![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Eukaryote (define & example) |
An organism with a true nucleus, DNA, and organelles enclosed in a membrane. Some have a cell wall. Examples: animals, plants, fungi, algae. |
YOU-karyote |
|
|
Prokaryote |
A single celled organism without a membrane bound nucleus and with minimal organelles. Example: bacteria. |
|
|
|
Three most used taxonomic ranks, and their structure (largest to smallest.) |
Family: 1st letter capitalized, all have -aceae ending. (Streptococcaceae)
Genus: 1st letter capitalized, and underlined OR italicized. (Streptococcus)
Species: no caps, underline OR italicize. (pneumoniae) |
FGS |
|
|
Cocci |
Bacteria with a spherical shape. |
|
|
|
Bacilli |
Bacteria that are rod shaped. |
|
|
|
Coccobacilli |
A shape between cocci and bacilli, easily mistaken for cocci. |
|
|
|
Arrangements of cocci |
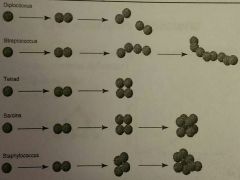
|
5 |
|
|
Vibrio |
Curved rod shaped bacteria (like macaroni.) |
|
|
|
Spirilla & spirochetes |
Spiral shaped bacteria. The first is more wavy, and the latter more corkscrew in shape. |
|
|
|
Pleomorphism (define & example) |
Bacteria with a variety of shapes and sizes, for example Haemophilus influenziae. |
|
|
|
The process of bacterial reproduction |
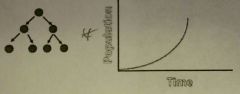
Reproduction is asexual, with every generation doubling the amount of bacteria. Growth is exponenrial. |
|
|
|
Flagellum (definition & function) |
A whip-like appendage protruding from bacteria. They aid movement by rotational movement (not whipping back and forth,) with clockwise rotation moving them forwards and counterclockwise rotation flipping outward and changing direction. Can have multiple flagellum.
They have antigens, so we produce antibodies against them. This also allows for antigenic typing. Generally only rods have flagella. |
|
|
|
Chemotaxis |
Movement of bacteria due to a chemical stimulus. Away from toxic environments and towards nutrient sources. |
|
|
|
Monotrichous |

Having only one flagella. |
|
|
|
Lophotrichous |
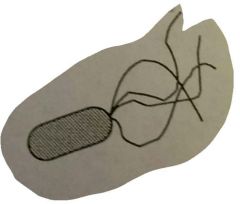
Having multiple flagella in the same area. |
|
|
|
Amphitrichous |

Having one flagella on each end. |
|
|
|
Peritrichous |
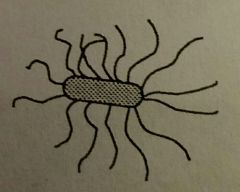
Having multiple flagella in multiple locations. |
|
|
|
Brownian Movement |
False, non-directional motion. Caused when cells are bombarded by water molecules. Truly motile bacteria have flagella. |
|
|
|
Pili vs Fimbriae |
Both primarily seen in Gram negative bacteria. They help to attach to a host cell. Without attachment, bacteria can wreak havoc but not cause infection. They are shorter than flagella, and fimbriae are shorter than pili. Pili may aid in genetic diversity. F-pili is a hollow tube which can join and transmit genetic information between bacteria. |
|
|
|
Capsule |
Not all bacteria have a capsule. It is a slick, slimy covering outside of the bacteria cell wall. It's composition is mainly polysaccharide, and it is huge compared to the bacteria. It is mainly for protection - WBC's slide off. Thus they can continue living and causing infection. Capsules do not stain. |
|
|
|
Cell Wall |
Mainly contributes to structural integrity of bacteria, so they don't lyse and are able to survive in salinity, (about 0.85% on average.) Main structural components are N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid, alternating to make up peptidoglycan. |
|
|
|
Gram + Cell Wall |
Made up of 60-100% peptidoglycan. It is thick, but simple. Teichoic acid (T.A.) extends through cell wall and helps regulate cell wall synthesis. |
|
|
|
Gram = cell wall |
Only about 5-10% peptidoglycan. 20-30% is phospholipid, and 40-50% is made up of protein. It is more complex, but thinner, than gram + cell walls. |
|
|
|
Protein in Cell Walls |
It is the most important part of the cell wall, and is highly likely to cause the body to produce antibodies. It stimulates fever, lowering blood presuure, and can cause D.I.C. |
|
|
|
Cytoplasmic Membrane |
Made up of phospholipids and proteins. Regulates passage of substances into and out of the cell. |
|
|
|
Porins |
A protein that cross the membrane and act as a pore through which molecules can diffuse. |
|
|
|
Ribosomes |
Serves as the site of mRNA translation and protein synthesis. |
|
|
|
Plasmids |
Extrachromasomal DNA that can give bacteria extra abilites. |
|
|
|
Endospores |
A survival tool - can survive in this form for long periods of time when environment is unfavorable. |
|
|
|
Gram Stain |
Gram pos is purple. Gram neg is red (bank account in the red is negative!) |
|

