristalsis, wait 1 hr after meals to drink |
|
|
For blood types: "o" is the universal donor (remember "o" in donor) |
AB is the universal recipient (every one wants an AB average) |
|
|
Disseminated Herpes zoster is airborne precautions |
As to localized Herpes Zoster is Contact precautions. A nurse with localized herpez zoster Can care for pt as long as the pt are NOT immunosuppressed and the lesions must be covered! |
|
|
Fat soluble vitamins are |
Just remember DEAK |
|
|
give NSAIDS, corticosteroids, drugs for bipolar, cephalosporins, and sulfonamides with food |
Food and drugs |
|
|
Ativan is the treatment of choice for |
Status elipticus |
|
|
when using a bronchodilator inhaler in conjunction with a gluccocorticoid inhaler |
Administer bronchodilator first |
|
|
theophylline |
Increases the risk of digoxin toxicity and decreases the effects of lithium and dilantin |
|
|
INtal, an inhaler used to treat allergy induced asthma may cause bronchospasm |
think: Into the Asthmatic lung |
|
|
Isoniazid |
causes peripheral neuritis |
|
|
Peptic ulcers caused by H. Pylori are treated with |
Flagyl, Prilosec, and Biaxin
This treatment kills bacteria and stops production of stomach acid, but does not heal ulcer |
|
|
Weighted NI (Nasointerstinal tubes) must float from stomach to intestine |
Don't take the tube right away after placement, may leave coiled next to the pt on HOB. position patient on RIGHT to facilitate movement through pylorus |
|
|
Diaphragm must stay in place for 6 hours after intercourse |
They are also fitted so must be refitted if you loose wgt. or gain a significant amount of wgt |
|
|
best time to take growth hormone PM |
best time to take steroids, diuretics, aricept= AM |
|
|
carafate (Sulcrafate) before meals |
mucosal barrier; constipation |
|
|
Tagamet with food |
H2; messes with elderly people be careful |
|
|
antacids take |
after meals |
|
|
long term use of amphojel |
binds to phosphates, increase Ca+ , robs the bones, leads to increased Ca+ resort ion from bikes and weak bones |
|
|
Cushing's |
Ulcers r/t brain injury |
|
|
Cushing's triad r/t ICP in BRAIN |
HTN, bradycardia, Irregular Respiration |
|
|
Thyroid storm |
is hot (hyperthermia) PTU given |
|
|
Myxedema coma is COLD |
Hypothermia |
|
|
Glaucoma intraoccular pressure is greater than the normal (22 mmHg) |
give miotics to constrict (pilocarpine) no atropine |
|
|
Non dairy sources of Ca+ include |
Rhuarb, sardines, collard greens |
|
|
you can pedal the rough edges of a plaster cast with take to avoid skin irritation |
with low back aches, bend knees to relieve |
|
|
Push fluids with Allopurinol |
Flush the uric acid (2.5-8) out of the system
BUN 8-25 / Uric Acid 2.5-8 |
|
|
Koplick's spots are red spots with blue center |
Characteristic or Prodromal stage of Measles usually in mouth |
|
|
INH can cause peripheral neuritis, take bit B6 to prevent; also hepatotoxic |
Peripheral neuritis: tingling in fingers and fingertips |
|
|
Rifampin |
Red organge tears and urine, also contraceptives don't work |
|
|
Ethambutol |
messes with your eyes |
|
|
Apply eye drop |
to conjunctival sac and afterwards apply pressure to nasolacrimal duct/ inner can thus |
|
|
Pancreatitis patients |
put them in a fetal position NPO GUT rest
They will probably be getting TPN/Lipids |
|
|
Trendelenburg test= for varicose veins |
if they fill proximally = varicosity |
|
|
Rule of 9's |
head=9 arm= 9 each (18) torso= 36 legs = 36 perineum=1
|
|
|
When giving Kayaxalate we need to WORRY about |
Dehydration (K has an inverse relationship with NA) |
|
|
Yougurt has live cultures |
do not give to immunosuppressed pt |
|
|
Itching under cast area |
cool air via blow dryer, ice packs for 10-15min
Never use anything to scratch the area |
|
|
Murphy's sign |
pain with palpitation of gall bladder area seen with CHOLECYSTITIS |
|
|
Cullen's sign |
Ecchymosis in the umbilical area seen with PANCREATITIS |
|
|
Truner's sign |
flank Grayish blue (turn arounds to see your flank) PANCREATITIS |
|
|
McBurnies point |
pain in the RLQ indicative of appendicitis |
|
|
LLQ |
Divertivulitis, low residue, no seeds, nuts, peas |
|
|
RLQ |
appendicitis, watch for peritonitis |
|
|
Guthrie Test |
Test for PKU, baby should have eaten source of protein first |
|
|
shilling test |
