![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Creatinine |
metabolism of creatine is muscles, and is a measure for GFR because for most part is neither secreted nor reabsorbed (slight secretion in PCT) |
|
|
Antibiotic that blocks creatinine secretion? |
Trimethoprim |
|
|
GFR |
measure of volume of plasma thats cleared of a solute (Creatinine) per unit of time |
|
|
Specific Gravity |
Compares density of urine to density of water. Normal value is 1.01. Increased values indicate dehydration |
|
|
Bilirubin in urine |
suggests liver disease or obstructive or obstructive jaundice |
|
|
urobilinogen |
usually from hemolytic anemia |
|
|
sterile pyruria |
Usually from Acute Interstitial Nephritis, can also be from kidney stones, mycobacterium TB |
|
|
best test for nephrolithiasis |
Non-con CT |
|
|
risk with gadolinium with Cr > 1.5 |
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis |
|
|
plasma osmolallty calculation |
2(Na) + Glucose/18 + BUN/2.8 |
|
|
causes of hypernatremia |
osmotic diarrhea, DI, mannitol, post-obstructive diuresis, |
|
|
K and acid-base status |
usually hyperkalemia assocaited with acidosis hypokalemia assocaited with alkalosis |
|
|
corrected anion gap formula |
2.5(4-albumin) |
|
|
delta delta |
Used in all AG metabolic acidosis: difference in anion gap (assume normal is 10) + measured serum bicarb If value >24 you have concurrent metabolic alkalosis If < 24 have concurrent NG acidosis |
|
|
Osmolar Gap |
Normal Osmolality: 285 2(Na) + Glucose/18 + BUN/2.8 When measured is > 10 from calculated, there is osmolar gap Causes: Ethylene glycol, Methanol, lactate, ethanol, contrast dye |
|
|
Causes of decreased anion gap |
Low Albumin, Hypercalemia, paraproteinemia, hypermagnesemia, hyperkalemia |
|
|
types of lactic acidoosis |
A: tissue hypoperfusion B: Propofol, metformin (mitochondrial dysfunction) D: Short bowel syndrome, bacterial overgrowth produces lactate |
|
|
fomepizole |
alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitor that is used for ethylene glycol and methanol toxicity |
|
|
urinary anion gap |
urinary Na + K - urinary Chloride **Titrable acids are excreted in urine with ammonium which cannot be measured directly, however because ammonium has a positive charge, chloride is excreted with it If kidneys are functioning, there will be a lot of chloride in the urine, and urinary AG will be negative |
|
|
Type 2 RTA and causes treatment |
Proximal defect resulting in inability to reabsorb bicarb **Urinary pH varies because initially HCO3 is lost in urine causing it to be basic, but once total body stores are depleted, distal tubules reabsorb the HCO3 Causes: Fanconi syndrome (will see elevated amino acids, phosphate, glucose in urine), paraproteinemias, tenofovir, tacrolimus,cyclosporine Treatment: alkali therapy alone insufficient, but given with a thiazide diuretic help enhances hco3 reabsorption because of volume contraction |
|
|
Type 1 RTA Causes Treatment |
Inability to secrete H ions distally. Acidosis stimulates reabosoprtion of citrate, so there are low levels of citrate in urine, leading to calcium phosphate stones Causes: SJOGRENS, SLE, RA, hypercalcicuria, Responds well to NaHCO3 Urinary pH ALWAYS > 5.5 |
|
|
Saline Responsive Metabolic Alkalosis |
Alkalosis due to volume depletion (Vomiting, NG Suction, Diurectics) Will see low urine Cl <15 mEQ |
|
|
Saline Resistant Metabolic Alkalosis |
Alkalosis due to mineralocorticoid excess Also Barter's Gittelmans (both have features of saline responsive metabolic alkalosis, but will have urinary Cl >15) |
|
|
TubuloInterstitial Diseases |
Autoimmune: SLE, Sarcoid, sjogren, Infectious: CMV, BK Virus, EBV, TB Malignancy: MM, Lymphoma, Meds: B-lactams, Sulfa, NSAIDs, PPI |
|
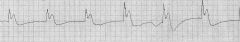
|
J wave, seen in hypothermia (osbourne wave) represents abnormality in repolarization |
|
|
nephrotic range proteinuria and associated labs |
> 3.5 g in 24 hours or protein/Cr ratio > 3500 mg/g hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia, HTN, |
|
|
Examples of nephrotic syndrome |
Minimal Change Disease, FSGS, Membranous Glomerulonephritis, Diabetic Nephropathy, |
|
|
Minimal Change Disease |
Most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in children, but not adults.
Biopsy is normal except for defacement of podocytes *** Associated with hodkgkin lymphoma |
|
|
Focal Segmental Glomerularsclerosis Causes |
HIV/HEP B/ Heroin |
|
|
Membranous Glomerularnephritis Causes |
Hep B, Malignancy, Mixed Connective TIssue disorders |
|
|
Biopsy of Membranous Glomerulonephrits |
Deposits of IgG and complement, SubEpithelial deposits, |
|
|
Nephritic Syndrome |
Hypertension, RBC casts, pyuria, mild proteinuria |
|
|
Causes of nephritic syndrome |
post-streptrococcal glomerularnephritis, rapidly progressive GN, Lupus nephritis, IgA Nephropathy, ANCA Vasculitis, Membranoproliferative Glomerularnephritis, |
|
|
Post Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis + Renal Biopsy |
Usually from skin or throat infections, typically 2-6 weeks after infection. Sub Epithelial humps |
|
|
Goodpastures Syndrome |
Autoimmune disease where antibodies develop against the basement membrane of the glomerulus and lungs. Present with glomerulonephritis, and hemoptysis |
|
|
IgA Nephropathy |
Will see a glomerularnephritis picture with concurrent URI (Different than PSGN in that PSGN takes a while for nephritis to develop) |
|
|
Granulomatosis with Polyangitis (Wegener's) |
C ANCA vasculitis where patient presents with purulent rhinorrhea, hemopytsis, nasal ulceration, glomerulonephritis, EFFECTS LUNGS AND SINUSES |
|
|
Churg Strauss |
P-ANCA vasculitis, associated with asthma, IgE, eosinophilia and glomerulonephritis |
|
|
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis |
Associated with Hep C, low complement levels |
|
|
Extrarenal manifestations of PCKD |
diverticulosis, hernias, mitral valve prolapse, aortic regurg, intracranial aneurysm |
|
|
Fe Urea |
Used to try an identify AKI in patient on diuretics < 35% indicative of Pre Renal etiology |
|
|
causes of ATN |
Vancomycin, Aminoglycocides (Gentamycin, Tobramycin, Amikacin), Amphotericin, contrast |
|
|
acute interstitial nephritis |
Caused by drugs (Penicillins, PPI) Autoimmune (SLE, Sjogrens) malignancy (Lymphoma) Will see rash, fever, eosinophila (UA will have sterile pyuria) |
|
|
Which conditions are complement levels low in glomerulonephritis?
|
Lupus, endocarditis, post infectious, cryoglobins
|
|
|
Types of Kidney stones |
Calcium Oxalate, Calcium Phosphate Struvite: Magnesium,Ammonium, Phosphate Uric Acid |
|
|
Kidney Stone size to dictate treatment |
If 10mm or less, can me managed medically, if > 10mm need urology |

