![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
173 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Describe how fungi differ from prokaryotes in terms of
reproduction size cell wall composition cytoplasmic organization |
reproduction-asexual and sexual
size- much larger, discrete nucleus cell wall composition-contains sterol cytoplasmic organization-structual units like mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Describe the two macroscopic variations of fungi
|
yeast-opaque, creamy conlonies
mold-cottony, wooly or powedery aerial growths |
|
|
define blastoconidia
|
blastoconidia-an asexual spore produced by budding from true yeasts and yeast like fungi
|
|
|
define pseudohyphae
|
pseudohyphae- fragile hypha-like chains of blastoconidia which elongate but fail to detach from the parent cell. They are constricted at the point of attachment but true hyphae are not
|
|
|
T/F yeast can reproduce sexually
|
true, two cells fuse
|
|
|
Describe the incidence of yeast in clinical specimens
|
the incidence of yeasts in clinical specimens in high but not always significant
|
|
|
What factors have lead to the increase in the incidence of yeast infections
|
steroid use, braod spectrum antibiotics, antitumor agents, AIDS
|
|
|
What are the two genera of medically important yeasts
|
Candida and Cryptococcus
|
|
|
Are Candida normal flora?
|
Yes. Candida species can be found in low numbers as indigenous flora of the mouth, throat, large intestine, and vagina
|
|
|
What diseases are cause by candida species
|
oral thrush, vaginitis, cutaneus infections
|
|
|
T/F C. albicans can cause blood stream infections
|
true
|
|
|
Where can Crytococcus neoformans be found?
|
lives naturally in soil containimnated with bird droppings particularly from pigeons
|
|
|
What is the most common disease associated with Crytococcus neoformans infection?
|
Meningitis
|
|
|
Give an example of a unique cellular component of Cryptococcus neoformans that is important for identification
|
large polysaccharide capsule, detected with india ink test
|
|
|
What is the difference between a vegetative and aerial hyphae
|
vegetative- secures the fungus to the substrate, absorb nutrients
|
|
|
define conidia
|
an asexual spore borne externally on the hyphae or on a conidiophore
|
|
|
What are the three groups of molds we learned about
|
1. opportunistic filamentous molds
2. dimorphs- systemic mycoses 3. dermatophytes- superficial and cutaneous mycoses |
|
|
List three opportunistic molds
|
Zygomycetes, Aspergillus, Alternaria
|
|
|
Define saprobic
|
soil loving
|
|
|
Describe the growth patterns of dimorphic fungi
|
most develop as yeasts when grown at 37 and molds at 25
|
|
|
How is infection with a dimorphic fungi obtained
|
inhlabtion of conidia (blastomycosis and histoplasmosis) or arthorconidia (coccidiomycosis)
|
|
|
What is unique about the location of infections with dimorphic fungi
|
infections can disseminate to internal organs of the body, bone, skin
|
|
|
What organism causes Histoplasmosis?
|
Histoplasma capsulatum
|
|
|
What cells does histoplasma capsulatum infect
|
cellls of the reticuloendothelial system= macrophage (intracellular parasite)
|
|
|
How would a human aquire an infection with Histoplasma capsulatum
|
Inhalation of conidia (microconidia) that are found in soil contaminated wit hbrid and bat droppings (guano)
|
|
|
Where is Histoplasma capsulatum endemic
|
eastern and central United States
|
|
|
What organism causes Blastomycosis
|
Blastomyces dermatitidis
|
|
|
Where is Blastomyces dermatitidis endemic
|
Misssissippi Valley region
|
|
|
How is Blastomycosis obtained and what it the progression of the infection
|
obtained through inhalation of conidia from moist soils, spreads and involves lungs, bone, and cutaneous tissue
|
|
|
What organism causes coccidioidomycosis
|
Coccidioides immitis
|
|
|
Describe the disease associated with Coccidioides immitis
|
generally acute, self limiting respiratory tract infection, less than 0.5% of people infected ever become seriously ill
|
|
|
Where is Coccidioidomycosis endemic
|
semi arid regions in southwestern US and northern Mexico
|
|
|
how do humans aquire coccidioidomycosis
|
inhalation of barrel shaped conidia (arthroconidia) from contaiminated soil, especially in the dry season
|
|
|
Describe the association of dermatophyte infection with host tissue
|
the fungi invade and digest the keratin in the skin, nails, and hair. There is no penetration into deeper tissue or invasion of the body
|
|
|
Describe the sxs associated with dermatophye infection
|
range from minimal to severe
|
|
|
how is infection with a dermatophyte obtained
|
contact with infected induviduals or animals or by contact with soil in which the dermatophyte is present
|
|
|
what are two other names for dermatophyte infections
|
tinea or ringworm
|
|
|
What are the three genera of dermatophytes that can cause mycoses
|
Microsporum, Trichophyton, Epidermophyton
|
|
|
How should a direct exam of a dermatophyte infection be preformed
|
Skin scraping using a KOH mount
|
|
|
How can a dermatophyte be cultured
|
use DM or SDA to isolate. then view the microscopic morphology of the hyaline growth with LPCB
