![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mitosis |
a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth
|
|
|
Chromosome number
|
46, each human has two copies of each type of chromosome |
|
|
Histones |
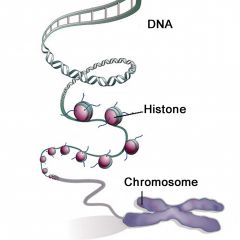
AT REGULAR INTERVALS, A DOUBLE STRANDEDDNA MOLECULE WINDS UP TWICE AROUNDSPOOLS OF PROTEIN CALLED HISTONES
|
|
|
Nucleosome |
THE SMALLEST UNIT OF STRUCTURALORGANIZATION IN EUKARYOTICCHROMOSOMES
|
|
|
Centromere |
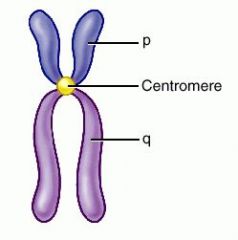
AS A DUPLICATED CHROMOSOME CONDENSESITS SISTER CHROMTIDS CONSTRICT WHERETHEY ATTACH TO ONE ANOTHER
|
|
|
Cell cycle |
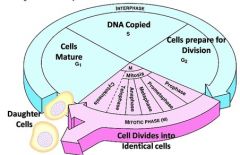
MITOSIS, CYTOPLASMIC DIVISION, ANDINTERPHASE CONSTITUTE ONE TURN OF THECELL CYCLE , interphase is usually longest stage
|
|
|
Interphase |
G1- cell growth and activity before replication S- Time of synthesis -> DNA replication G2- prepares for division |
|
|
Prophase |
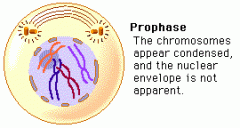
the first stage of cell division during which the chromosomes become visible as paired chromatids and the nuclear envelope begins to disappear.
|
|
|
Metaphase |
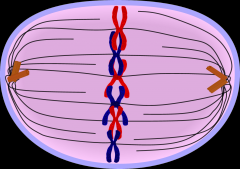
the second stage of cell division, between prophase and anaphase, during which the chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibers.
|
|
|
Anaphase |
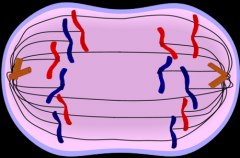
the chromosomes move away from one another to opposite poles of the spindle.
|
|
|
Telophase |
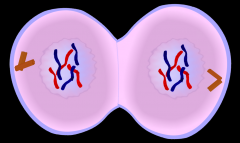
final phase of cell division in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.
|
|
|
All stages of mitosis (visual) |
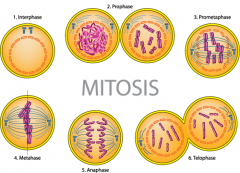
|
|
|
Contractile ring |
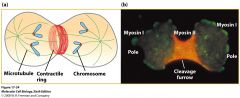
A BAND THAT IS ANCHORED TO THE PLASMAMEMBRANE
|
|
|
Cytokinesis |
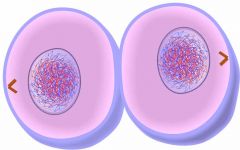
the cytoplasmic division of a cell at the end of mitosis or meiosis, bringing about the separation into two daughter cells.
|