test for pernicious anemia how well one absorbs Vit B12
|
|
|
Allen's test |
Occlude both ulnar and radial artery until hand blanches then release ulnar and radial artery until hand blanches then release ulnar. If the hand pinks up, ulnar artery is good and you ban carry on with ABG/Radial stick as planned. ABGs must be put on ice and whisked to the lab |
|
|
Its ok to have abdominal cramps, blood tinged outflow and leaking around site if the Peritoneal Dialysis cath was placed in the last 1-2 wks. |
Cloudy outflow never normal |
|
|
amniotic fluid yellow with particles |
meconium stained |
|
|
Hyper reflexes |
UPER motor neuron issue "your reflexes are over the top" |
|
|
Absent reflexes |
Lower motor neuron issue |
|
|
Rhogam |
Given at 28 weeks, 72 hours pos partum, IM, Only given to Rh Negative mother |
|
|
Vit K is to Coumadine |
As Protamine Sulfate is to Heparine as Ca+ glucose is to MgSo4 as mucomyst is to acetaminophen as Amicar is to TPA |
|
|
Order of assessment |
inspection palpatation percussion auscultation
except with abdomen Inspect auscultate Percuss then palpate |
|
|
Latex Allergies |
Assess for allergies to bananas, apricots, cherries, grapes, kiwi, passion fruit, avocados, chestnuts, tomatoes, peaches |
|
|
myesthenia gravis |
is caused by a disorder in the transmission of impulses from nerve to muscle cell |
|
|
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) |
is a condition in which there is a degeneration of motor neurons in both the upper and lower motor neuron systems |
|
|
Transesophogeal Fistula (TEF) |
esophagus doesn't fully develop (this is a surgical emergency The 3 C's of TEF in the newborn: Chocking Coughing Cyanosis |
|
|
MMR vaccine is given SQ |
not IM |
|
|
Red-unstable; occluded airway, actively bleeding see first
Yellow- stable, can wait an hour for treatment, burns, see second
Green- stable, can wait even longer to be seen "walking wounded"
Black- unstable clients that will probably not make it, need comfort measure
DOA - dead on arrival |
Greek heritage - they put an amulet or any other use of protective charms around their baby's neck to avoid "evil eye" or envy of others |
|
|
4 y/o kids cannot interpret time in relationship to a known Common eVENt |
Example: Mom will be back after supper |
|
|
anaphylactic reaction to baker's yeast is contraindication for HEP B vaccine |
ask for allergy to eggs before flu shot |
|
|
ask for anaphylactic reaction to eggs or neomycin before MMR |
When nitroprusside, monitor thiocynate (cyanide) normal value should be 1, >1 heading toward toxicity |
|
|
If kid has a cold, can still give immunizations |
SARS (severe acute reps. syndrome) airborne + contact (just like varicella)
|
|
|
Hep. A is contact precautions |
Tetanus, Hep B, HIV, are STANDARD precautions |
|
|
william's position |
Semi Fowler's with knees flexed (inc. knee hatch) to relieve lower back pain |
|
|
signs of a fractured hip: |
external rotation, shortening, adduction |
|
|
Fat Embolism |
Blood tinged sputum (r/t inflammation), increasing ESR, respiratory alkalosis (not acidosis r/t tachypnea), hypocalcemia, increased serum lipids, "snow storm" effect on Chest X-ray |
|
|
pager's disease |
tinnitus, bone pain, enlargement of bone, thick bones |
|
|
NO vitamin C with Allopurinol |
IVP required bowel prep so they can visualize the bladder better |
|
|
Acid ash diet- cheese, corn , cranberries, plum, prunes, meat, poultry, pastry, bread |
Alk Ash diet- milk, veggies, rhuarb, salmon
|
|
|
orange tag in triage is non emergent psych |
Greenstick fractures, usually seen in kids bone breaks on one side and bends on the other |
|
|
Insomnia is a side effect of thyroid hormones: Increased met. rate, your body is to busy to sleep as opposed to the folks with hypothyroidism who may report somnolence (dec. met rate, body is slow and sleepy) |
botox for strabismus. Patch the good eye so that the weaker eye to get stronger |
|
|
Tidal Vol. is 7-10 ml/kg |
COPD patients Remember: 2 LNC or less (hypoxic not hercapnic drive), PaO2 of 60-ish and SaO2 90% is normal for them b/c they are chronic CO2 retainers |
|
|
Neostigmine/Atropine (anticholinergic to reverse effect of pancronium |
Ampho B causes hypoKalemia (amongst many other things... gotta premeditate before giving) pt will most likely get a fever |