|
|
|
How can the histology of mycotic infections be observed
|
use HE, PAS or Silver stains
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the KOH in KOH mounts
|
-breaks down extrneous debris and softens deratin
-does not damage the fungal cell wall -fungi are easily visible but unstained |
|
|
Describe the purpose of the calcofluor white stain
|
nonspecific fluorochrome dye used for direct detection of fungal elements in clinical materials. The dye binds chitin and appears apple green when exposed to UV light.
|
|
|
What does calcofluor white bind
|
chitin
|
|
|
why is the gram stain less often used in mycology
|
the cell wall of mycotic organisms, which is composed of chitin, glucan, and mannan, does not always bind the stain
|
|
|
For definitive identificatino fungi must be...
|
cultured and observed
|
|
|
what media is most commonly used for fungal culture
|
Sabouraud dextrose agar
|
|
|
What medium should be used to culture clinical fungal samples from non sterile sites
|
selective media containing cyclohexamine
|
|
|
What is the purpose of each component of LPCB
|
lactic acid- preserves the fungal structures
phenol- kills the fungi cotton blue- stains |
|
|
What is the disadvantage of a tease mount
|
manipulating the fungi may disrupt the delicate microscopic structures (relationship betweeen conidia and hyphae)
|
|
|
Describe how to prepare a slide culture
|
-tease hyphal elements and spore from edge of mold growth
-inoculate the top and side of the four edges of the potato flake agar block -place a sterile cover slip on top of the block -transfer 3mL sterile water into bottom of Petri dish to saturate filter paper -the fungus will grow on the sides of the agar and out on to the slide and coverslip |
|
|
Describe how to harvest a slide culture
|
-romve the coverslip from the culture
-place drop of LPCB onto clean slide -lay the coverslip onto the slide, do not press down!! -observe hyphal growth from the block edge around the square void -for permanent preps, rim the slide with clear nail polish |
|
|
describe how a mycology slide should be viewed
|
-reduced light
-10x or 40x not 100x -no oil |
|
|
Describe how the chlamydospore production test is carried out
|
-used to Dx C.albicans
-plate on cornmeal tween 80 agar -innoculate plates at 30C for 24 to 48 hours -look for pseudohyphae, cltusters of arthroconidia, blastoconidia, or think walled round chlamydosproes at the terminal end of the hyphae |
|
|
List two morphological tests that can be used to Dx C. albicans
|
-chlamydospore production on cornmeal tween 80 agar
-germ tube formation in serum |
|
|
Describe how a germ tube test is preformed
|
-colony of yeast in suspended in rabbit or human serum
-tube incubated at 37C for NO MORE THAN 3 HOURS -use wet prep to look for prescence of germ tube |
|
|
What is a germ tube
|
nonseptate extension 1/2 the width and 3-4 times the length of the yeast cell. Characteristic of C. albicans
|
|
|
What is the india ink test primary used to identify
|
Cryptococcus neoformans, ID pased on large polysaccharide capsule
|
|
|
How does the india ink test work?
|
small drop of ink is placed on glass slide then small amount of specimen is mix in
prep is viewed under 10 then 40x abscence of stain is positive for a capsule (negative staining technique) |
|
|
draw a picture of microsporum macroconidia
|
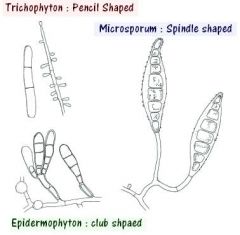
oval shpaed with tapered ends
|
|
|
Draw a picture of microsporum microconidia
|
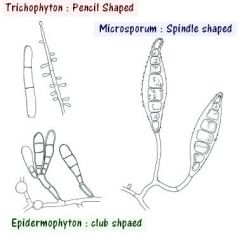
few, slightly clubbed
|
|
|
Draw a picture of trichophyton microconidia
|
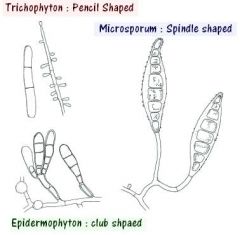
numbers, club shaped, singly or in grape like clusters
|
|
|
Describe the macro and micro scopic morphology of zygomycetes
|
macro- "Don King" aerial growth, fuzzy, white, hyaline
micro-"lolipops" sporgangium on |
|
|
Describe the macro and micro scopic morphology of Aspergillus
|
macro- yellow. greeenish, hyaline growth
micro-Joanne's hat, vesicle with beadead conidia |
|
|
Describe the macro and micro scopic morphology of alternaria
|
macro-black on top and bottom, dematiaceous
micro- oval shapled conidia continuous within the conidiophores |
|
|
describe the morphology of a C. albicans chlamydospore
|
thick walled, spherical swelling at the terminus of the pseudohyphae
|
|
|
compare the mold forms of the dimorphic fungi
|
coccidiodes- rectangular sections
blastomyces- lolipop histoplasma- spike ball |
|
|
What type of organism would you suspect if a direct exam revealed:
-budding yeast forms only -yeast and pseudohyphae -hyphae only |
budding yeast only= yeast
yeast and pseudohyphae= Candida albicans hyphae only= filamentous mold |
|
|
what is the full name of SDA agar?
|
sabouraud dextrose agar
|
|
|
Houw might the two hyaline filamentous molds be differentiated microscopically
|
aspergillus- septate hyphae, branched conidia
zygomycetes- aseptate hyphae, sporangiophores with spores |
|
|
what types of infections are usually associated with zygomycetes, a hyaline opportunistic filamentous mold
|
rhinocerebral, gastric, cutaneous
|
|
|
What types of infections are usually associated with aspergillus a hyaline opportunistic filamentous mold
