![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is mitosis? |
When one cell divides to from two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. |
|
|
What is meiosis? |
When one cell divides to form four daughter cells, which are all different from one another and from the parent cell. They have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. |
|
|
What are the three phases in the cell cycle during the period between cell division? |
-Interphase -Karyokinesis -Cytokinesis |
|
|
What happens in the interphase? |
Cell growth and DNA replication takes place. After that the single stranded chromosome now consists of two identical units known as chromatids. |
|
|
What is DNA replication? |
When all the genetic material is replicated. |
|
|
What are the two main stages of mitosis? |
-Karyokinesis -Cytokinesis |
|
|
Explain karyokinesis: |
It's the division of the nucleus and chromosomes. |
|
|
Explain cytokinesis: |
It's the division of the cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane. |
|
|
What are the four phases of mitosis? |
-Prophase -Metaphase -Anaphase -Telophase |
|
|
What happens in the prophase? |
-Chromatin network condenses and is now visible as chromosomes (double stranded). -Each chromosome consists of 2 identical legs known as the chromatids. -Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear. -Centriole seperates and moves to the opposite poles of the cell. -Spindle fibres form between the 2 centrioles to form the spindle. |
|
|
What does the interphase look like? |
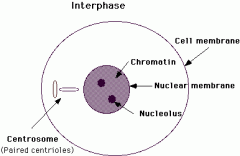
|
|
|
What doe the prophase look like? |
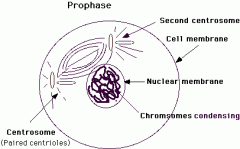
|
|
|
What does the metaphase look like? |
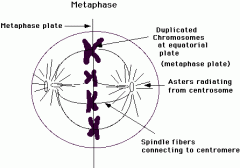
|
|
|
What does anaphase look like? |
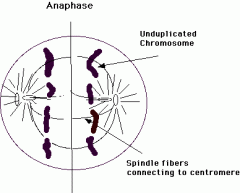
|
|
|
What happens in the metaphase? |
-The chromosome moves to the equator and arrange themselves in a single row on the equator. -Spindle fibres attach to the centriole. |
|
|
What happens in the anaphase? |
-The centromere of each chromosome divides into two. -The two chromotids seperate from each other and move to the opposite poles. -Chromotids are now known as daughter chromosomes. -The centromeres are positioned towards the poles. -Cytokinesis (division of cytoplasm begins) |
|
|
What happens in the telophase (for plants)? |
-The daughter chromosomes arrange themselves at the pole. -The spindle fibres disappear. -A nuclear membrane forms around the pair of daughter chromosomes. -Karyokinesis is now complete -Cytoplasm divides |
|
|
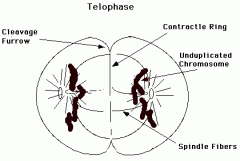
What happens in the telophase (for animals)? |
-Invagination occurs in the cytoplasm at the equator. -A transverse wall forms in the cytoplasm in the equator. -Cytokinesis is now complete (two identical daughter cells are formed) - Both new nuclei contain the same number of chromosomes as the original mother nucleus. |
|
|
What is the role of mitosis? |
-It's responsible for the replacement of cells and repair of work out or injured/damaged cells. -It produces new individuals during asexual reproduction. |
|
|
What does the telophase look like? |
|