|
|
Test 4 hypersensitivity before administration of asparginase |
Take Vermox with high fat diet (increase absorption) |
|
|
Amphojel and Renegal take with MEALS |
Kidney glucose threshold is 180 |
|
|
Stranger anxiety is greatest at 7-9 month, separation anxiety peaks in toddlerhood
|
MMR is a SQ shot |
|
|
Lyme s found mostly in Conneticut |
Asthma and arthritis -swimming is best
|
|
|
Asthma has intercostal retractions be concerned |
Tardive dyskinesia -irreversible-involuntary movements of the tongue, face and extremities, may happen after prolonged use of antipsychotics |
|
|
Akathisia |
motor restlessness, need to keep going, tx with antiparkinson's meds, can be mistaken for agitation |
|
|
when drawing an ABG you need to put the blood in a heparinized tube, make sure there are no bubbles, put on ice immediately after drawing, with label indicating if the pt was on room air or how many liters of O2 |
Remember to perform the allen's test prior to doing an ABG to check for sufficient blood flow |
|
|
Before going for Pulmonary function test (PFT's), a pt's bronchodilators will be withheld and they are not allowed to smoke for 4 hrs, prior |
for a lung biopsy, position pt lying on side of bed or with arms raised up on pillows over bedside table, have pt hold breath in mid expiration, chest x-ray done immediately afterwards to check for complication of pneumothorax, sterile dressing applied |
|
|
for lumbar puncture, pt is positioned in lateral recumbent fetal position, keep pt flat for 2-3 hrs. afterwards, sterile dressing, frequent neuro assessments |
EEG, hold meds for 24-48 hrs. prior, no caffeine or cigarettes for 24 hrs. prior, pt can ea,t pt must stay awake night before exam, pt may be asked to hyperventilate and watch a bright flashing light, after EEG, assess pt for seizures, pt will be at increased risk |
|
|
Diamox |
Used for glaucoma, can cause hypoKAlemia |
|
|
Dexedrine |
uses for ADHD, may alter insulin needs, avoid taking with MAOI's, take in morning (insomnia possible side effect) |
|
|
Cytovene |
used for retinitis caused by cytomegalovirus, pt will need regular eye exams, report dizziness, confusion, or seizures immediately |
|
|
INH, used to treat and prevent TB, do not give with dilantin, can cause phenytonin toxicity, monitor LFT's, give B6 along with, hypotension will occur initially then resolve |
rifampin, or TB, dyes bodily fluids orange |
|
|
If mixing antipsychotic (ex. haldol, thorazine, prolixin) with fluids, meds is incompatible with caffeine and apple juice |
haldol preferred anti-psychotic in elderly, but high risk extrapyramidal side effects (dystonia, tarditive dyskinesia, tightening of jaw, stiff neck, swollen tongue, later on swollen airway) monitor for early signs of reactions and give IM benadryl |
|
|
Risperdal, antipsychotic, doses over 6 mg can cause tarditive dyskinesia, first line antipsychotic in children |
Levodopa, for parkinson's, contraindicated in pts. with glaucoma, avoid B6 |
|
|
Sinemet, for parkinson's, contraindicated with MAOIs |
hydroxyurea, for sickle cell, report GI symptoms immediately, could be a sign of toxicity |
|
|
Zocor, for hyperlipidemia, take on empty stomach to enhance absorption, report any unexplained muscle pain, especially fever |
Decorticate is toward the "core" Decerebrit is the way out |
|
|
BOtox (Botulin Toxin) can be used with strabismus also to relax goal cords in spasmodic dysphonia |
Munchausen Syndrome: is a psychiatric disorder that causes an individual to self inflict injury or illness or to fabricate symptoms of physical or mental illness, in order to receive medical care or hospitalization. In a variation of the disorder, Munchausen by proxy (MSBP) an individual typically a mother, intentionally causes or fabricates illness in a child or other person under her care |
|
|
Multiple sclerosis: |
Is a chronic, progressive disease with demyelinating lesions in the CNS which affect the white matter of the brain and the spinal cord
Motor S&S: limb weakness, paralysis, slow speech sensory S&S: numbness, tingling, tinnitus Cerebral S&S: nystagmus, ataxia, dysphagia, dysarthria
|
|
|
Huntington's Chorea |
50% genetic, autosomal dominant disorder
S&S chorea- writhing, twisting, movements of face, limbs and body -gait deteriorates to no ambulation -no cure, just palliative care |