|
allergies, pulmonary, cutaneous
|
|
|
Compare the growth rates of the three different type of fungi that we studied
|
aspergillus or zygomycete 2-5 days
dermatophytes 7-14 days dimorphic molds- more than 14 days |
|
|
what types of infections are associated with yeasts
|
mucocutaneous, cutaneous, systemic
|
|
|
list two morphological tests associated with C, albicans diagnosis
|
1. germ tube test
2. clamydospores on cornmeal tween 80 agar |
|
|
How does C. glabrata differ from C. albicans on cornmeal agar and germ tube test
|
germ tube- not formed
conrmeal- no pseudo hyphae, blastoconidia only |
|
|
What would you see on conrmeal agar for Cryptococcus neoformans
|
blastoconidia only, no pseudohyphae
|
|
|
describe the route of infection for a thermal dimorph
|
inhalation, respiratory infection, dissemination to organs, skin, etc
|
|
|
Describe the temperature dependent growth morphology of dimorphs in vitro
|
@25= mold
@37= yeast except C. immitis |
|
|
What is the diagnostic form of Histoplasma capsulatum
|
mold @25, tuberculate macroconidia (spiky ball)
yeast @37 small yeast |
|
|
What is the natural habitat of aspergillus
|
ubiqutious, poants, soil
|
|
|
what is the infectious form of aspergillus
|
conidia
|
|
|
what is the mode of transmission of aspergillus
|
inhalation
|
|
|
what is the clinical in vivo form of aspergilllus
|
hyphae, septate and parallel
|
|
|
what is the diagnostic form of aspergillus (in vitro)
|
mold at 25 and 37, hyaline growth rate,
vesicle with branched conidia |
|
|
what is the natural habitat of blastomyces dermatitidis
|
WATERWAYS! soil, wood
|
|
|
what is the infectious form of blastomyces
|
conidia
|
|
|
what is the mode of transmission of blastomyces dermatidis
|
inhalation
|
|
|
what is the clinical, in vivo form of blastomyces dermatidis
|
yeast
BBBB! big broad based buds of blasto |
|
|
What is the in vitro diagnostic form of blastomyces
|
mold @ 25 with lolipop conidia, hyaline
yeast @ 37 with big broad based buds |
|
|
What is the natural habitat of Candida albicans
|
human flora
|
|
|
What is the infectious form of C. albicans
|
yeast, pseudo and true hyphae
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission of C. albicans
|
contact, change in normal flora leading to dissemination
|
|
|
What is the clinical, in vivo form of C. albicans
|
yeast, pseudohyphae and true hyphae
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic, in vitro form of C. albicans
|
yeast at 25 and 37, germ tube in serum, chlamydospores on cornmeal agar
|
|
|
what is the natural habitat of coccidioides immitis
|
soils of aird regions
|
|
|
What is the infectious form of coccidioides immitis
|
arthroconidia
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission of coccidioiodes immitis
|
inhlalation
|
|
|
What is the clinical, in vivo form of Coccidioides immitis
|
spherules with endospores
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic in vitro form of Coccidioides immitis
|
mold @25, arthroconidia, hyaline
NO yeast, spherules/ endospores in tissue |
|
|
What is the natural habitat of Crytococcus neoformans
|
bird feces, soil
|
|
|
What is the infectious form of Crytococcus neoformans
|
yeast
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmission of cryotococcus neoformans
|
inhalation
|
|
|
What is the clinical in vivo form of cryptococcus neoformans
|
yeast w/ capsule
|
|
|
what is the diagnostic in vitro form of cryptococcus neoformans
|
mucoid yeast colony at 25 and 37
india ink view of capsule biochems, latex agglutination for capsule |
|
|
What is the natural habitat of Histoplasma capsulatum
|
bat and bird feces
|
|
|
what is the infectious form of crytococus neoformans
|
yeast
|
|
|
What is the mode of transmisson of histoplasma capsulatum
|
inhalation
|
|
|
what is the clincal in vivo form of histoplasma capsulatum
|
small yeast within macrophages
|
|
|
what is the in vitro diagnostic form of histoplasma capsulatum
|
mold @25 with tuberculate conidia, hyaline
yeast @37, small yeast |
|
|
What is the natural habitat of dermatophytes
|
human/ animal disease and soil
|
|
|
What is the infectious form of dermatophytes
|
conidia, hyphae
|
|
|
What is the clinical, in vivo form of dermatophyes
|
hyphae w/ KOH, septate and parallel
|
|
|
What is the diagnostic in vitro form of dermatophytes
|
mold @ 25, 37, hyaline
micro and macro conidia shapes ` |
|
|
What is the natural habitat of zygomycetes
|
ubiquitous
|
|
|
what is the infectous form of zygomycetes
|
spores
|
|
|
what is the mode of transmission of zygomycetes
|
inhalation, ingestion, cutaneous
|
|
|
what is the clincal, in vivo form of zygomycetes
|
aseptate hyphae, not parallel
|
|
|
what is the diagnostic, in vitro form of zygomycetes
|
mold at 25 and 37, hyaline
micro morphology with sporangium and spores, lid lifter areial growth |
|
|
What is the natural habitat of dematiaceous molds (alternaria)
|
ubiquitous
|
|
|
what is the infectious form of the dematiaceous molds (alternaria)
|
conidia
|
|
|
what is the mode of transmission of the dematiaceous molds (alternaria)
|
inhalation, trauma
|
|
|
what is the clinical, in vivo form of the dematiaceous molds (alternaria)
