![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the different kinds of Strategic positioning a firm can do?
|
Low-cost
-Offering a similar product/service at a lower cost than competitors Differentiation -Offering a differentiated product at a price premium Combination strategies -Combining quality and low cost (e.g. customised product at a competitive cost) |
|
|
What are the sources for increased profitability for the MNC?
|
Expanding its markets through selling its products/services internationally
Realising location economies by locating value chain activities (marketing, manufacturing etc.) in countries where they can be performed most effectively Realising cost economies through economies of scale by serving the global market from centralised operations Leveraging the MNC’s core competencies abroad or leveraging skills developed in national subsidiaries for the benefit of the entire MNC |
|
|
What are the pressures for cost reductions that a firm might face?
|
Growing uniformity in consumer preferences
The emergence of global consumers Changing industry economics - escalating research and development costs, shortening of product life cycles Competitors’ strategic moves These developments have been enabled by trade liberalisation and technological change => Necessitate MNCs to gain international scale and search for cost efficiencies |
|
|
What are the pressures for local responsiveness that a firm might face?
|
Differences in consumer needs and preferences
Differences in infrastructure, traditional practices, national culture Differences in host government demands The CAGE framework (Ghemawat 2001**) points to a range of differences between countries National differences, whilst evolving, persit There is pressures upon MNCs to adapt to national countries |
|
|
How does the relative strengths of costs vs. naional responsiveness pressures differ across industries?
|
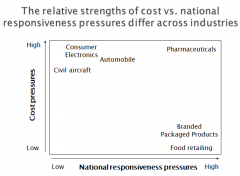
|
|
|
What are the four internationalisation strategies?
|
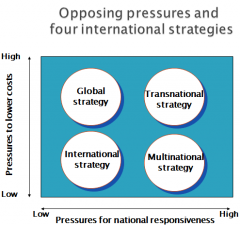
|
|
|
What is the global (or "global standardisation") strategy?
|
Main goal: global efficiency
One standardised product design Marketing in the same fashion throughout the world Location of value chain activities (e.g. research & development (R&D), production, marketing): concentrated in a few favourable locations |
|
|
What are the strengths and weaknesses of the Global strategy?
|
Strengths:
-Efficiency through the realisation of economies of scale in product development, manufacturing, marketing etc. -Helps to create uniform standards of quality throughout the world -Strategy more suited to industries where cost pressures are dominant Weaknesses: -Limited ability to adapt to national markets -Concentration of activities means dependence on a few facilities which can increase risks of disruption (e.g due to host government policy changes, currency fluctuations) |
|
|
What are Levitt's (1983) arguments in facour of a global strategy?
|
Universal needs and demands of consumers
Powerful homogenising forces of technological change and globalisation MNCs can force change in consumer preferences National cultural differences should be seen as residues and should not be a prominent consideration in MNCs’ strategies |
|
|
What is the Multinational (or "localisation") strategy?
|
Main goal: national responsiveness
Customisation of products/services to the needs of national markets Location of value chain activities: most activities carried out in highly autonomous national subsidiaries. Each subsidiary mainly serves its local market. -E.g. Unilever |
|
|
What are the Strengts and Weaknesses of the Multinational strategy?
|
Strengths:
-Flexible and responsive to local environments -More appropriate strategy where pressures for local responsiveness are dominant Weaknesses: -Inefficiencies resulting from duplication of activities across countries -Inability to exploit the knowledge and competencies of the various national subsidiaries for the benefit of the entire MNC |
|
|
What is the International Strategy?
|
Main goal: transfer of products and knowledge on a worldwide basis
Strategic goals and posture captured by the international product life cycle Sells products or services developed in the home country to less advanced host environments with minimal adaptation Location of value chain activities: R&D centralised in home country, manufacturing and marketing decentralised in host countries -E.g. traditionally US-based MNCs (General Electric) |
|
|
What are the Strengths and Weaknesses on the international strategy?
|
Strengths:
-Ability to create and leverage innovations -More appropriate in industries where pressures for local responsiveness and cost reduction are low Weaknesses: -Deficiencies in flexibility and national responsiveness -Deficiencies in global efficiency |
|
|
What is the Transnational Strategy?
|
Main goals: efficiency, national responsiveness, global knowledge transfer
Products, services or knowledge may arise in any of the MNC’s national subsidiaries Knowledge flows among national subsidiaries and from subsidiaries to headquarters Location of value-chain activities: complex configuration in which some activities are dispersed in locations which are most favourable to perform that activity, whilst others are concentrated to achieve economies of scale. Mixture of centralised and decentralised activities. |
|
|
What are the strengths and weaknesses of the transnational strategy?
|
Strengths:
-Overcomes the weaknesses of the other three strategies: simultaneously realises efficiencies, global knowledge transfer whilst adapting to national differences -Best suited to industries which face strong pressures for cost reductions and local responsiveness -From the 1990s onwards, intensification of these dual pressures has led many MNCs to shift from traditional strategies (global, multinational, international) towards a transnational strategy Weaknesses: -Complex strategy to implement |
|
|
What does Ghemawat (2010) say are the environmental trends after 2008?
|
Strengthening of pressures for cost reductions
-Intensification of global competitive pressures -Financial resources scarcity Strengthening of pressures for national differentiation -Consumer demands for local products -Anti-globalisation movement -Protectionist trends -Greater political and economic instability Continuation of transnational strategies with some evolving features: -Relatively greater emphasis on national differentiation whilst recognising price pressures -Re-assessment of the risks of internationalisation -Simplification of international supply chains -Intensification of the internationalisation of R&D functions in growth markets and with highly-skilled, cheaper workforce -Continuation of global learning e.g. leveraging of innovations from emerging economies within MNCs -Importance of building corporate reputation |
|
|
What are the conclusions from this slide?
|
In choosing their competitive strategies abroad, MNCs face conflicting pressures for cost reductions and national responsiveness
Those pressures will vary across industries Depending on the relative strengths of those pressures, MNCs have four basic international competitive strategy options; each is underpinned by a different philosophy as to how the world should be served and has pros and cons. Intensifying pressures for cost reductions and national responsiveness have led many MNCs to adopt a transnational strategy from the 1990s onwards The 2008 financial crisis has led to new challenges in the global environment with various strategic implications for MNCs |