|
|
WBC shift to the left in a pt with pyelonephritis (neutrophils kick in to fight infection) |
Definitive diagnosis for abd. arotic aneurysm (AAA)--- CT scan if 4 every 6 months, if higher than 6 it is bad |
|
|
Do not use Kayexalate if patient has hypoactive bowel sounds |
uremic fetor-> smell urine on the breath |
|
|
Hirschsprung's |
bile is lower obstruction, no bile is upper obstruction, ribbon like stoolsP |
|
|
Pancreatic enzymes are taken with each meal |
Not before, not after, but with each meal |
|
|
Cataloupe is high in Vit C and Vit C causes a false + for occult blood. |
Hypospadias: abnormality in which urethral meatus is located on the ventral (back) surface of the penis anywhere from the corona to the perineum (remember hypo, low (for lower side or under side) |
|
|
Epispadias: |
Opening of the urethra on the dorsal (front) surface of the penis P |
|
|
Priapism |
Painful erection lasting longer than 6 hours |
|
|
Anticholinergic effects |
Assessment; dry mouth can't spit Urinary retention- can't pee Constipated- can't poop Blurred vision- can't see |
|
|
When you see Coffee- brown emesis, think peptic ulcer |
anytime you see fluid retention. think heart problems first |
|
|
An answer that delays care or treatment is always WRONG |
For PVD remember DAVE (legs are Dependent for Arterial & for Venous elevated |
|
|
when choosing an answer think in this manner if you can only do ONE thing to help this pt what would it be? Pick the most important intervention |
If two answers are the exact opposite like bradycardia or tachycardia.... one is probably the answer |
|
|
If two or three answers are similar or are alike, none is correct |
When asking patients questions NEVER use "why" questions. Eliminate all why answer options |
|
|
If you have never heard of it... don't pick it |
Never release traction UNLESS you have an order from dr. to do so |
|
|
Questions about halo? remember safety first have a screwdriver nearby |
Remember compartment syndrome is an emergency situation. Paresthesias and increased pain are classic symptoms. Neuromuscular damage is irreversible 4-6 hrs after onset |
|
|
Always deal with actual problems or harm before potential problems |
Always select "patient focused" answer |
|
|
An answer option that states "reassess in 15 min" is wrong |
Interpersonal model (sullivan) Behavior motivated by need to avoid anxiety and satisfy needs
1) infancy 0-18 months other will satisfy needs 2) childhood >6 y/o learn to delay need gratification 3) juvenile 6-9 y/o learn to relate to peers 4) preadolescence 9-12 y/o learns to relate to friends of opposite sex 5) early adolescence 12-14 y/o learn independence and how to relate to opposite sex 6) late adolescence 14-21 y/o develop intimate relationship with person of the opposite sex |
|
|
Fetal alcohol syndrome |
FUTS: flat nasal bridge Upturned nose Thin upper lip SGA (small for gestational age) |
|
|
Vastus lateralis is IM administration site for 6 month infants
ventrogluteal is IM administration for 18 months and above
Deltoid and Gluteus maximus are appropriate sites for children |
UA- both eyes OS -left eye OD-right due (dominant right eye or derecha) |
|
|
COAL cain walking:
C- cane O- opposite A- affected L-leg |
thoracentisis- prep:
Take VS, shave area around needle insertion, position patient with arms on pillow on over bed table or lying on side, no more than 1000cc at a one time.
Post- listen for bilateral breath sounds, VS, check leakage, sterile dressing |
|
|
CT - asess allergies |
MRI-assess claustrophobia, no metal, assess pacemaker |
|
|
Cardiac cath- NPO 8-12hr., empty bladder,pulses, tell pt may feel heat palpitations or desire to cough with dye injection
POST- VS keep leg straight bed rest for 6-8hrs |
Cerebral angio prep- well hydrated, lie flat, shave, pulses marked
Post- keep flat 12-14 hours check site, pulses, force fluids |
|
|
Lumbar puncture- fetal position
Post- neuro assess q15-30 min until stable, flat 2-3 hr., encourage fluids, oral analgesics for H/A, observe dressing |
EEG - no sleep the night before, meals not withheld, no stimulants for 24 hr before, tranquilizer, stimulant meds held 24-48 hr. before, may be asked to hyperventilate 3-4 min and watch a bright light |