|
melanin pigmented septate and parallel hyphae
|
|
|
What is the in vitro diagnostic form of dematiaceous molds (alternaria)
|
mold at 25 and 37, dematiaceous
|
|
|
what are three ways to grow virus
|
1. in lab animals
2. in embryonated eggs 3. in cell cultures |
|
|
How might viral growth be observed in each of the three ways to culture them given that they are too small to be stained
|
in lab animals- symptoms, death
in eggs- death of embryo, leisions on tissue of egg, aggultination with fluid in cell culture- cytoplathic effect |
|
|
How do influenza type A and B differ
|
different ribonucleoprotein antigens
|
|
|
What is the difference between antigenic drift and antigenic shift
|
drift-minor changes to surface antigens
shift-major change in surface antigen |
|
|
What is serialy diluted in the hemagglutination assay
|
virus
|
|
|
what is keep constant in the hemagglutination assay
|
the amount of RBCs
|
|
|
What is a positive result in a HA assay
|
a shield, indiactes that there were virus particles present that were able to agglutinate the RBCs
|
|
|
what controls should be used in the HA assay? What do they tell you
|
RBC control with no virus, ensures that cells are not spontaneously aggultinating
|
|
|
what is diluted in the HAI test
|
serum
|
|
|
what is held constant in the HAI test
|
the amount of virus
|
|
|
What is a positive result in an HIA test
|
A button, indiactes that there were antibodies to the virus that were able to inhibit the virus from agglutinating the RBCs
|
|
|
What are the controls used in a HIA assay? What do they tell you
|
cell control- RBCs alone, controls for spontaneous agglutiation
virus control- RBCs +virus, no serum, ensures that the virus can agglutinate the cells |
|
|
What fold increase in titer is consididered significant
|
4 fold increase (2 tubes)
|
|
|
What are the two main antigenic glycoproteins on the influenza virus
|
1. hemagglutinin- use to attach to the mucoprotein receptor of the respiratory endothelial cells, agglutinates RBCs
2. Neuraminidae- associated with relase of virus from infected cells |
|
|
T/F HA assay quantifies viable virus
|
false, the dest cannot distinguish beteween active and inactive virus particles
|
|
|
What assay is required to quantify infectious virus
|
cell culture
|
|
|
What are the two ways to use the HIA assay
|
1. use to detect viral antibody by adding unknown serum to known virus
2. use to identify an unknown virus by adding knownw specific monoclonal antiboides |
|
|
What happens to the HI titer if more than the standard amount of virus is added
|
The titer decrease because there is more virus to agglutinate so the avaiable antibody is used up faster
|
|
|
What happens to the HI titer if less than the standard amount of virus is added
|
The titer increases because there is less virus there for the antibody to inhibit, you can "strech" the antibody farther
|
|
|
What is the principle behind BSC's
|
laminar flow, the working environment is protected from dust and contamination by a constant, stable flow of filtered air passing over the work surface
|
|
|
What is the pupose of HEPA filters
|
-High efficiency particulate air
-filters airborne particles with 0.3um filter size |
|
|
Describe a class II vertical laminar flow hood
|
-room air is pulled into unit
-blows down onto the work surface and drawn through work surface |
|
|
What three things does a class II BSC protect
|
-personnel
-product -environment |
|
|
How should items be placed in a hood
|
clean to dirty, never place non sterile items upstream of sterile items
|
|
|
define primary culture
|
cells fresh from a tissue speciumen, not passaged
|
|
|
describe the procedure for transfering cells
|
1. remove old media
2. wash old plate x2 to remove serum 3. add trypsin EDTA and incubate at 37 for 3-10min 4. add new media with serum 5. remove appropriate amount of cells and dilute in new flask or plate |
|
|
describe the titration of infectivity test
|
used to quantify infectious virus. virus is added at ten fold dilutions to monolayer, observe cytopathic effect
|
|
|
define diploid cell strain
|
subculture of primary culture
|
|
|
how should TC media be sterilized
|
Do not autoclave, filter with gas pressue
|
|
|
what type of microscopy is used to view cell lines
|
phase contrast, based on different indicies of refraction
|
|
|
what is the TCID 50
|
the amount of virus needd to infect 50% of wells at that specific concentation. a standard amount of virus used in Viral neutralization assays
|
|
|
what the purpose of using methylcellulose in viral titrations
|
localized infections so each plaque is formed by one virus
|
|
|
Describe the viral neutralization assay
|
If antibody is present, the infectivity of the virus is neutralized and the cytopathic effect will not be observed can detect and quantify the patient antibody
|
|
|
What controls should be used in the viral neutralization assay
|
1. virus control to ensure that virus leads to cytopathic effect
2. normal cell control to ensure that uninfected cells are growing normally |
|
|
what control should be used in a viral titration
|
dilutent only to ensure that the cells are growing normally
|
|

What is this
|
This is the dematiaceous hyphae of Alternaria. Notice the conidium continuous withing the conidiophore. The melanin pigment excludes the LPCB stain.
|
|

What is this?
|
This is the macroconidia of microsporum canis, a dermatophyte mold
|
|

What is this?
|
This is the microconidia of trichophyton
|
|

What is this
|
This is the microscopic morphology of Zygomycetes. Notice the sporganium and spores
|
|

What is this?
|
This is the microscopic morphology of Aspergillus. Notice the vesicle with beaded conidia
|
|

What is this?
|
This is the blastoconidia/ pseduohyphae morphology of C. albicans
|
|
|
What is this
|
This is the chamydospore morphology of C. albicans on cornmeal tween 80 agar
|
|

What is this
|
This is the chlamydospore morphology of C. albicans on conrmeal tween 80 agar
|
|

What is this
|
This is tissue infected with Cryptococcus neoformans. Notice the "halo" around the yeast which is a result of the capsule.
|
|

What is this?
|
This is the diagnostic form of Histoplasma. Notice the tuberculate macroconidia
|
|

What is this?
|
This is the lolipop conidia of blastomyces
|
|

What is this
|
This is the yeast form of blastomyces. Notice the Big Broad Based Buds (BBBB)
|
|

What is this?
|
This is the barrel shaped arthroconidia of Coccidioides immitits
|
|

What is this?
|
This is the spherule with endospore, the in vivo form of coccidioides immitis
|

